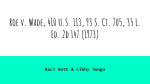* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 6
Lesbian sexual practices wikipedia , lookup
Slut-shaming wikipedia , lookup
Reproductive health care for incarcerated women in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Unintended pregnancy wikipedia , lookup
Female promiscuity wikipedia , lookup
Human female sexuality wikipedia , lookup
Sexual attraction wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Protestant views on contraception wikipedia , lookup
Reproductive rights wikipedia , lookup
History of birth control wikipedia , lookup
Prenatal development wikipedia , lookup
Reproductive health wikipedia , lookup
Christian views on birth control wikipedia , lookup
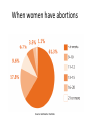
February 23, 2015 NURS 330 Human Reproductive Health Agenda • • • • • Review 2.16.15 In-Class Assignment Quiz Group Project Review & Preparation Contraception Lecture No In-Class Assignment Quiz Group Project • Project and presentation due on 3/2/15 • Assign order of presentation • Q &A CONTRACEPTION Methods of Contraception and Birth Control Birth control any means of preventing a birth from taking place; includes contraception and abortion Contraception The prevention of conception Technique designed to either prevent the release of an ovum, prevent the fertilization of an ovum, or prevent a fertilized ovum from implanting in the uterine wall Alternatives to Intercourse Abstinence-refraining from sexual intercourse (vaginal, oral, & anal) Celibacy-not engaging in any kind of sexual activity Outercourse-a method of birth control using all avenues of sexual intimacy except sexual intercourse Choosing a Method Best method is the one you will use consistently Theoretical effectiveness User/Typical effectiveness Failure Rates • Typical use failure rate – Percentage of typical users of a contraceptive method who will get pregnant within one year • Theoretical use failure rate – Percentage of users of a contraceptive method who will get pregnant within one year while using the method perfectly each time Chance • Not a “method” at all • Withdrawal (aka: Coitus interruptus) • Douching • Assumption: cleanses the vaginal canal by squirting a liquid into the vagina • Actuality: Not recommended for any use; no good purpose and can promote infections • Urination after intercourse METHODS BARRIER HORMONAL LONG-TERM NATURAL FAMILY PLANNING Cervical Cap Depo-Provera Lunelle Female Sterilization Basal Body Temperature Diaphragm Emergency Contraception IUD Cervical Mucus/ Ovulation Method Male Sterilization Rhythm Method Female Condom Implants Male Condom Patch The Sponge Pill Ring Hormonal Methods work by.. • Preventing the release of an ovum • Can also cause the cervical mucus to thicken which prevents sperm from entering the uterus • The ingestion or injection of estrogen or progestin or a combination of the two. Emergency Contraception Emergency contraceptive pill (EC) Also known as Plan B Estrogen and progesterone or just progestin. For use within 72 hours of unprotected sex. No later than 5 days. “morning Must after pill” is not an appropriate name be taken well BEFORE implantation. Oral Contraceptives (OC)– The Pill Two forms of pills Estrogen & Progestin (the combination pill) Most women choose this method Side effects from estrogen include severe headaches and high blood pressure Progestin Mostly (the mini pill) selected due to side effects experienced from estrogen in the combo pill Combo pill is best for: • Any woman (including those over 35) with no risk factors that preclude OCs. • Women with mild headaches or migraines • Women who have diabetes without any blood vessel related complications • Women with a history of abnormal, precancerous Papsmears (displasia). Implants Works by inserting progestin rods under the skin and continuously release tiny amounts of progestin into the bloodstream – Norplant (used five rods and lasted five years) • is no longer available in the United States – Replaced by implanon • Uses one rod • Provides protection against pregnancy for up to three years – Can be removed at anytime – After removal, can resume menstruation in one month Injectibles under a clinician's supervision • Depo-Provera – Progestin – Administered four times a year • Lunelle – Estrogen + Progestin – Administered every 4 weeks Ortho Evra Patch • Estrogen and Progestin • A once-a-week birth control option that's as effective as the Pill. • It is the first weekly, non-invasive form of reversible contraception • How does it work? • What are advantages and disadvantages? Nuva Ring • NuvaRing® delivers steady low-dose contraceptive hormones around the clock. – Progestin and Estrogen • One ring is used each month. The ring stays in for 3 weeks and then is removed for one week. Then you insert a new NuvaRing®. Barrier Methods work by… • Preventing fertilization of an ovum • Providing a physical barrier between the semen and the cervix in order to prevent sperm from reaching the egg cell Condoms • Male • Female • Use either one or the other at one time – Never both at the same time Today Sponge • Back on the US market • blocks sperm from entering the uterus and absorbs and kills off the sperm. • Intended to be used with spermicide Diaphragm Cervical cap • Work to prevent sperm from entering the uterus – Intended to be used with spermicide • Diaphragm – a flexible ring around the top, the diaphragm is inserted into the vagina prior to sexual intercourse. • Cervical Cap – smaller and fits more tightly around the cervix when in place – must be fitted by your doctor and then purchased from a local pharmacy – can leave the cervical cap in place for up to 48 hours Spermicides Spermicide - substance toxic to sperm Contraceptive foam Contraceptive film Creams, jellies & Vaginal suppositories Non-oxynol 9?? Long-term Methods • IUD • Female Sterilization • Male Sterilization Intrauterine Device (IUD) Tiny T-shape plastic or copper device inserted into uterus Multiple theories on how it works Insertion can be painful, heavy cramping and menstrual flow Two currently available in the United States: – Progestasert (~ 10 years) – ParaGard (~ 1 year) Sterilization WOMEN Laparoscopy- closing the tubes by electrocauterization – – – – Minilaparotomy-tubes are tied off or sealed Culpotomy-tubes tied and cut Culdoscopy- Same as Culpotomy; however, leaves less visible scars Hysterectomy-surgical removal of the uterus MEN Vasectomy cut or tie off the Vas deferens Abortion • Spontaneous abortion – aka miscarriage – Loss of baby before 20 weeks of pregnancy • Induced abortion – Surgical – Drug-based Surgical Method • Vacuum Aspiration – First trimester method • Dilation and Extraction (D & X) – Late surgical method Drug-Based Methods • Mifepristone (RU 486) –Injection, 0rally – An anti-progesterone • prevents progesterone from making uterine lining hospitable for implantation • If fetus is already implanted, causes the uterus to shed its lining and, along with it, the fertilized fetus – Approved by FDA in September 2000 for abortion • As an alternative to surgical procedure – Effectiveness is increased if used with another drug, Misoprostol (95-98%) – Most effective within 7 weeks of fertilization Drug-Based Methods (cont) • Methotrexate –Injection; orally (rarely) – Prevents cell division and multiplication – Can be used to induce an abortion • Effectiveness is increased if used with another drug, Misoprostol (95%) – Approved by FDA for treatment of cancer, arthritis and psoriasis – Most effective within 7 weeks of fertilization • Misoprostol – orally or vaginally – Legal Drug used in conjunction with above drugs – The second drug used to complete the abortion procedure • Taken a day or two after administration of the first drug – Causes the uterus to contract and expel its contents – Approved in the US for coating the stomach of people who take stomachirritating anti-inflammatory drugs. Abortifacient • A method or substance that causes a fertilized egg that has implanted in the uterine wall or fetus to be expelled. • Which of the drug-based methods is an abortifacient? Incidence of Abortions • Nearly half of pregnancies among American women are unintended, and four in 10 of these are terminated by abortion. • Twenty-two percent of all pregnancies (excluding miscarriages) end in abortion. • In 2005, 1.21 million abortions were performed, down from 1.31 million in 2000. From 1973 through 2005, more than 45 million legal abortions occurred. • Each year, about two percent of women aged 15-44 have an abortion; 47% of them have had at least one previous abortion. Source: Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health When women have abortions Source: Guttmacher Institute Cost • Surgical – In 2005, the cost of a non-hospital abortion with local anesthesia at 10 weeks’ gestation ranged from $90 to $1,800; the average amount paid was $413 (Source: Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health) • Drug-based – most providers do charge more for this method Abortion and the Law • Roe v. Wade – 1973 Supreme Court decision stating • 1st trimester abortions cannot be regulated by states and the decision to abort is between woman and physician • 2nd trimester abortions permitted when mental or physical health of mother at risk • 3rd trimester abortions allowed when life of mother at risk California Law • California does not have any of the major types of abortion restrictions – such as waiting period, mandated parental involvement or limitations on publicly funded abortions – often found in other states. Source: Alan Guttmacher Institute The Pro-Life and Pro-Choice Controversy • Anti-abortion (Pro-life) position • Pro-choice position