* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Economics for Today 2006
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
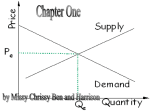
Market Demand and Supply ©2006 South-Western College Publishing 1 The Market Forces of Supply and Demand Supply and demand are the two words that economists use most often. Supply and demand are the forces that make market economies work. Modern microeconomics is about supply, demand, and market equilibrium. Markets A market is a group of buyers and sellers of a particular good or service. The terms supply and demand refer to the behavior of people . . . as they interact with one another in markets. Markets Buyers determine demand. Sellers determine supply. Market Type: A Competitive Market A competitive market is a market. . . with many buyers and sellers. that is not controlled by any one person. in which a narrow range of prices are established that buyers and sellers act upon. Competition: Perfect and Otherwise Perfect Competition Products are the same Numerous buyers and sellers so that each has no influence over price Buyers and Sellers are price takers Competition: Perfect and Otherwise Monopoly One seller, and seller controls price Oligopoly Few sellers Not always aggressive competition Competition: Perfect and Otherwise Monopolistic Competition Many sellers Slightly differentiated products Each seller may set price for its own product What is demand? Demand represents the choice making behavior of buyers 9 Demand Schedule Price $0.00 0.50 1.00 1.50 2.00 2.50 3.00 Quantity 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 Law of Demand The law of demand states that there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. What is a demand curve? Depicts the relationship between price and quantity demanded 12 Why do demand curves have a negative slope? At a higher price buyers will buy fewer units, and at a lower price they will buy more units 13 Ceteris Paribus Ceteris paribus is a Latin phrase that means all variables other than the ones being studied are assumed to be constant. Literally, ceteris paribus means “other things being equal.” The demand curve slopes downward because, ceteris paribus, lower prices imply a greater quantity demanded! Market Demand Market demand refers to the sum of all individual demands for a particular good or service. Graphically, individual demand curves are summed horizontally to obtain the market demand curve. 15 IMPORTANT - KNOW THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN A CHANGE IN THE QUANTITY DEMANDED AND A CHANGE IN DEMAND 16 When price changes, what happens? The curve does not shift - there is a change in the quantity demanded 17 Change in Quantity Demanded Change in Price 18 When something changes other than price, what happens? The whole curve shifts,there is a change in demand 19 What can cause a demand curve to shift? A change in: • Number of buyers in the market • Tastes and preferences • Income • Expectations of consumers • Prices of related goods 20 Decrease or increase in demand Leftward or rightward shift in the demand curve Change in a Nonprice determinant 21 Why does Sunkist http://www.sunkist.com, a major producer of oranges, provide free orange recipes? To increase the demand for oranges, of course 22 Consumer Income As income increases the demand for a normal good will increase. As income increases the demand for an inferior good will decrease. What are substitute goods? Goods that compete with one another for consumer purchases 24 What happens when the price increases for a good that has a substitute? The demand curve for the substitute good increases 25 What happens when the price decreases for a good that has a substitute? The demand curve for the substitute good decreases 26 What does a direct relationship between price and quantity mean? The two move in the same direction 27 What are complementary goods? Goods that are jointly consumed with another good 28 What happens when the price increases for a good that has a complement? The demand curve for the substitute good decreases 29 What happens when the price decreases for a good that has a complement? The demand curve for the substitute good increases 30 What does an inverse relationship between price & quantity mean? It means that the two move in opposite directions 31 What is supply? Supply represents the choice making behavior of sellers 32 Supply Schedule Price $0.00 0.50 1.00 1.50 2.00 2.50 3.00 Quantity 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 What is the law of supply? The principle that there is a direct relationship between the price of a good and the quantity sellers are willing to offer for sale in a defined time period, ceteris paribus 34 Why do supply curves have a positive slope? Only at a higher price will it be profitable for sellers to incur the higher opportunity cost associated with supplying a larger quantity 35 What is market supply? The horizontal summation of all the quantities supplied at various prices that might prevail in the market 36 IMPORTANT - KNOW THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN A CHANGE IN THE QUANTITY SUPPLIED AND A CHANGE IN SUPPLY 37 When price changes, what happens? The curve does not shift - there is a change in the quantity supplied 38 Change in Quantity Supplied Change in Price 39 When something changes other than price, what happens? The whole curve shifts there is a change in supply 40 Change in supply Change in nonprice determinant 41 What can cause a supply curve to shift? A change in: • Number of sellers in the market • Technology • Resource prices • Taxes and subsidies • Expectations of producers • Prices of other goods the firm could produce 42 What is the equilibrium price? The price towards which the economy tends 43 Where is the equilibrium price? At the price where the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied are equal 44 Surplus When the price is above the equilibrium price, the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded. There is excess supply or a surplus. Suppliers will lower the price to increase sales, thereby moving toward equilibrium. 45 Shortage When the price is below the equilibrium price, the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied. There is excess demand or a shortage. Suppliers will raise the price due to too many buyers chasing too few goods, thereby moving toward equilibrium. 46 Steps To Analyzing Changes in Equilibrium Determine the Event Decide whether the event shifts the supply or demand curve (or both in very rare cases). Shift demand or supply to the left or to the right. (Make a cheat sheet!) Find the new equilibruim Examine how the shift affects equilibrium price and quantity.