* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Ring of Fire wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Hotspot Ecosystem Research and Man's Impact On European Seas wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
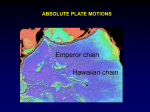
Hotspots, Plumes and Mass Extinctions Is Hawaii more than a great vacation spot? How does life respond to geologic catastrophes? Plate Tectonics - Distribution of Volcanic and Earthquake Activity The Earth’s surface is broken into plates Wilson Cycle (ocean basin fm) Examples: 1. East African Rifts 2. Red Sea 3. Atlantic Ocean 4. Pacific Ocean 5. Mediterranean Sea 6. Himalayas, Tibet 1 2 3 4 5 6 Hawaii Easter Galapagos Samoa The Hawaiian Hotspot Volcanoes to atolls (Darwin) Tahiti -- shield volcano Moorea -- fringing reef Raiatea - barrier reef Bora Bora -- lagoon Maupiti -- the oldest volcano next stage is the coral atoll French Polynesia from space atoll barrier reef fringing reef Pacific Hotspot Volcanic Chains Questions: • Where do Hotspots come from? • How do Hotspots start? • How long do they last? Indian Ocean • Hotspot tracks and 3 spreading ridges • A complete record of hotspot activity JOIDES Resolution drillship Reunion hotspot track, central Indian Ocean “flood” basalts in western India >300 lava flows, each 1000 km3 Western India • An accumulation of lava flows 5 km thick! • Occurred at the same time as the extinction of the dinosaurs Mass Extinction (K-T Boundary) • What killed the Dinosaurs? • 65 million yr ago • A meteorite, or volcanic activity, or BOTH? Impact Site: Yucatan Peninsula Volcanic catastrophes and Mass Extinctions Greenland • Birth of the Iceland hotspot • Next came the opening of the North Atlantic Ocean basin Global Distribution of large, rapidly-erupted volcanic events red = hotspot-related volcanism since 250 Ma Flood basalts, India Columbia River Basin Flood Basalts with source at Yellowstone Large Igneous Provinces are: • BIG!! • NOT explained by Plate Tectonics • Initial Plume and Hotspot Activity Mantle Plumes • • • • Part of the circulation in the Mantle Driven by temperature differences Hot and cold => density differences Gravity Rules! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f37Gf6IVj6o&feature=related Mantle convection the driving force for plate tectonics What causes the warmer material to rise? Mantle Plumes Mantle convection and hotspot formation Cross-sections of the Earth Red = hot upwelling from core-mantle boundary Cold lithosphere sinks, hot plumes rise. Cartoon Schematic Blue = cold downwelling Computer Model Which is not a hotspot? Yellowstone Iceland Hawaii Mt. St. Helens Degassing Magma • Gases include CO2, SO2, Cl, F that make “acid rain” • Shuts down photosynthesis Laki, Iceland (1783) -- the year without a summer Laki, Iceland (1783) -- the year without a summer Submarine: Hydrothermal Exchange – Release of Metals Ocean Anoxic Events productivity or preservation? Marine sedimentary layers exposed in Italy Hydrothermal Plumes from LIPs Effects of Submarine Plateaus • Release of “reduced” metals uses up oxygen in the oceans • Trace metals are “nutrients”, so promote rapid growth of plankton • Sinking organic matter also uses up oxygen in the oceans • Extinctions of “benthic” marine organisms Two Styles of Mantle Convection Evolution of Life • “Punctuated” by rapid change events • Where there is chaos there is opportunity • Extinctions lead to new ecosystems