* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Aggregate-Demand
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Gross domestic product wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Circular economy wikipedia , lookup
Long Depression wikipedia , lookup
Economic calculation problem wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
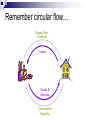
Remember circular flow… Wages, Rent, Dividends Labour Goods & Services Consumption Spending Aggregate Demand the total demand for goods and services produced within the economy AD = C + I + G + (X-M) Price Level AD GDP / Real National Output Slopes downward & to the right: 1. a general fall in prices increases the real value of wealth so increases AD (we can afford to buy more!) 2. It also lowers the prices of our goods compared to other countries leading to increased exports. Shifts in AD changes in the components of aggregate demand will cause a shift in the AD curve ( C, I, G, X or M) Price Level AD1 This outward shift could be caused by C,I,G,X or M AD AD GDP AD does not always increase. If it decreases it can lead to recession. This would be as a result of C,I,G,X or M.