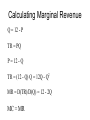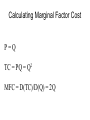* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Industrial Organization
Marginal utility wikipedia , lookup
Economic equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Externality wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Market (economics) wikipedia , lookup
Supply and demand wikipedia , lookup
Marginalism wikipedia , lookup
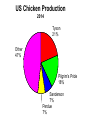
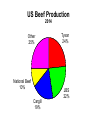
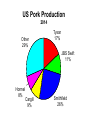
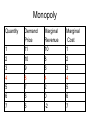
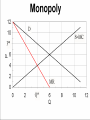
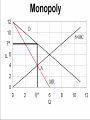
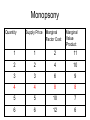
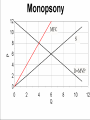
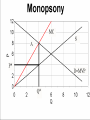
Industrial Organization AG BM 102 Introduction • • • • • Willard’s Mistake Competitive Environment Relevant Market Market power Market structure – Market Conduct-Market performance Market Structure – those characteristics of the market that significantly affect the behavior and interaction of buyers and sellers US Chicken Production 2014 Tyson 21% Other 47% Pilgrim's Pride 18% Sanderson 7% Perdue 7% US Beef Production 2014 Other 25% National Beef 10% Cargill 19% Tyson 24% JBS 22% US Pork Production 2014 Other 29% Tyson 17% JBS Swift 11% Hormel 8% Cargill 9% Smithfield 26% Market Conduct – a firm’s policies toward its market and toward the moves made by its rivals in that market Market Performance – how well does an industry do what society might reasonably expect it to do Market – a collection of firms, each of which is supplying products that have some degree of substitutability, to the same potential buyers • Common buyers for sellers • Common sellers for buyers • Relatively homogeneous product Industry- sellers of a particular product or closely competing products Relevant market – the portion of the total market that a participant views as including his or her direct competitors and customers (or suppliers) Some market models • Pure competition • Monopoly – a single seller • Monopsony – a single buyer Marginal Revenue The change in total revenue from expanding sales by one more unit Marginal revenue Quantity Price 1 11 Total Revenue 11 Marginal Revenue 9 2 10 20 7 3 9 27 5 4 8 32 Calculating Marginal Revenue Q = 12 - P TR = PQ P = 12 - Q TR = (12 - Q) Q = 12Q - Q2 MR = D(TR)/D(Q) = 12 - 2Q MC = MR Calculating Marginal Revenue • • • • Solve the demand function for P P = 12 –Q Take the coefficient of Q and double it MR = 12 – 2Q Monopoly Quantity 1 Demand Price 11 Marginal Revenue 10 Marginal Cost 1 2 10 8 2 3 9 6 3 4 8 4 4 5 7 2 5 6 6 0 6 7 5 -2 7 For Monopoly, find where MC =MR and then go up to the price on the demand curve Marginal Factor Cost The change in total factor cost from buying one additional unit of an input Marginal Factor Cost Quantity Price Total Expenditure 1 1 1 Marginal Expenditure 3 2 2 4 5 3 3 9 7 4 4 16 Calculating Marginal Factor Cost P=Q TC = PQ = Q 2 MFC = D(TC)/D(Q) = 2Q Calculating Marginal Factor Cost • • • • • Solve the Supply curve for P P=Q Double the coefficient of Q MFC = 2Q Ordinarily the line doesn’t run through the origin • The process is the same – solve for P – double the coefficient of Q Monopsony Quantity Supply Price Marginal Factor Cost Marginal Value Product 1 1 2 11 2 2 4 10 3 3 6 9 4 4 8 8 5 5 10 7 6 6 12 6 For Monopsony, find where MFC =MVP and then go down to the price on the supply curve Concluding Comments • Where does a 500 pound gorilla sit? • Market power is important • Understanding it helps you understand market behavior