* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 6 - PHS-Econ
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
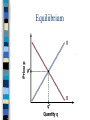
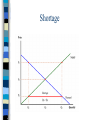
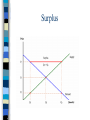
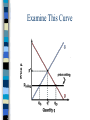
Chapter 6 Prices as Signals Reaching Equilibrium The point where supply and demand come together is called the equilibrium It is the point of balance at which quantity demanded equals quantity supplied Equiliibrium Benefits of Equilibrium Buyers will purchase exactly as much of a good as firms are willing to sell Both buyers and sellers benefit Disequilibrium Occurs when quantity supplied is not equal to quantity demanded in a merket Disequilibrium can produce two outcomes, shortage surplus Shortage Shortage Excess demand Exists when the quantity demanded in a market is more than the quantity supplied How do you eliminate a shortage? Increase Price Suppliers will keep raising the price in order to reach equilibrium When the price has risen enough to close the gap, suppliers will have found the highest price that the market will bear Surplus Surplus Exists when quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded Indicates that the price is too high Must lower the price to reach equilibrium Price Ceiling Markets trend toward equilibrium, but in some cases the government intervenes to control prices Maximum price that can be legally charged for a good or service Where to Set Price? The price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price An example of price ceilings in our economy are rent controls Apartments in NYC Rent Controls Price ceiling placed on apartment rents, to prevent inflation during a housing crisis Helps people live in a neighborhood that they could otherwise not afford Examine This Curve Page 138 Turn to Page 136 to see this clearly… Negative Aspects of Rent Control How do you determine who gets the apartments? Long waiting lists, discrimination, lottery systems, and bribery Sometimes only way to get one is to inherit it Many are Unkept Since landlord profits are cut, it shows in the upkeep Why would they update the painting and fix minor maintenance issues? No incentive, long list of people who would want these apartments Ending Rent Controls? Landlords would make more money Those living in rent controlled apartments would no longer be able to afford them Economists do not like them Price Floor Minimum price that must be paid for a good or service Best example of this is the minimum wage Minimum Wage A full time worker being paid minimum wage will earn less than the federal government says is necessary to support a couple with one child Curve Effects of Price Floors Page 139 In this example, the minimum wage creates a surplus of labor The Role of Prices Chapter 6: Section 3 Price Monetary value of a product as established by supply and demand A signal that helps us make our economic decisions 4 Advantages of Prices Neutral Flexible No administration cost Familiar Neutral Favor neither the producer or the consumer Due to prices being a result of competition between buyers and sellers A compromises the both parties agree to Flexible Unforeseen disasters and war affect prices of many items The price system can absorb these “shocks” Allows market to accommodate change No Administration Cost Markets find their own price without outside help or interference Will explain this in more detail later Familiar Have known about prices our entire lives Allows us to make decisions quickly and efficiently Easily understood Alternatives to Price System? Let’s take a look at rationing and see if it would be a viable alternative Rationing System under which an agency such as government decides everyone’s “fair share” Citizens receive a ration ticket or coupon for goods and services Ration Ticket Entitles you to a certain amount of a product Problems with Rationing 4 Problems Fairness High Administration Cost Diminishing Incentive Black Markets Problem of Fairness Almost everyone feels that their share is too small Almost had gas tickets in the 1970’s, but couldn’t decide how to ration them High Administration Cost Someone has to pay for the coupons and salaries of the people who distribute them Always have risk of them being stolen or counterfeited Diminishing Incentive Has a negative incentive on people’s desire to work and produce Working harder does not equal more ration coupons…so why do it? Black Markets Market in which goods are sold illegally, without regard for government controls on price or quantity Allows consumers to pay more so they can buy a product when rationing makes it otherwise unavailable