* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Update on the Side Effects of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
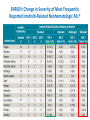
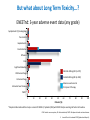
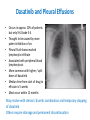
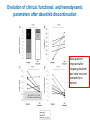
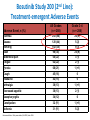
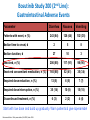
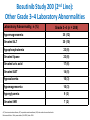
Update on the Side Effects of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Dr Jenny Byrne Nottingham University Hospitals Trust Imatinib is a Safe Drug.... IRIS Study: Most Frequently Reported AEs Most Common Adverse Events (by 5 Years) • • All Grade AEs Patients, % Grade 3/4 AE’s Patients % Superficial Edema 60 2 Nausea 50 1 Muscle cramps 49 2 Musculoskeletal pain 47 5 Diarrhea 45 3 Rash/skin problems 40 3 Fatigue 39 2 Headache 37 <1 Abdominal pain 37 4 Joint pain 31 3 Only Serious Adverse Events (SAEs) were collected after 2005 Grade 3/4 adverse events decreased in incidence after years 1-2 IRIS 8 year update IRIS SAEs in Year 8 No unique, previously unreported AEs attributed to imatinib observed over the past 24 months Since year 5 only 9 SAEs with suspected relationship to imatinib have been reported (2%): Congestive Heart Failure (n=3): all of the patients had pre-existing cardiac disease prior to study entry Second malignancy (n=3)* Myositis (n=1); elevated CK (n=1); multiple sclerosis (n=1) Pancreatitis (n=1); vomiting (n=1) Dermatitis (n=1) *With >400,000 patient years of estimated imatinib exposure, the analysis of clinical safety data from clinical trials and spontaneous reports did not provide evidence for an increased incidence of malignancies for patients treated with imatinib compared to that of the general population IRIS 8 year update But many patients have low level side effects... Which can affect their quality of life… ENRICH STUDY: Changes in Toxicity and QoL in Patients Switched from Imatinib to Nilotinib 45 / 52 patients had a total of 182 low-grade (grade 1/2), imatinib-related, nonhematologic AEs at baseline. Of the 182 AEs, 130 were grade 1 and 52 were grade 2. 71.4% ENRICH: Change in Severity of Most Frequently Reported Imatinib-Related Nonhematologic AEs* Cortes J, et al. Blood. 2012;120(21):[abstract 3782]. ENRICH: Change from Baseline in QoL bCycle* Cortes J, et al. Blood. 2012;120(21):[abstract 3782]. Nilotinib is Generally Better Tolerated… But what about Long Term Toxicity...? ENESTnd: 3-year adverse event data (any grade) Symptomatic QT prolongation Pancreatitis Hepatotoxicity Fluid retention Effusions Rash Significant bleeding Nilotinib 300 mg BID (n=279) CNS haemorrhage Imatinib 400 mg BID (n=280) GI haemorrhage Adverse event onset in third year of therapy Ischaemic heart disease PAOD* 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Patients (%) *No patient discontinued the study as a result of PAOD. 6/7 patients (85%) with PAOD had pre-existing risk factors at baseline. CNS: Central nervous system; GI: Gastrointestinal; PAOD: Peripheral arterial occlusive disease. 1. Larson RA et al. Leukemia 2012 [Epub ahead of print]. ENESTnd: 3-year grade 3/4 laboratory abnormalities AST increased ALT increased Bilirubin (total) increased Lipase (blood) increased Glucose increased Nilotinib 300 mg BID (n=279) Haemoglobin Imatinib 400 mg BID (n=280) Adverse event onset in third year of therapy Absolute neutrophils (seg. + bands) Platelet count (direct) 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Patients (%) ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aminotransferase; Seg.: segmented. 1. Larson RA et al. Leukemia 2012 [Epub ahead of print]. ENESTnd: arterial Events by 4 Years Patients, n (%) IHD (3 yrs in brackets) PAOD (3 yrs in brackets) Nilotinib 300 mg BID n = 279 Nilotinib 400 mg BID n = 277 Imatinib 400 mg QD n = 280 11 (9) 4 (4) 14 (11) 5 (3) 3 (3) 0 Between years 3 and 4, five new patients had an IHD event (2 in the nilotinib 300 mg BID arm and 3 in the nilotinib 400 mg BID arm), and 2 new patients had a PAOD event (both in the nilotinib 400 mg BID arm) 1 patient in the nilotinib 400 mg BID arm with previously reported PAOD had a newly reported drug-related SAE (arterial stenosis limb) leading to treatment discontinuation Mechanism not clear - ? Related to high glucose levels Worrying – need more data, especially as now approved 1st line 11 Data cutoff: 27Jul 2012. Novartis Communication 25 Feb 2012: Atherosclerotic Related Events Imatinib 400 mg qd N=280 Any Grade 3/4 grade n (%) n (%) Nilotinib 300 mg bid N=279 Any grade Grade 3/4 n (%) n (%) Nilotinib 400 mg bid N=277 Any grade Grade 3/4 n (%) n (%) Any AREs 4 (1.4) 17 (6.1) 23 (8.3) Risk factors for ARE’s 4/4 (100%) 15/17 (88%) 0 0 0 0 10 (3.6) 8 (2.9) 0 0 4 (1.4) 3 (1.1) 5 (1.8 ) 1 (0.4) 3 (1.1) 3 (1.1) 11 (3.9) 6 (2.2) 14 (5.1) 9 (3.2) 1 (0.4) 0 3 (1.1) 2 (0.7) 5 (1.8 ) 4 (1.4) AREs leading to discontinuation Peripheral Arterial Occlusive Disease (PAOD) Ischemic Heart disease Ischemic cerebrovascular 3 (1.1) 11 (3.9) 14 (5.1) 22/23 (96%) ‘Clinicians should vigorously manage cardiovascular risk factors and AREs according to standard international guidelines regarding treatment of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and diabetes as well as smoking cessation’ Is Dasatinib any better...? DASISION: 2-year adverse event data Fluid retention Superficial oedema Any grade Pleural effusion Myalgia Nausea Diarrhoea Dasatinib 100 mg QD (n=258) Vomiting Rash Imatinib 400 mg QD (n=258) Headache Grade 3/4 Fatigue Neutropenia Thrombocytopenia Anaemia 0 • • 10 20 30 40 50 60 Patients (%) 70 80 90 100 Grade 3/4 biochemical abnormalities occurred in ≤3% of patients and with similar frequency in treatment arms except hypophosphataemia (dasatinib: 7%; imatinib 25%) Pulmonary arterial hypertension was diagnosed in 3 patients but did not lead to treatment discontinuation 1. Kantarjian HM et al. Blood 2012; 119(5): 1123–1129. Dasatinib and Pleural Effusions • Occurs in approx. 20% of patients but only 5% Grade 3-4 • Thought to be caused by more potent inhibition of src • Pleural fluid shows marked lymphocytic infiltrate • Associated with peripheral blood lymphocytosis • More common with higher / split doses of dasatinib • Median time from start of drug to effusion is 5 weeks • Most occur within 12 months May resolve with steroid / diuretic combination and temporary stopping of dasatinib Others require drainage and permanent discontinuation Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension • • • • • • • • Circulation 2012, Montani et al French study of 9 cases between 2008-2010 Estimated incidence 0.45% of patients exposed to dasatinib Src inhibition thought to be implicated in pathogenesis Late complication occurring 8-48 months after starting dasatinib More common in females Median age of patients 51 years 6/9 patients also had concomitant pleural effusions but PAH persisted even after effusions resolved • ? Reversible on stopping dasatinib Evolution of clinical, functional, and hemodynamic parameters after dasatinib discontinuation Most patients improved after stopping dasatinib but none returned completely to normal How about the ‘new’ TKIs...? Bosulif (bosutinib) and Iclusig (ponatinib) both now licensed for 2nd line in the USA and are coming... Can we Predict their Side Effects..? Target kinases for the 5 Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Imatinib (Phos. IC50) PDGFR 72 nM Nilotinib (Phos. IC50) BcrAbl 20 nM Dasatinib (Phos. IC50) Src 0.1 nM Bosutinib (Phos. IC50) Src 3 nM Ponatinib (Phos. IC50) BcrABl1 0.37 nM 1. Manley PW, et al. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res 2007;48:772. 2. Weisberg E, et al. Cancer Cell 2005;7:1129. 3. Remsing Rix LL, et al. Leukemia 2009;23:477. 4. O’Hare T. et al (2009) Cancer Cell. 16: 401-412 > Kit 99 nM > PDGFR 75 nM > BcrAbl 1.8 nM > BcrAbl 85 nM > PDGFR 1.1 nM > BcrAbl 221 nM > Kit 209 nM > PDGFR 2.9 nM > PDGFR >3000 > Src 5.4 nM > Src >1000 nM > Src >1000 nM > Kit 18 nM > Kit >10000 nM > Kit 12.5 nM Bosutinib Study 200 (2nd Line): Treatment-emergent Adverse Events All Grades (n = 288) Grade 3–4 (n = 288) Diarrhea Nausea Vomiting Rash Abdominal pain Fatigue Pyrexia 243 (84) 128 (44) 102 (35) 98 (34) 64 (22) 62 (22) 60 (21) 26 (9) 5 (2) 9 (3) 25 (9) 3 (1) 2 (1) 1 (<1) Cough 45 (16) 0 Headache 42 (15) 0 Arthralgia 38 (13) 1 (<1) Decreased appetite 36 (13) 2 (1) Nasopharyngitis 34 (12) 0 Constipation 32 (11) 1 (<1) Asthenia 31 (11) 5 (2) Adverse Event, n (%) Brümmendorf et al. Oral presentation, EHA 2010; abstr 1136. Bosutinib Study 200 (2nd Line): Gastrointestinal Adverse Events Parameter Diarrhea Nausea Vomiting 243 (84) 128 (44) 102 (35) Median time to onset, d 2 5 8 Median duration, d 27 10 3 Resolved, n (%) 206 (85) 117 (91) 98 (96) Received concomitant medication, n (%) 165 (68) 52 (41) 35 (34) Required dose reduction, n (%) 13 (5) 6 (5) 7 (7) Required dose interruption, n (%) 35 (14) 10 (8) 15 (15) 6 (3) 2 (2) 4 (4) Patients with event, n (%) Discontinued treatment, n (%) Start with low dose and build up gradually. Warn patients & give loperamide! Brümmendorf et al. Oral presentation, EHA 2010; abstr 1136. Bosutinib Study 200 (2nd Line): Other Grade 3–4 Laboratory Abnormalities Laboratory Abnormality, n (%) Grade 3–4 (n = 288) Hypermagnesemia 35 (12) Elevated ALT 30 (10) Hypophosphatemia 23 (8) Elevated lipase 23 (8) Elevated uric acid 17 (6) Elevated AST 14 (5) Hypocalcemia 10 (3) Hypomagnesemia 10 (3) Hyperglycemia 9 (3) Elevated INR 7 (2) ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; INR, international normalized ratio. Brümmendorf et al. Oral presentation, EHA 2010; abstr 1136. Study 200 (2nd Line): Grade 3–4 Hematologic Laboratory Abnormalities Laboratory Abnormality, n (%) Grade 3–4 (n = 288) Thrombocytopenia 71 (25) Neutropenia 48 (17) Anemia 35 (12) Generally less haematological toxicity than other 2nd line agents – may be useful for patients who cannot tolerate other TKIs due to low counts Brümmendorf et al. Oral presentation, EHA 2010; abstr 1136. Bosutinib Study 200 (2nd Line): Other Adverse Events of Interest • Pleural effusion – Observed in 10 (3%) patients (all grades) – Grade 3–4 pleural effusion reported in 1 (<1%) patient • Effects on QTcF interval – On treatment, 25 (9%) patients had grade 1–2 prolongation and 1 (<1%) patient had grade 3–4 prolongation – At treatment completion, 2 (2%) patients had grade 1–2 prolongation and none had grade 3–4 prolongation Brümmendorf et al. Oral presentation, EHA 2010; abstr 1136. Ponatinib PACE Study: Treatment Emergent AEs CP-CML (N=270) ≥ 20% any grade Total Any Grade % Non-hematologic Rash* 43 Abdominal pain 40 Headache 40 Dry skin 40 Constipation 38 Fatigue 27 Pyrexia 23 Nausea 24 Arthralgia 26 Hypertension 23 Lipase increased 23 Pancreatitis 7 Amylase increased 7 Hematologic Thrombocytopenia 44 Neutropenia 18 *Combines the terms erythematous, macular and14 papular rash Anemia 14 Total Population (N=449) Grade 3/4 % Any Grade % Grade 3/4 % 4 9 3 2 2 1 1 1 3 7 11 6 1 38 38 35 35 34 27 27 26 25 21 19 6 7 4 9 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 7 12 5 2 34 16 8 42 24 20 34 21 14 Ponatinib Phase 2 PACE Study: Treatment Emergent Serious AEs SAEs in >6 Patients Total Non-hematologic Pancreatitis Abdominal pain Lipase increased Diarrhea Myocardial infarction Cardiac failure Atrial fibrillation Hypertension Coronary artery disease Pneumonia Pyrexia Sepsis Dehydration Cellulitis Hematologic Anemia Febrile neutropenia Thrombocytopenia Pancytopenia Neutropenia CP-CML (N=270) n (%) Total Population (N=449) n (%) 17 (6) 10 (4) 5 (2) 3 (1) 8 (3) 5 (2) 8 (3) 6 (2) 6 (2) 7 (3) 7 (3) 2 (1) 2 (1) 2 (1) 24 (5) 18 (4) 7 (2) 7 (2) 14 (3) 13 (3) 12 (3) 8 (2) 6 (1) 22 (5) 15 (3) 8 (2) 6 (1) 6 (1) 5 (2) 1 (<1) 4 (1) 1 (<1) 2 (1) 13 (3) 13 (3) 13 (3) 6 (1) 6 (1) • Serious adverse events of arterial thromboembolism, including arterial stenosis, were observed in patients with 15 cardiovascular risk factors Iclusig Given FDA Approval but with Black Box Warning (Dec 2012) • Important for haematologists to be aware of these toxicities • Ponatinib forms part of the new SPIRIT 3 trial for newly diagnosed patients Summary • • • • • • No drug is side effect free! Side effect profile depends on the degree of inhibition of the kinases Side effects rarely recur on switching to different TKI Long term toxicity may be emerging but more data needed Choice of drug needs careful consideration for each patient Refractory patients: main consideration must be to achieve disease control • Intolerant patients: ideally choose drug depending on other comorbidities / risk factors (if funding allows) – Diabetes / cardiovascular risk factors: ? avoid nilotinib / ponatinib – Pulmonary issues: ? Avoid dasatinib – Low blood counts: consider bosutinib • May need to brush up on cardiology skills!