* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pure Competition
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
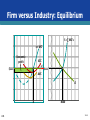
Chapter 10 Pure Competition in the Short Run Copyright © 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. Four Market Models • • • • Pure competition Pure monopoly Monopolistic competition Oligopoly Pure Competition Monopolistic Competition Oligopoly Pure Monopoly Market Structure Continuum LO1 10-2 Pure Competition: Characteristics • • • • LO2 Very large numbers of sellers Standardized product “Price takers” Easy entry and exit 10-3 Purely Competitive Demand • Perfectly elastic demand • Firm produces as much or little as they wish at the market price • Demand graphs as horizontal line LO3 10-4 Average, Total, and Marginal Revenue • Average revenue • Revenue per unit • AR = TR/Q = P • Total revenue • TR = P X Q • Marginal revenue • Extra revenue from 1 more unit • MR = ΔTR/ΔQ LO3 10-5 Profit Maximization: TR – TC Approach • The competitive producer will ask three questions • Should the firm produce? • If so, in what amount? • What economic profit (loss) will be realized? LO4 10-6 Loss-Minimizing Case • • • • LO5 Loss minimization Still produce because MR > minimum AVC Losses at a minimum where MR = MC Producing adds more to revenue than to costs 10-7 3 Production Questions Output Determination in Pure Competition in the Short Run Question Answer Should this firm produce? Yes, if price is equal to, or greater than, minimum average variable cost. This means that the firm is profitable or that its losses are less than its fixed cost. What quantity should this firm produce? Produce where MR (=P) = MC; there, profit is maximized (TR exceeds TC by a maximum amount) or loss is minimized. Will production result in economic profit? Yes, if price exceeds average total cost (TR will exceed TC). No, if average total cost exceeds price (TC will exceed TR). LO6 LO3 10-8 Firm and Industry: Equilibrium Firm and Market Supply and Market Demand LO6 LO4 (1) Quantity Supplied, Single Firm (2) Total Quantity Supplied, 1000 Firms (3) Product Price (4) Total Quantity Demanded 10 10,000 $151 4000 9 9000 131 6000 8 8000 111 8000 7 7000 91 9000 6 6000 81 11,000 0 0 71 13,000 0 0 61 16,000 10-9 Firm versus Industry: Equilibrium S = ∑ MC’s s = MC Economic profit ATC d $111 $111 AVC D 8 LO6 8000 10-10 Fixed Costs: Digging Out of a Hole • Shutting down in the short run does not mean shutting down forever • Low prices can be temporary • Some firms switch production on and off depending on the market price • Examples: oil producers, resorts, and firms that shut down during a recession 10-11