* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Essentials of Glycobiology Lecture 31 May 23, 2000 Jeff Esko
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
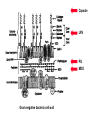
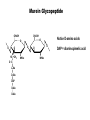
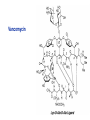
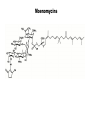
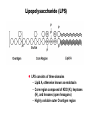
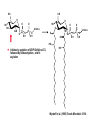
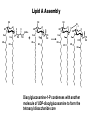
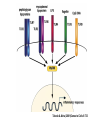
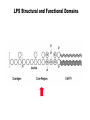
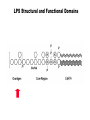
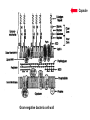
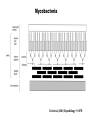
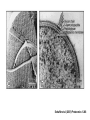
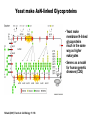
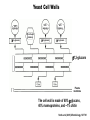
Unicellular Organisms: Eubacteria, Archea, Yeast Lecture 27, Chapter 21 May 13, 2004 Jeff Esko Overview General structure of bacterial cell walls Structure, function and assembly of peptidoglycan (murein) Periplasmic -glucans (MDO) Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) - endotoxin Capsular polysaccharides - mimicry Archea glycoproteins - a new area Yeast glycosylation and cell walls Capsule LPS PG MDO Gram-negative bacteria cell wall Peptidoglycan A D G A A D G A A G D A A D G A A D G A A G D A A D G A A G D A A D G A A D G A A G D A A G D A A D G A A G D A A D G A A G D A A D G A A G D A [GlcNAc1,4MurNAc1,4]n A G D A A G D A A D G A A G D A A G D A Heijenoort (2001) Glycobiology 11:25R Murein Glycopeptide CH2 OH CH2OH O O O HC CH3 O C L-Ala D-Glu DAP D-Ala D-Ala NHAc Notice D-amino acids O O O O NHAc DAP = diaminopimelic acid Peptidoglycan A D G A A D G A A G D A A A D G A A D G A A G D A A D G A A G D A A A D G A A D G A A G D A A G D A A D G A A G D A A A G D A A A D G A A G D A A D G A A G D A The final step involves cleavage between the D-Ala-D-Ala unit and transpeptidation to the amino group of DAP of another unit A G D A A D G A A G D A A G D A Vancomycin Moenomycins Peptidoglycan Biosynthesis P Undecaprenyl phosphate MDO Gram-negative bacteria cell wall Membrane Derived Oligosaccharides (MDO) 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 + Phosphoethanolamine + Phosphoglycerol + Succinate Branched -glucans Represent about 1-5% of dry weight Charged substituents act as an osmolyte and protects the inner membrane against the large difference in osmolarity inside the cell compared to outside the cell LPS Gram-negative bacteria cell wall Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) LPS consists of three domains – Lipid A, otherwise known as endotoxin – Core region composed of KDO (K), heptoses (H), and hexoses (open hexagons) – Highly variable outer O-antigen region HO OH O O O HO HO AcN P O HO O O OH P Uri din e O OH O O O O NH C O P O O OH P Uri din e O OH HO Initiates by acylation of UDP-GlcNAc at C3, followed by N-deacetylation, and Nacylation HO Wyckoff et al. (1998) Trends Microbiol. 6:154 Lipid A Assembly OH OH O HO O O O C O HO HO O HO NH P O P O O OH OH Uridine + O HO O O O C O HO OH HO NH P O O OH O CH 2 O O O HO NH O C O O O O C O HO HO HO HO Diacylglucosamine-1-P condenses with another molecule of UDP-diacylglucosamine to form the tetraacyl disaccharide core NH P O O OH Lipid A Assembly KDO transferases initiate the formation of the core Additional C12 fatty acids added to -hydroxy groups (wax) Lipid A translocates to the outer leaflet of the outer membrane by msbA (ABC transporter) Doerrler et al. (2001) J Biol Chem. 276:11461 Lipid A Biology Lipid A, the heat stable endotoxin of gram negatives Resistant strains of mice defined a locus, lps, which was positionally cloned. lps turned out to be homologous to toll receptors in Drosophila, which were known to be involved in innate immunity to fungal infection lps turns out to beTlr4, a member of a family of signaling receptors (10 members known). - Tlr4 binds to Lipid A. - Tlr2 apparently binds and responds to muramyldipeptide Takeda & Akira (2001)Genes to Cells 6:733 LPS Structural and Functional Domains Core region contains unusual sugars CH2 OH HOHC O OH CH2 OH CHOH O COOH OH OH OH 3-deoxy-D-mannooctulosonic acid (KDO) OH OH OH L-glycero-D-mannoheptulose The inner core contains 1-4 KDO residues, which look like an analog of sialic acid. The core also contains heptopyranoses, which can vary stereochemically The rest of the core consists of various combinations of Glc and Gal LPS Structural and Functional Domains O-antigens O-antigen Structure O9 a3 O6 a3 O124 3 a2 2 a4 a2 4 3 6 a3 a2 a4 6 GlcLA GlcLA = glucolactillic acid O-antigens consist of 2-8 sugars, repeated ≤50 times O-antigens gives rise to different serotypes and some are correlated with disease a3 Capsule Gram-negative bacteria cell wall Capsule type K1, polysialic acid K5, N-acetylheparosan Group A Streptococcus (hyaluronan) Structure a8 a8 a8 a8 a8 a4 4 a4 4 a4 4 3 4 3 4 Mucoid strains contain a polysaccharide capsule >80 different capsules types are known just in E. coli Extraordinary diversity of structure Mycobacteria Crick et al. (2001) Glycobiology 11:107R Crick et al. (2001) Glycobiology 11:107R Crick et al. (2001) Glycobiology 11:107R Bacterial Glycoproteins Surface-layer (S-layer) glycoproteins Prevalent in Bacteria and Archaea, but structures differ, e.g., N-linked glycosylation only in Archaea Structural analyses have revealed unusual carbohydrate-linkage regions…. ….and unusual nucleoside diphosphate-linked oligosaccharides Schaffer et al (2001) Proteomics 1:248 Notice diversity of linkages Similarity in sequence of Nlinked attachment sites and mechanism of assembly of glycan (dolichol pathway) Burda & Aebi (1999) Biochim Biophys Acta 1426:239 Yeast make AsN-linked Glycoproteins • Yeast make membrane N-linked glycoproteins much in the same way as higher eukaryotes • Serves as a model for human genetic diseases (CDG) M Aebi (2001) Trends in Cell Biology 11:136 Yeast Mannans a6 a6 a3 a2 a2 a3 a2 a2 a3 a2 a2 a3 a6 a3 a6 a3 a3 a3 a2 a2 a2 a2 a6 a6 -1-P a2 a2 a4 a2 a2 a a Ser/Thr Ser/Thr -P- a6 a3 a6 a6 a3 a6 4 4 Asn Willer et al (2003) Curr Opin Struct Biol 13:621 a3 Vertebrate a-dystroglycan Yeast Cell Walls GPI proteins 1,6-glucans Pir cell wall proteins GPI proteins GPI proteins 1,6-glucans 1,6-glucans 1,3-glucans Plasma membrane The cell wall is made of 60% -glucans, 40% mannoproteins, and ~1% chitin Smits et al (2001) Microbiology 147:781 Summary • Bacterial cell walls are complex layered structures composed of multiple classes of glycans • Bacterial wall glycans provide an exoskeleton, define shape, protect against turgor pressure, create antigenic serotypes, and provide a way to prevent immune recognition • Glycosylated proteins are present in eubacteria and in archaea • Yeast produce many of the same glycans found in higher eukaryotes, but the mecahnism of assembly differs in subtle way • Yeast cell walls are composed of glycans (glucans and chitin) • Yeast and bacteria provide powerful genetic systems for understanding membrane and cell wall assembly