* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download New Demand Curve
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
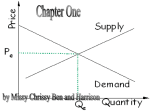
Markets A market is where buyers and sellers meet to exchange products These buyers and sellers negotiate a price that each is happy with, and then exchange the good The buyers of products make up the DEMAND for the good The sellers of products make up the SUPPLY of the good The MARKET PRICE for a good is the price where the Number of Buyers = Number of Sellers Supply Market or Equilibrium Price Demand number of buyers = number of sellers Market or Equilibrium Quantity A market can react to changes in either the buyers or the sellers These changes can cause one of the curves to move Supply Market or Equilibrium Price Demand number of buyers = number of sellers Market or Equilibrium Quantity If all the BUYERS change their minds about buying the product, the Demand curve will move If all the SELLERS change their minds about buying the product, the Supply curve will move When an entire curve moves, it is known as a SHIFT of the curve A Shift of a curve will cause the Equilibrium Price and Equilibrium Quantity for the Market to change Supply New Market or Equilibrium Price Original Market or Equilibrium Price New Demand Curve Demand Original Market or Equilibrium Quantity New Market or Equilibrium Quantity This is a shift of the Demand curve Either the Demand curve can shift or the Supply curve can shift The things that can shift a curve are called DETERMINANTS We are going to focus on the Demand Curve first and how it impacts the Equilibrium Price and Quantity for a good Buyers of products make up the for the good Need a definition? Demand for a good consists of all the buyers who are willing and able to purchase the good at various prices Here’s an example of Demand…. Let’s look at the Demand for Bosco Sticks in a classroom of 32 students Price Quantity Demanded $0 30 At a price of $0 (no price), there are 30 students willing to buy Bosco Sticks The other two students choose not to eat Bosco Sticks, even if they do not have to pay for them (these 2 students are not part of the Demand for Bosco Sticks) At different prices, there are different numbers of buyers for the Bosco Sticks As the price of the Bosco Sticks increases, fewer and fewer buyers want to purchase them Price Quantity Demanded $0 .50 1.00 1.50 2.00 2.50 3.00 3.50 4.00 30 28 25 20 12 8 4 3 1 A chart with price and quantity data is called a Demand Schedule If you put the Demand Schedule information on a graph, it would look like this: Price and Quantity Demanded are INVERSELY related If price rises, the number of buyers decreases If price falls, the number of buyers increases Price D Quantity As you can see, the Demand curve slopes DOWNWARD This relationship is called the Sometimes, things cause every person to change their willingness or ability to buy a good This means that we have new data for our demand curve This will cause us to draw a NEW demand curve to show the changes in willingness and ability Let’s look at the Bosco example again… What if the surgeon general found that eating Bosco Sticks prevented cancer??? Old Demand Schedule Price Quantity Demanded New Demand Schedule We are assuming that everyone will want more Bosco Sticks…now they’re good for you!!! Price Quantity Demanded $0 32 .50 30 1.00 27 1.50 23 2.00 18 2.50 14 3.00 10 $0 30 .50 28 1.00 25 1.50 20 2.00 12 2.50 8 3.00 4 3.50 3 3.50 7 4.00 1 4.00 3 Since the quantity demanded has changed at every price, we say that there has been a A Change in Demand causes the demand curve to shift or move Quantity Demanded of Bosco Sticks 4.5 4 3.5 3 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 Quantity Demanded of Bosco Sticks D1 D 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 This graph shows an increase in Demand 35 This is shown by drawing a new curve and labeling it as D plus a number D1 D D D1 Increase in Demand •New demand curve is to the right of the original •It moves towards the bigger numbers in the number line Decrease in Demand •New demand curve is to the left of the original •It moves towards the smaller numbers in the number line What causes a Demand curve to shift?? There are 4 categories of things that will cause a Demand curve to shift. These categories are called Determinants… It’s easy to remember the determinants if you use this mnemonic device These are goods that are used together, like… Peanut Butter and Jelly If the price of one good changes, it impacts the Demand of the other good Oreos and Milk If the Price of peanut butter increases, the quantity demanded of the peanut butter decreases This causes a decrease in the Demand for jelly (if people buy less peanut butter, they will need less jelly) The reverse is true also… Goods that can be used in place of each other If the price of Pepsi increases, the quantity demanded of Pepsi decreases This causes an increase in the Demand for Coke like Coke and Pepsi If the income of the consumers changes, it changes their ability to buy goods An increase in consumer income results in an increase in Demand for goods like cars or televisions A decrease in consumer income results in a decrease in Demand for goods Things like changes in income taxes or inflation rates will impact consumer income Any of these items will cause a good to change in popularity, which will result in a change in Demand If a good is more popular, the Demand for it will increase. If it is less popular, Demand will decrease •New information such as impact on health •Trends are things like fads (Rubik’s Cubes) •Number of Consumers: more consumers = more demand and vice versa Add info about how D slopes downward How can you tell if there is a change in Demand or a change in Quantity Demanded? Use the flow chart to help you Is there a price change? YES! NO! Is the price change for the good being measured on the graph? YES! This is a change in Quantity Demanded You should move along the curve NO! It’s a change in Demand You should shift the curve appropriately The determinant is either Complementary Goods or Substitute Goods It’s a change in Demand You should shift the curve appropriately The determinant is one of the following: •Attitudes, Trends, Number of Consumers •Income of Consumers When the price of the Bosco Sticks changed, the number of buyers changed. Economists call this a… Price Quantity Demanded $0 .50 1.00 1.50 2.00 2.50 3.00 3.50 4.00 30 28 25 20 12 8 4 3 1 If we put this data on a graph, it looks like this…. Quantity Demanded of Bosco Sticks 4.5 4 3.5 3 is always 2.5 located on 2 this axis 1.5 1 0.5 0 Quantity Demanded of Bosco Sticks Price 0 5 10 15 20 25 Quantity Is always located on this axis 30 35 The line is called the Demand Curve and always slopes Downward If the price of the good changes, it causes a change in quantity demanded…. On the graph, this is a movement along the curve from one point to another If the price falls from P1 to P2 P1 P The quantity demanded will increase from QD1 to QD2 P2 D QD1 QD2 Q