* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPC
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Criticisms of socialism wikipedia , lookup
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Participatory economics wikipedia , lookup
Steady-state economy wikipedia , lookup
Consumerism wikipedia , lookup
Economic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Economic calculation problem wikipedia , lookup
Perspectives on capitalism by school of thought wikipedia , lookup
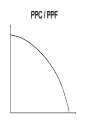
Economics Economics Social science Economics The study how society chooses what to produce, who to produce for and how much to produce. “Economics is the study of mankind in the ordinary business of life” – Alfred Marshall “Economics is the study of how men and society choose with or without the use of money to employ scarce productive resources to produce various commodities over time and distribute them for consumption, now and in the future, among various people and groups in society” – P.A.Samuelson Ceteris paribus All other things remaining equal Micro and Macro – The study of individual parts of the economy, such as individual markets or firms. Macroeconomics – The study of the whole economy which deals with such things as employment/unemployment, investment, inflation, etc. Microeconomics Normative and positive Normative – These are matters of opinion which cannot be proved or disproved by reference to facts, since they are based on a value judgement. They are subjective and can be recognised by words such as “should” or “ought”. Positive – These are statements of fact that be checked against the facts and can be proved correct or incorrect. They are not necessarily true, but can be proved true or false. Normative and positive The world’s food supply should be shared equally as there is enough to go round There is sufficient food in the world, and if it was shared out equally then all people would have enough to eat. Economic problem Limited resources/factors of production Unlimited wants and needs Economic Problem • What to produce? • Who to produce for? • How much to produce? Factors of production Land Labour Capital Management/Enterpreneurship Interest, rent, profit, wages Opportunity cost As resources (factors of production) are scarce we are required to make choices and sacrifice one thing to obtain another. The cost of a choice is know as the Opportunity Cost. The cost of a choice in terms of the next best opportunity forgone. Free and economic goods goods – these are goods that have limited supply, i.e. they are scarce, so there needs to be some system for allocating them. Free goods – these are goods not created from scarce resources and are available in abundance, and as a result there is no need to have a system to allocate them. Economic PPC / PPF Production possibility curve (ppc) Production possibility frontier (ppf) This is a way of representing the choices to society in the form of a diagram PPC / PPF