* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemical Cycling
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
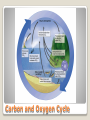
Biogeochemical Cycles Need to consider interactions between abiotic (non living) and biotic (living) factors. Also consider energy flow and chemical cycling. Carbon, nitrogen and oxygen can be recycled between living and nonliving things in an ecosystem and the biosphere. Even though energy flow and chemical cycling are different in nature, they are related to feeding patterns within ecosystems… Producers incorporate chemicals from nonliving environment into organic compounds. Consumers feed on producers, incorporating some chemicals into their bodies and release some as waste. As organisms die, decomposers break them down to supply chemicals in the inorganic form for soil, water and air. Three types of cycling: ◦ Carbon and Oxygen Cycle ◦ Nitrogen Cycle ◦ Water Cycle Chemical Cycling In the atmosphere carbon is found in its inorganic form CO2. Producers use the CO2 to form organic compounds during photosynthesis. During cellular respiration, both producers and consumers break down organic compounds and release CO2 as a waste product. Non-living processes contribute to CO2 production: Carbon and Oxygen Cycle ◦ Burning of fossil fuels Oil Coal Natural gas ◦ Burning of wood ◦ Forest fires ◦ Human activities ◦ Volcanic eruptions Carbon and Oxygen Cycle Nitrogen ◦ Found in all living organisms ◦ An element of Amino Acids Produce proteins ◦ Makes up 80% of the Earth’s atmosphere ◦ Producers can use it in the form of ammonium or nitrate Nitrogen fixation ◦ Nitrogen gas to ammonia Nitrification ◦ Ammonium to nitrates Nitrogen Cycle Nitrogen Cycle Solar energy evaporates water from land and water surfaces adding gaseous water vapor into the atmosphere. Water vapor cools and condenses falling to the ground as precipitation. ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Rain Snow Hail Sleet Plants get water from soil, consumers by eating and drinking. Water Cycle Some water can be lost by plants through the process called transpiration, which is then evaporated into the atmosphere. Water not retained by plants or soil will run off into rivers and streams, or restore ground waters. Water Cycle