* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Help - London Centre for Corporate Governance and Ethics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
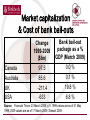
Varieties of Liberalism: Anglo-Saxon Capitalism in Crisis? Sue Konzelmann & Marc Fovargue-Davies (Gerhard Schnyder) REFGOV / DEMOGOV Brussels 26-28 May 2010 Market capitalization & Cost of bank bail-outs Change 1999-2009 ($bn) Bank bail-out package as a % GDP (March 2009) Canada 97.5 0.0 % Australia 85.6 0.1 % UK -211.4 19.8 % USA -633 6.8 % Source: Financial Times, 23 March 2009, p.9. 1999 values are as of 31 May 1999; 2009 values are as of 17 March 2009; Stewart 2009. Overview • The logic & rise of economic liberalism • Early effects & responses to crises • Industrial restructuring & the market for corporate control • Financial market liberalization • Regulators & the regulated • Financial alchemy & the US sub-prime bubble • Conclusions & implications for policy reform The logic & rise of economic liberalism • Classical versus ‘Ordo’ Liberalism • The collapse of Bretton Woods and relaxation of international money movements • Globalization and the onset of deindustrialization • Growing confidence in markets and the ‘reregulation’ of the real & financial sectors of the economy Early effects of liberalization & responses to crises • Australia & America – Australian corporate & financial scandals (1980s) – US Savings & Loan Crisis (1980s & 1990s) • Canada & Britain – Bank, insurance trust & investment house failures (1980s & 1990s) • All four systems had looked into the abyss … Industrial re-structuring & the market for corporate control • Leveraged buyouts & hostile take-overs in Britain (1960s & 70s) & America (1980s) • The ‘market for managerial control’ & industrial re-structuring • Take-over markets in the Anglo-Saxon world • The structure of the economy & opportunities for investment Financial market liberalization • Stock market liberalization – ‘May Day’ 1975 (New York) – 1986 ‘Big Bang’ (London) • The structure of financial markets – Domestic banks & financial institutions in Canada & Australia – A global marketplace in London & New York • The structure of regulation – fragmentation versus a single regulator Regulators & the regulated • Britain & America: ‘light touch’ regulation – Increasing relative power (economic & political) of the regulated • Australia & Canada: prudential regulation & high levels of own capital reserves – ‘Banks are bastards; bigger banks are bigger bastards.’ (Maiden 2008) – ‘Our job is to tell you what to do, not to make it grow.’ (Freeland 2010) Financial Alchemy & the American sub-prime bubble • Presence of the pre-conditions for financial instability • Conditions uncomfortable for banks in London and New York • Financial ‘innovation’ & exploitation of the American sub-prime real estate market • Loss of confidence precipitates crisis • Financial market crisis has re-bound effects on the real economy & the recession deepens Conclusions & Implications for Policy • The philosophy shaping liberalization • Relationship between the regulator & regulated • Investment opportunities outside of finance & rebalancing a ‘post-industrial’ economy • National political context • The role of the state & philosophy of government • The direction of reform