* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types of Economic Systems
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
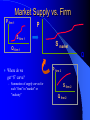
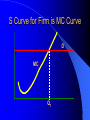
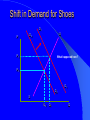
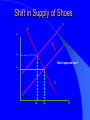
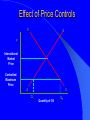
Chapter 2 Theoretical Foundations: Prices, Markets, and Management UNDERLYING FORCES Demographics, Beliefs, Values, Cultures, International Events, Discoveries, Resources, Natural Events Societal Element Changes Public Sector Response Energy and the Physical Environment Labor & Human Resources Technology Economic Climate Regional & Local Issues International Trade Market System Political System Social InvolvementBusiness Social Responsibility Regulation Taxation Spending Provision of Services Political System Marketplace Response Business Response Managerial Decision-Making Strategy Implementation Prices Quantities Produced Product Quality Costs of Production Market System Types of Economic Systems Laissez Faire Capitalism Modern Mixed Economy Democratic Socialism Communism Laissez Faire Capitalism Ownership of Resources Markets Government Involvement Modern Mixed Economy Ownership of Resources Markets Government Involvement Democratic Socialism Ownership of Resources Markets Government Involvement Communism Ownership of Resources Markets Government Involvement The Concept of Demand Demand is a Schedule of the different quantities of a good or service that a consumer is Willing and Able to purchase at each and every possible price Determinants of Demand What are some determinants of the demand for a good or service? Determinants of Demand Income – Normal Goods and Services – Inferior Goods and Services Price Price of Substitute Goods and Services Price of Complementary Goods and Services Attitudes and Tastes An Individual’s Demand for Beer Price/ glass $ 0.40 $ 0.80 $ 1.20 $ 1.60 $ 2.00 $2.50 Price per Glass Glasses 8 6 4 2 1 $2.00 $1.50 $1.00 $0.50 $0 2 4 6 Glasses Demanded 8 10 The Law of Demand The lower the price, the more of a good or service that will be purchased, the higher the price, the less that will be bought Market Demand Curve Summation of all individual demand curves in the market Law of Demand Downward Sloping Determinants of Demand Supply Supply is a schedule of the different quantities of a good or service that a seller is ready and willing to sell at each and every possible price Price of Product Hypothetical Firm Supply Curve Quantity Supplied Factors Affecting Supply What factors affect the supply of a good or service? Factors Affecting Supply Resource Prices Labor Costs Taxes Subsidies Technology Market Supply vs. Firm P firm 1 P S firm 1 Q firm 1 S market Q Where do we get “S” curve? – Summation of supply curves for each “firm” in “market” or “industry” P firm 2 S firm 2 Q firm 2 Marginal Cost The additional or extra cost incurred in producing one more unit of a good or service MC = TC/ Q Price, Cost Hypothetical Firm’s Marginal Cost Curve $1.80 $1.60 $1.40 $1.20 $1.00 $0.80 $0.60 $0.40 $0.20 $0.00 MC 480 500 520 Quantity Produced 540 560 S Curve for Firm is MC Curve D P1 MC Q1 Price Price and Quantity Determination in a Competitive Marketplace D S P’ E PE P’ S QE D Quantity Role of Prices In a Free Enterprise System (I) Transmits Information ... – To producers, consumers, resource suppliers, labor – Signals to produce more or less, to enter new markets, produce new products, etc. Shift in Demand for Shoes D1 P S D0 P1 What happened here? P0 D1 D0 S Q0 Q1 Q Shift in Supply of Shoes S’ D P S P1 What happened here? P0 D S Q1 Q0 Q Effect of Price Controls D S P International Market Price Controlled Maximum Price S D QS Quantity of Oil QD Role of Prices (II) Provides Incentives ... to consumers, producers, labor and owners of productive resources Allocate Resources ... alternative ways to provide goods and services Affect Distribution of Income Two Goals of Society Increase Incomes and Living Standards Fairness and Equity in Income Distribution Two Goals in Conflict Conflict Between Goals Income Distribution Over Time Poor Vs. Rich or Impact on Income over Lifetime Food Distribution in Chicago How does it happen? The Invisible Hand of the Marketplace Adam Smith, 1776 ...“Wealth of Nations” Individuals pursue their own self interest ... greater good of society is served Individuals moved by an “Invisible Hand” to promote social welfare Example: Food distribution Environmental Analysis and Forecasting Environmental Scanning •Analyzing and Forecasting Environmental Change •Describing the Current Environment •Projecting Future Changes Step I - Define Areas Define Areas to Study Primary Involvement - Exchange relationships or marketplace relationships Secondary Involvement -Relationships, activities and impacts that are ancillary or consequential to primary involvement Step II - Delineate Topics External Topics Internal Topics Step III - Determine Time Frame and Forecasting Requirements Short Range Long Range – Delphi Technique – Scenario Method Step IV - Design and Implement Strategy External/Short-term External/Long-term Internal/Short-term Internal/Long-term Step V - Analyze Data Cross Impact Analysis T1 T2 T3 Enhanced 50% in 3 years Enhanced 50% in 3 years Television technologies (probability, year) T1 interactive (.9,2010) T2 digital (.7, 2010) -10% in 2 years T3 HDTV (.8, 2010) -10% in 2 years -60% in 2 years Enhanced 25% in 2 years Step VI - Integrate into the Organization Short-term Long-term – Organizational Change – Inform Top Management Poland Case Problems of a Socialistic System Everybody has money Too much money chasing too few goods Money becomes worthless Resort to barter Long lines for food Poland Case Why did they have long lines? How does food distribution under Communism compare to the system in the USA? Poland Case How well can government controls replace the free enterprise system? What is happening in Poland today?