* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Market Efficiency and Market Failure
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
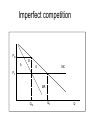
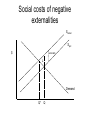
Market Failure SPHA511, John Ries Market Failure • There are situations, known as "market failure," when private markets fail to achieve Pareto efficiency, and thus provide a potential role for the government to intervene and improve their efficiency. • What are the four broad categories of market failures? Imperfect competition Definition: "imperfect competition" is rivalry among firms in situations where there is an insufficient number of sellers to achieve perfect competition. Specifically, a firm can influence the price that it charges (it faces a downward sloping demand curve). Imperfect competition What types of industries are characterized by imperfect competition? What are the consequences of imperfect competition? • price greater than marginal cost • too little production • a reallocation of wealth from consumers to firms, and • deadweight loss. Imperfect competition PM B A G MC PC MR QM QC Q Public goods Definition: a "public good" is one whose benefits are collective or indivisible in nature. Technically speaking a public good is one which is (1)"non-rival" (my consumption doesn't affect how much you can consume). (2) "non-exclusive" (it is impossible or extremely costly to prevent anyone from consuming it). Which is a public good? • • • • • • City bus Lighthouse Police Parks Highways Art paintings Why are efficient levels of public goods not provided by private markets? Externalities Externalities are costs or benefits imposed on third parties (without the effects being “priced”) What are examples of negative externalities? What are examples of positive externalities? Social costs of negative externalities Ssocial Spriv $ externality L Demand Q* Q Social costs of positive externalities $ S L externality MBsocial D=MBpriv Q Q* Quantity Imperfect information If consumer’s demand (willingness to pay) is “faulty” due to imperfect information (lack of knowledge of product attributes or deceptive marketing practices) then “true” willingness to pay may deviate from realized willingness to pay. In this case, demand is “wrong” and the competitive market fails to achieve allocational efficiency. Imperfect information can lead to problems of - Adverse selection (hidden type) - Moral hazard (hidden action) Imperfect Information The market for lemons: What will a consumer be willing to pay if she cannot judge used car quality and the price of a “good” used car is P and a “lemon” is X? What will this do to the market for good used cars? What are remedies to the imperfect information problem that do not involve government action? Health care and market failure • The health care industry violates conditions necessary for perfect competition – Imperfect information: Health care service providers have specialized knowledge that can potential be used to exploit consumers. Consumers face risk of major illness and associated high costs. – Externalities: There are external benefits to an individual maintaining good health (especially when health care is publicly funded) – Imperfect competition: Insurers, doctors, and hospitals all have power to influence prices Remedies to imperfect information problems • Labeling • Standards (set and enforced by government, business, or professional organizations) – When are standards preferred to labeling? – Both interventions create administration costs Standards Standards serve two distinct purposes: public safety and coordination. When we buy a toaster, we need to be sure it conforms to safety standards and will not explode when it’s used. We also need to establish standards that coordinate activities. The metric standards allow us to communicate size. We adopt the standard that “green” means “go.” Firms standardize product dimensions and specifications (fax paper size, voltage, etc.) so that products are compatible with each other. Different Keyboard Standards QWERTY France’s AZERTY What share of the world drives on the left? 1/3 of the world’s population drives on the left! (so their cars should have steering wheels on the right) Standard changes are rare, but there are strong pressures to conform to practices of neighboring countries. BC (1922), New Brunswick (1922), Nova Scotia (1923), PEI (1924), and Newfoundland (1947) switched. Sweden switched twice! (in 1736 to the left and 1967 back to the right) “Metrication” everywhere (except US, Liberia, and Burma) How Drugs are Regulated in Canada Sara 1. What happened to Vanessa Young? 2. What evidence suggests that Health Canada was too slow to issue a warning about the drug? 3. What are drugs? 4. How are drugs approved? What are clinical trials and who performs them? 5. What problems exist in Health Canada’s monitoring of new drugs? How might they be remedied? Graduated drug licensing proposed Julie • What is the “fundamental shift” in prescription medicines regulation proposed by Health Canada? • What events motivated this proposed reform? • What stakeholders prefer speedy approval of new drugs? • How will the proposal be implemented? Who will pay? • What are possible obstacles to the implementation? “Drug Approval is Not a Shield from Lawsuits, Justices Rule” • Who made the ruling? What was the vote? What was the award? • What happened to Diana Levine? • What were Wyeth’s arguments? • Why should Wyeth have known of the danger? • Why did the Court rule against Wyeth? Leila “Nurses not reporting faulty devices to Ottawa” Victoria • What is the difference in reporting requirements concerning faulty medical devices for manufacturers and distributors versus doctors and nurses? • How frequently do nurses encounter malfunctioning equipment? What percent know that they should report it to Health Canada? • How many reports were sent to Health Canada in 300304? How many products were recalled? • How many patients die in Canada because of preventable medical errors? – What are the causes of preventable medical errors? (not in article) The cost of regulation Winnie • How much did the cost of regulation increase for government from 1973/1974 to 1997/1998? • How do compliance costs compare to costs of government administration of regulations? • How are compliance costs estimated? • If it is businesses that must comply with regulatory standards, why does the article say that households bear substantial costs? • How do compliance costs of households compare to other household expenditures? Canada mulls joint drug review with US regulator • What is the proposal and its objectives? • What are potential benefits and costs? Why is the experience of the morning after pill relevant? • Who will benefit? • What is the different times for drugs to be approved in Canada and the US? What is the reason for these differences? Steven