* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reasons of the Financial Crisis
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
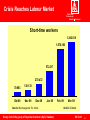
Wirtschaft Technologie Umwelt Vorstand Answers of IG Metall to the Financial and Economic Crisis - Protection of Jobs - Stabilisation of the Economy - Shaping the Future Wilfried Kurtzke Reasons of the Financial Crisis Wirtschaft Technologie Umwelt Vorstand 1. Excess of capital caused by a wrong income distribution 2. Deregulation of financial markets 3. Securitization of credits – a huge risk for financial markets 4. Worldwide imbalances – the stimulation of speculation Study visit of the group of impartial chairmen (OpO, Sweden) 09-10-01 2 Reasons of the Financial Crisis Wirtschaft Technologie Umwelt Entwicklung von Sozialprodukt und Finanzvermögen weltweit, 1980-2010 in Billionen US-Dollar 214 Sozialprodukt Finanzvermögen Vorstand Worldwide development of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) [blue bar] 140 and 93 64 63,3 44,5 29,4 10,1 financial capital [red bar] 31,7 12 1980 1995 2000 2005 2010* Quelle: McKinsey Quarterly, January 2007, Mapping the global capital markets, S.8 Study visit of the group of impartial chairmen (OpO, Sweden) 09-10-01 3 Economic Framework Wirtschaft Technologie Umwelt Vorstand Cyclical decline Financial market crisis influences the producing economy Too high dependence of foreign trade Weak domestic economy Result: massive collapse of foreign demand lead to a heavy recession in Germany Study visit of the group of impartial chairmen (OpO, Sweden) 09-10-01 4 Economy Faces Deep Crisis Wirtschaft Technologie Umwelt Vorstand The largest decline of the GDP for 80 years gross domestic product, annual percentage change 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 -2 -4 -6 -8 1951 1955 1959 1963 1967 1971 1975 1979 1983 1987 1991 1995 1999 2003 2007 Quelle: Statistisches Bundesamt, alle Zahlen vor 1992 w egen diverser statistischer Änderungen nur bedingt vergleichbar, Zahlen für 2009 und 2010 Frühjahrsprognose der Institute Grafik: IG Metall Study visit of the group of impartial chairmen (OpO, Sweden) 09-10-01 5 German Economy Faces a Deep Crisis Wirtschaft Technologie Umwelt Vorstand Gross Domestic Product, 2000=100, seasonally adjusted 114 112 110 108 106 104 102 100 98 96 1. VJ 05 2. VJ 05 3. VJ 05 4. VJ 05 1. VJ 06 2. VJ 06 3. VJ 06 4. VJ 06 1. VJ 07 2. VJ 07 3. VJ 07 4. VJ 07 Quelle: Statistisches Bundesamt Study visit of the group of impartial chairmen (OpO, Sweden) 1. VJ 08 2. VJ 08 3. VJ 08 4. VJ 08 1. VJ 09 2. VJ 09 Grafik : IG Metall 09-10-01 6 German Economy Faces a Deep Crisis Wirtschaft Technologie Umwelt Vorstand The sharpest decline of GDP for 80 years gross domestic product, annual percentage change Forecast 3,2 2,0 2,0 3,0 1,2 1,1 0,0 98 99 00 01 02 +1,2 2,5 1,3 0,8 -0,2 03 to -4,9 -0,5 to -6,5 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 Quelle: Statistisches Bundesamt, Prognosen der Institute im Frühjahr/Sommer 2009 Grafik: IG Metall Study visit of the group of impartial chairmen (OpO, Sweden) 09-10-01 7 German Economy Faces a Deep Crisis Wirtschaft Technologie Umwelt Vorstand Aggregated Components of GDP 2009 Forecast annual percentage change -6,5 Gross domestic product 1,7 Public consumption 0,2 Private consumption -3,7 -17,8 -22,0 Building investments Exports Investment in new equipment Quelle: IMK, Juli 2009 Study visit of the group of impartial chairmen (OpO, Sweden) Grafik: IG Metall 09-10-01 8 Crisis Reaches Labour Market Wirtschaft Technologie Umwelt Vorstand Rising Unemployment annual percentage change 7,9 5,0 7,9 8,6 5,3 2,2 -1,8 -4,7 -8,9 -11,6 -12,7 Okt 08 Nov 08 Dez 08 Jan 09 Feb 09 Mrz 09 Apr 09 Mai 09 Jun 09 Jul 09 Aug 09 Quelle: Bundesagentur für Arbeit Study visit of the group of impartial chairmen (OpO, Sweden) Grafik: IG Metall 09-10-01 9 Crisis Reaches Labour Market Wirtschaft Technologie Umwelt Vorstand Short-time workers 1.246.618 1.076.160 572.217 270.472 70.983 Okt 08 130.133 Nov 08 Dez 08 Jan 09 Quelle: Bundesagentur für Arbeit Study visit of the group of impartial chairmen (OpO, Sweden) Feb 09 Mrz 09 Grafik: IG Metall 09-10-01 10 A Sharp Decline of Orders Wirtschaft Technologie Umwelt Vorstand Orders in different branches organized by the IG Metall Change July 2009/08 in percent Maschinenbau Bekleidungsindustrie Elektr. Ausrüstungen Metallerzeugnisse -40,7 -32,4 -29,5 -21,7 Metall- und Elektroindustrie -21,7 Metallerzeugung und -bearbeitung -16,8 Textilindustrie -16,5 Automobilindustrie DV, Elektronik, Optik Quelle: Statistisches Bundesamt, Darstellung ohne sonstigen Fahrzeugbau Study visit of the group of impartial chairmen (OpO, Sweden) -15,7 -6,4 Grafik: IG Metall 09-10-01 11 Production Collapses Overall Wirtschaft Technologie Umwelt Vorstand Production collapses in all branches organized by the IG Metall Change July 2009/08 in percent Maschinenbau Metallerzeugung und -bearbeitung Luft-, Wasser-, Schienenfahrzeuge DV, Elektronik, Optik -31,5 -28,4 -26,4 -25,2 Elektrische Ausrüstungen -24,5 Metall- und Elektroindustrie -24,5 Metallerzeugnisse Automobilindustrie -23,5 -20,7 Textilindustrie Bekleidungsindustrie Möbelindustrie Holzgewerbe Quelle: Statistisches Bundesamt Study visit of the group of impartial chairmen (OpO, Sweden) -15,3 -14,1 -11,9 -10,0 Grafik: IG Metall 09-10-01 12 Economy is Going Through the Trough Wirtschaft Technologie Umwelt Vorstand Orders in metalworking industry Index: 2005 = 100 130 calendar and seasonally adjusted 120 110 100 90 original data 80 July 09/ Jun 09: + 3,7% July 09/ July 08: -21,7% 70 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 Quelle: Statistisches Bundesamt Study visit of the group of impartial chairmen (OpO, Sweden) 2007 2008 2009 Grafik: IG Metall 09-10-01 13 No dismissals – the agenda of IG Metall against the crisis Wirtschaft Technologie Umwelt Vorstand As an answer to the crises in November 2008 IG Metall released seven points in order to protect employment and to stabilise the economy 1. No dismissals 2. Protection of temporary working persons 3. Corporate financing must be guaranteed (by banks and the government) 4. Stabilising private demand by „cash for clunkers“ (2500.- Euro for an at least 10year-old junk car) 5. Stabilising private demand by „consumption cheques“ 6. Public Future Fund „Work - Education - Environment“ 7. Increase of participation of workers and employees Study visit of the group of impartial chairmen (OpO, Sweden) 09-10-01 14 No dismissals – the agenda of IG Metall against the crisis Wirtschaft Technologie Umwelt Vorstand Still facing the crises in March 2009 IG Metall created another action program Leaving the crises actively behind – united for good working and living conditions 1. Protection of employment in the producing economy 2. More democracy in the economy, i.e. more participation for the working class 3. A stronger regulation of financial markets 4. The costs and burden of the crises should be paid by the wealthy Study visit of the group of impartial chairmen (OpO, Sweden) 09-10-01 15 Anticyclical policy of the government Wirtschaft Technologie Umwelt Vorstand The government had to act and must still act in order to stabilise the economy. The government acted unassertively. But by taking off the ideological blinkers the government decided to switch to an anti-cyclical economic policy. So it prevented a worse economic development. An improved regulation of “short-time work” helped to reduce the rise of unemployment. “cash for clunkers / junk cars” strengthened car sales. Tax- and duty-reductions are not helpful to stimulate economic growth. Instead: More public investment is the better way to generate economic growth. Especially here we need stronger efforts. Annually eight to nine billions Euro are much to less. All in all the economic programs of the government are created not big enough and come much too late. The Macroeconomic Policy Institute (IMK) estimates the impulses for growth of the whole package of measures only at 0.6 percentage points in this year. Study visit of the group of impartial chairmen (OpO, Sweden) 09-10-01 16 Assumptions of Economic Trends Wirtschaft Technologie Umwelt Vorstand GDP-Forecast 2009 bis 2013 4 possible trends 2008 = 100 102,0 S 4: high grow th(101,1) 100,0 S 3: low grow th (98,2) 98,0 96,0 S 2: stagnation (96,2) 94,0 92,0 90,0 S 1: depression (91,1) 88,0 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 Quelle: Statistisches Bundesamt. Ab 2009: Szenarien IG Metall Study visit of the group of impartial chairmen (OpO, Sweden) 09-10-01 17