* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
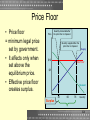
Chapter 5 Policy Analysis With Supply and Demand McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2009 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Learning Objectives • • • • • • • • • What is a price floor? What is the effect of minimum wage on the market? What is a price ceiling? What is rent control? What is economics of a draft vs. voluntary enlistment? What is economics of market for human organs? What is economics of healthcare? What is economics of parking meters? What is economics of agricultural subsidies? 2 5-2 Price Floor • Price floor = minimum legal price set by government. • It affects only when set above the equilibrium price. • Effective price floor creates surplus. Price Quantity demanded after the price floor is imposed. Quantity supplied after the price floor is imposed. $12 Supply Price Floor $8 Demand 40 60 78 Quantity Surplus 3 5-3 Minimum Wage and Market for Unskilled Labor • Minimum wage = price floor in labor market. • Minimum wage law increases wages of unskilled workers with jobs. • However it also creates surplus labor, which equals unemployment. • It may cause firms to raise product prices. Wages per hour Unemployment Supply $6 Minimum wage $4 Demand 8,000 13,000 20,000 Number of unskilled workers 4 5-4 Elasticity of Demand and Minimum Wage Number of workers employed with Number of and workers minimum wage employed with inelastic demand minimum curve wage and an elastic demand curve. Supply of unskilled labor Minimum Wage An elastic demand for unskilled labor Number of workers employed with no minimum wage An inelastic demand for unskilled labor 9,800 10,000 Wage Rate 2,000 • Inelastic demand = demand for labor is not price sensitive. • Elastic demand = demand for labor is very price sensitive. • The more elastic demand for labor, the more jobs eliminated by minimum wage law. Number of Workers 5 5-5 Minimum Wage • Minimum wages increase wages of workers with jobs. • Surplus of labor created by minimum wage can result in worse working conditions. • Minimum wages impose the greatest cost on those with the least skills. • Minimum wages increases demand for skilled workers and hence their wages. • Minimum wage law creates incentives for black market and illegal workers. 6 5-6 Price Ceiling • Price ceiling = maximum legal price set by government. • It affects only when set below the equilibrium price. • Effective price ceiling creates shortage. Price Quantity demanded after the price ceiling is imposed. Quantity supplied after the price ceiling is imposed. Supply $8 Price ceiling $6 Demand 50 60 71 Quantity Shortage 7 5-7 Rent Control • Rent control = price ceiling in market for apartments. • Rent control creates shortage of apartments, specially in the long run. • The greater the price elasticity of demand, the greater the shortage. Monthly Rent Demand for apartments Supply of apartments $900 Rent control $600 7,100 13,000 Quantity Shortage 8 5-8 Rent Control • Landlords and potential tenants who can’t find apartments lose. • Existing apartment holders can gain. • It creates incentives for individuals to take up more housing space than they otherwise would. • It reduces individuals’ mobility. • It reduces quality of apartment buildings. • It creates incentives for black market and illegal activities. 9 5-9 Draft vs. Voluntary Enlistment • With voluntary enlistment, the government has to pay market wages to get its desired number of soldiers. • With a draft, the government can pay whatever wages it wants. Soldiers lose with lower wages. • A draft forces transfer of wealth from soldiers to civilians not subject to the draft. 10 5-10 Market for Human Organs • In the U.S., market for human organs is illegal. • So, legal price of human organs = $0. • It creates shortage. • Free markets correct shortages by raising prices. • The ban promotes barter exchange, other illegal activities and black market in organ transfers. $ Price of kidneys Demand for Kidneys Supply of Kidneys 15,000 Quantity of kidneys Size of shortage if price is zero. 11 5-11 Should Government Pay for Health Care? • Free health care benefits create shortages for services with very priceelastic demand. • Governments offering free healthcare limit costs by rationing services. • Price controls over necessities create incentives for producers to develop luxury goods instead of necessities. The point on the supply curve where quantity = 110,000 Price An elastic demand for MRIs Supply of MRIs $2,000 $1,000 If price = $0 consumers will be here on their demand curve 50,000 110,000 Number of scans 12 5-12 Parking Meters • Parking meter = government set parking price. • Below equilibrium price creates shortage and deadweight loss of waiting on weekdays. • Higher price eliminates shortage by reducing quantity demanded. • Above equilibrium price creates surplus on weekends. Price Supply of parking spaces Demand for spaces on a weekend Government set parking price Demand for spaces on a weekday 800 1,000 1,900 Quantity 13 5-13 Agricultural Subsidies • Government supported price for agricultural produce is higher than equilibrium price. • The greater the price elasticities of demand and supply, the higher cost of agricultural support price. • Artificial agricultural prices lead to wastage of resources. • Government can reduce supply by paying farmers not to grow crops. Price per bushel Surplus Demand for wheat Supply of wheat $4 $3 14 20 30 Number of bushels in millions 14 5-14 Do You Know? • When does a price floor have no effect on a market? Price floor will not be effective if it is set below the market equilibrium price. • Why can the minimum wage law and rent control create black markets? The minimum wage law and rent control prevent markets from reaching equilibrium. Since it can not legally reach equilibrium, markets develop unofficial ways to do so. 15 5-15 Do You Know? • How does the elasticity of demand for health care affect the cost to a government that provide free health care to all of its citizens? When a government offers it free, the price of health care is zero for its citizens. If the demand for health care is elastic, quantity demanded increases by manifolds. Hence, the government has to bear the higher costs. 16 5-16 Summary • • • • • Price floor = minimum legal price. Price floor creates surplus. Price ceiling = maximum legal price. Price ceiling creates shortage. Government distorts efficient functioning of market by artificially controlling prices such as minimum wage law, rent control, military draft, ban on market for human organs, parking meters and agricultural subsidies. 17 5-17 Coming Up How is wealth created and destroyed? 18 5-18