* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hello
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Schmerber v. California wikipedia , lookup
Autotransfusion wikipedia , lookup
Blood transfusion wikipedia , lookup
Hemorheology wikipedia , lookup
Blood donation wikipedia , lookup
Jehovah's Witnesses and blood transfusions wikipedia , lookup
ABO blood group system wikipedia , lookup
Plateletpheresis wikipedia , lookup
Men who have sex with men blood donor controversy wikipedia , lookup
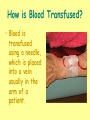
Hello Blood Transfusion What is a Blood Transfusion? • Blood transfusion is a medical procedure that needs to be ordered by a physician. • It is the introduction of blood or blood components directly into the bloodstream of an individual. How is Blood Transfused? • Blood is transfused using a needle, which is placed into a vein usually in the arm of a patient. What are blood components? • • • • • • • Whole Blood (WB) Packed Cell (PC) Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP) Concentrated Platelet Cryo Precipitation Albumin ……. What is Donated Blood Tested for? • Blood type and red blood cell antibodies • Syphilis • Viruses: HIV (which causes AIDS) Hepatitis B & C HTLV Why do I need a blood test before a transfusion? Your blood will be tested against the donor units to be sure they are a good match for you and your blood type What are some of the risks associated with blood transfusions? • Allergic reactions, with hives (1%). • Fever. Increase in temperature (1%). • Hemolytic reactions. Rare, testing prior to transfusion reduces the risk (approximately .001%). • Incompatible red cells. Sometimes the patient will react to donor red cells because they are a different type. • Bacterial contamination. Uncommon, most often associated with platelet transfusion. • Infectious disease transmission (HIV, Hepatitis C ,Hepatitis B ,West Nile Virus , CJD( What are some Alternatives to Blood Transfusion? • Autologous Transfusion • Directed Transfusion • Blood Dilution • Blood Salvage (recycling) • Controlled Hypotension • Drugs What is an Autologous Donation? • An autologous donation enables you to donate and store your own blood prior to elective surgery. This stored blood will then be used, if needed, during or after your surgery Why use Autologous Blood? • It removes the risk of disease transmission and transfusion reactions. • It eliminates the risk of alloimmunization, i.e., developing antibodies against the cells. What is a Directed Donation? • In certain circumstances, family members who have the same blood types are regular blood donors and able to donate blood for a relative. • The most commonly used directed donation is ‘parent to child’. What is Blood Dilution? This process occurs during surgery. Also known as hemodilution, blood dilution is a process where 2-3 units of blood are removed and replaced with fluids. The blood is returned to the patient, if required. What is Blood Salvage? During or after surgery, patients may encounter blood loss. In some circumstances, blood can be recycled using a blood salvage machine to collect, filter and return blood to the patient. What drugs are used in conjunction with transfusion and how are they used? • Drug that increases the hemoglobin level is erythropoietin. • Drugs that reduce bleeding (antifibrinolytic activity)include: aprotinin, tranexamic acid, and epsilon amino caproic acid. • Drugs may be administered before or during surgery.