* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
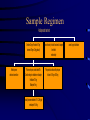
Management of Behavioral Difficulties in Dementia Patients Josepha A. Cheong, MD University of Florida Departments of Psychiatry and Neurology Chief, Division of Geriatric Psychiatry What are common behavioral disturbances? • Agitation – Physical – Verbal – Resistiveness • Mood – Depression – Anxiety What are common behavioral disturbances? • Psychosis – Disruption in the ability to differentiate real from unreal – Hallucinations – Illusions • “Sundowning” Assessment • Rule out any environmental disturbance – change in home setting – change in the staff/family members – death of a pet • R/o any possible medical illness – urinary tract infection – dehydration Assessment • R/o drug-drug interactions or drug intolerance • When does the behavior occur – constant regardless of stimuli – specific time of day – with caregiving activity Assessment • Endocrine • Iatrogenic - consider non-prescription medications • Injury • Intoxication Treatment • Behavioral Intervention – redirection – no-fail environment • adjusting the environment to meet the needs and the limitations of the patient – structure and consistency – avoid overstimulation Treatment • Antidepressants – start at a lower dose (1/3 or 1/2) of the recommended usual starting dose – increase the dose very gradually, be aware of the side effects profile and sensitivity of patient What and How? Paroxetine Q2weeks or as tolerated 25 – 50 mg Q 2 weeks or 100 – 150mg as tolerated 20 mg Q 2 weeks or 40 – 60 mg as tolerated 15 mg Q weeks or as tolerated 37.5 mg Q week or as 150 mg – 225 tolerated mg (Paxil) Sertraline (Zoloft) Citalopram (Celexa) Mirtazipine (Remeron) Venlafaxine (Effexor XR) 30 – 40mg 5-10 mg 30 – 45 mg Sample Regimen Antidepressant treatment Sertraline 25mg or Paroxetine 5-10mg increase to 50mg or 20mg gradually Patient improves continue at current dose Pt does not improve, cannot tolerate SFx Consider change to venlafaxine or mirtazapine Venlafaxine 37.5mg Mirtazepine 15mg Gradually increase venlafaxine to 150 - 225mg/day or mirtazepine 15-45mg Assess for anxiety - treat with low doses of lorazepam time limited monitor closely Pt improves but continues with symtpoms Inc dose to 100mg or 30-40mg assess for psychotic features Antipsychotic Medications • • • • • haloperidol (Haldol) .5 - 2.0mg risperidone (Risperdal) .5 - 6.0mg olanzapine (Zyprexa) 2.5 - 10.0mg ziprasidone (Geodon) 20-40mg quetiapine (Seroquel) 25mg - 300mg Rules of Thumb • Not everything needs to be treated with a medication Rules of Thumb • Not everything needs to be treated with a medication • Start at a low dose and titrate slowly Rules of Thumb • Not everything needs to be treated with a medication • Start at a low dose and titrate slowly • Not everything needs to be treated with a medication Baker Act - 52/32 • 52 - involuntary evaluation • 32 - involuntary committment Referral Shands at UF Inpatient Geriatric Psychiatry Unit Intake Coordinator 352-265-5411 GO GATORS!