* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Saving
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
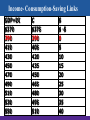
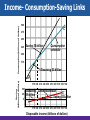
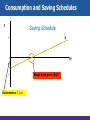
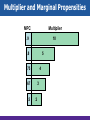
Chapter 27 Basic Macroeconomic Relationships Income- Consumption-Saving Links Let’s introduce some assumptions: 1. Two-sector economy: households and business: • Aggregate spending = C + I only • No G, No T: DI = PI 2. All savings are personal saving: No business savings 3. Depreciation = 0; Gross I = Net I 4. Net foreign factor income = 0; Citizens earn as much abroad as foreigners earn inside. 5. No Exports , No Imports : Closed economy. Income- Consumption-Saving Links • • • • • Relationship between income & consumption (C). Relationship between income & saving (S). - What is saving ? Relationship between consumption (C) & saving (S) - Primarily determined by Disposable Income (DI) S = DI – C It has been approved that C is positively related to DI. The 45o line represents points where each point on this line would have C=DI. Income- Consumption-Saving Links C 45o DI Income- Consumption-Saving Links Consumption & Saving Schedule • Schedule shows the various amounts that households would plan to consume at each various level of DI. • Schedule shows the various amounts that households would plan to save at each various level of DI. • DI = C + S • How much goes to C and S out of DI? • We use consumption and saving schedule. Income- Consumption-Saving Links GDP=DI $370 390 410 430 450 470 490 510 530 550 C $375 390 405 420 435 450 465 480 495 510 S $ -5 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 Income- Consumption-Saving Links Based on the table; • If C > DI, then there is a decline in savings (Dissaving) • When can households’ C > households’ DI ? ( two reasons ) • When DI = C, then S = 0. • This is “Break-even” income; where households plan to consume their entire incomes (C=DI). • What if DI=0? Will C=0 too? • Autonomous consumption: level of C when DI =0. (Independent C) Consumption (billions of dollars) Income- Consumption-Saving Links 500 C 475 450 425 Saving $5 billion Consumption schedule 400 375 Dissaving $5 billion Saving (billions of dollars) 45° 370 390 410 430 450 470 490 510 530 550 50 25 0 Dissaving Saving schedule S $5 billion Saving $5 billion 370 390 410 430 450 470 490 510 530 550 Disposable income (billions of dollars) Income- Consumption-Saving Links Average & Marginal Propensities • • Average propensity to consume (APC) is a Fraction of total income consumed Average propensity to save (APS) is a Fraction of total income saved Note: APC falls and APS rises as DI increases (Check the table) consumption saving APC = APS = income income APC + APS = 1 Income- Consumption-Saving Links Average & Marginal Propensities • • Marginal propensity to consume (MPC) is a proportion of a change in income consumed Marginal propensity to save (MPS) is a proportion of a change in income saved MPC = change in consumption change in income MPS = MPC + MPS = 1 change in saving change in income Income- Consumption-Saving Links • MPC and MPS are slopes: The slope of the consumption schedule = MPC, the slope of the saving schedule = MPS. • Even when DI=0, C≠0. Consumption and Saving Schedules Marginal Propensities (Slopes) C Consumption 15 MPC = 20 = .75 C ($15) Saving DI ($20) MPS = 5 = .25 20 S S ($5) DI ($20) Disposable income Consumption and Saving Schedules Consumption and Saving Schedules (in Billions) and Propensities to Consume and Save (4) (1) Level of Output and Income GDP=DI (2) Consumption (C) (3) Saving (S), (1) – (2) (1) $370 $375 (6) Average Propensity to Consume (APC), Average Propensity to Save (APS), (2)/(1) $-5 (7) Marginal Propensity to Consume Marginal Propensity to Save (3)/(1) (MPC), (2)/(1)* (MPS), (3)/(1)* 1.01 -.01 .75 .25 (5) (2) 390 390 0 1.00 .00 .75 .25 (3) 410 405 5 .99 .01 .75 .25 (4) 430 420 10 .98 .02 .75 .25 (5) 450 435 15 .97 .03 .75 .25 (6) 470 450 20 .96 .04 .75 .25 (7) 490 465 25 .95 .05 .75 .25 (8) 510 480 30 .94 .06 .75 .25 (9) 530 495 35 .93 .07 .75 .25 (10) 550 510 40 .93 .07 .75 .25 Consumption and Saving Schedules Consumption Schedule C Income (Y) Break-Even Point (C=Y) C Saving Dissaving 45o DI Consumption and Saving Schedules Consumption Schedule C Income (Y) Break-Even Point (C=Y) C Saving Dissaving 45o DI Autonomous C (a) Consumption and Saving Schedules S Saving Schedule + S 0 - DI Break-Even point (S=0) Consumption and Saving Schedules S Saving Schedule + S DI - Autonomous C (-a) Break-Even point (S=0) Determinants of Consumption and Saving • The most important factor is income (DI): an increase in DI will lead to an increase in C by (MPC.DI) and increase in S by (MPS.DI). • This will be a move along the C schedule and S schedule. • The same result applies when DI declines. • DI is the only factor that leads to a move along the lines. Non-income Determinants Non-income factors will shift the C and S schedules 1. Wealth: an increase in wealth will increase C and reduces S (shift the C schedule upward, S schedule downward). • This is the case since people save to accumulate wealth. • As wealth increases, no need to save as much as before. • This is called “wealth effect”. Non-income Determinants 2. Expectations: about future prices and income level. • Expectations affect spending (C) and saving. • Expectations of an increase in price level (or future income): increase C and reduce S today, C schedule shifts upward while S schedule shifts downward. Non-income Determinants 3. Borrowing: - household borrowing increases consumption, and will shift both C schedule upward: - since borrowing money allows C to shift upward, but if the debt is large, then C may shift downward. Non-income Determinants 4. Real Interest Rate: - lower real interest rates encourage households to borrow more, so consume more, & save less. - lower real interest rates allow C to shifts upward, but S shifts downward. Other Important Considerations • Switching to real GDP Change DI to Real GDP • Changes along schedules Differences between movements from point to point along the curve versus upward/downward shift of the entire schedulable • Simultaneous shifts The four non-economic factors will shift the consumption schedule in a one direction and the saving schedule to the other direction at the same time. Other Important Considerations • Taxation Taxation factor will shift the consumption schedule and the saving schedule in same direction. • Stability The consumption schedule and the saving schedule stay unchanged (stable) relatively unless major tax increases. Shifts of C & S Schedules C1 C0 Saving (billions of dollars) Consumption (billions of dollars) C2 0 45° S2 S0 S1 + 0 Real GDP (billions of dollars) Interest-Rate-Investment Recall the definition of I; spending on new plants, capital equipment, machinery & inventories. Expected rate of return • is the marginal benefit from I. • Expected rate of return is calculated be (Profit expected after adopting the new machine / Cost of that machine) Interest-Rate-Investment The Real Interest Rate • • • • The Interest Rate (%) is the financial cost of borrowing the money to purchase the machine. The Interest cost is ( interest rate X amount borrowed to purchase the machine) if Expected Rate of Return > Interest Rate , then the Investment should be undertaken (Profitable I ). if Expected Rate of Return < Interest Rate , then the Investment should not be undertaken(Unprofitable I) Interest-Rate-Investment • • • • The Real Interest Rate rather than the Nominal Interest Rate is important in making investment decisions. The Real Interest Rate is ( Nominal Interest Rate Inflation) if Expected Real Rate of Return > Real Interest Rate , then the Investment should be undertaken (Profitable I ). if Expected Real Rate of Return < Real Interest Rate , then the Investment should not be undertaken (Unprofitable I). Interest-Rate-Investment Investment Demand Curve • What determine the amount of funds that investors borrow? • Real interest rate (i): an increase in rr will increase the cost of borrowing funds, thereby reducing the amount of I demanded. • A decline in (i) will reduce the cost of borrowing funds, thereby increasing I demanded. • At each amount of I demanded, there is a certain expected rate of return (r) equals or exceeds (i). (r) and (i) 16% Investment (billions of dollars) $0 14 5 12 10 10 15 8 20 6 25 4 30 2 35 0 40 Expected rate of return, r and real interest rate, i (percents) Investment Demand Curve 16 14 Investment demand curve 12 10 8 6 4 2 ID 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 Investment (billions of dollars) 40 Investment Demand Curve • Changes in the level of Real interest rate (i) will lead to a move in ID curve. • This is the only factor leading to a move along the ID curve. • All other factors will shift the ID curve. Shifts of Investment Demand • • • Acquisition, maintenance, and operating costs The initial and then the operating cost of capital affect the expected rate of return in I negatively (Shifting ID to the left) Business taxes Increase in taxes will reduce expected profitability (Shifting ID to the left) Technological change Stimulates investment and lower production costs (Shifting ID to the right) Shifts of Investment Demand • • • Stock of capital goods on hand as inventories rise, expected rate of return on investment increase (Shifting ID to the right) Planned inventory changes If a firm expects higher sales in the future, it would keep more inventory in stock now. Thus increasing ID (Shifting ID to the right) Expectations Expected rate of return depends on firm’s expectations about its sales, future operation costs, future profitability, thus optimistic outlook about the future performance of the firm leads to higher I (Shifting ID to the right), versus the pessimistic outlook. Expected rate of return, r, and real interest rate, i (percents) Shifts of Investment Demand Increase in investment demand Decrease in investment demand 0 ID2 ID0 ID1 Investment (billions of dollars) Instability of Investment Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis, http://www.bea.gov. Instability of Investment Factors Explaining Variability in I • Durability The quicker capital goods need to be replaced, the higher the level of I. The opposite in the case of keeping older capital goods after repairing them. • Irregularity of innovation Innovations in sectors such as railroads, electricity occur quite irregularly, but if they occur it would lead to a sharp growth of investment spending Instability of Investment • Variability of profits Expanding profits give firms greater incentives and then greater means to invest, The opposite in the case of declining profits. • Variability of expectations Any change in expectations ( because of i.e economic outlook, trade policy, exchange rate policy, stock market, political reasons) would lead to a change in business expectations and then reach instability in investment spending. The Multiplier Effect • • • More spending leads to more real GDP. BUT!! a change in spending (i.e I) changes real GDP more than the initial change in spending (i.e I) Thus, the Multiplier states that how much larger that change in Real GDP will be… Multiplier = change in real GDP initial change in spending Change in GDP = multiplier x initial change in spending Example; if (I) in the economy rises by 30$ million and thus Real GDP increases by 90$ million, what is the Multiplier? The Multiplier Effect (1) Change in Income (2) Change in Consumption (MPC = .75) (3) Change in Saving (MPS = .25) $5.00 $3.75 $1.25 Second round 3.75 2.81 .94 Third round 2.81 2.11 .70 Fourth round 2.11 1.58 .53 Fifth round 1.58 1.19 .39 All other rounds 4.75 3.56 1.19 $20.00 $15.00 $5.00 Increase in investment of $5.00 Total Cumulative income, GDP (billions of dollars) 20.00 $4.75 15.25 13.67 $1.58 $2.11 11.56 $2.81 8.75 $3.75 5.00 $5.00 1 2 3 4 5 All others Multiplier and Marginal Propensities • • Multiplier and MPC directly related Large MPC results in larger increases in spending Multiplier and MPS inversely related Large MPS results in smaller increases in spending Multiplier = 1 1- MPC Multiplier = 1 MPS Note: 1) The lower MPS , the larger is the fraction of (1/MPS), thus the greater the multiplier and the greater the increase in income (Real GDP) 2) Think of MPC !! Multiplier and Marginal Propensities MPC Multiplier .9 10 .8 5 .75 4 .67 .5 3 2 The Actual Multiplier Effect? In reality actual multiplier is lower than the model assumes ( only two sectors Households Sector & Business Sectors), this is because of ; • Consumers buy imported products We should consider the external sector • Households pay income taxes We should consider the Government sector • Inflation Since we deal with Real GDP, this ignores people’s behaviors (to save or to consume) when price changes.