* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download United States: class 1
Economic planning wikipedia , lookup
Economic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Steady-state economy wikipedia , lookup
Economic growth wikipedia , lookup
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Chinese economic reform wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Italy under fascism wikipedia , lookup
Transformation in economics wikipedia , lookup
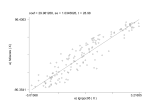
THE UNITED STATES: 1 Phases of economic development Revolution--1890: catch up to core European economies technologically 1890--1940:industrial concentration & modern corporation 1945--1970:rapid ec. growth & hegemony over world economy 1970--1990: deteriorating performance 1990’s: mixed performance WWII --late 1960s (HEGEMONY) WWII consequences – GNP trends 1929 1939 1944 – $100B $91B $210B role of government--public spending 1940 $9B 1945 $98B >1/3 of all mfg. structures and equipment existing in 1945 was constructed by government 1. Economic Growth put at head of U.S. political agenda gov’t involvement in economy did not decline/govt expenditure as % of GNP rose ---12% (1940)--- 25% (1950)--35%(1965) gov’t agrees to give private sector public money to produce growth (tax shift) economic consequences – – mixed performance in 1950s productive capacity nearly triples in 1960s Bases of economic growth consumer durables residential construction role of suburbanization backed by government policy – – – FHA mortage guarantees IRS deducts mortgage interest interstate highway system 2. Business/labor relationships period of so-called SOCIAL CONTRACT between big business and big unions business concedes higher wages and control over working conditions labor agrees not to strike (to keep producing) 3. Dominating role of U.S. in World Economy 1950--just under 50% of world industrial production. Still over 40% in 1963 1971 U.S. share of all FDI is 50% FDI by U.S. corporations was encouraged by U.S. tax policy U.S. firms (and workers) earn SUPERPROFITS thanks to technology and worker productivity edge Pillars of the Post-war American Economic Advantage (Dertouzos, 1989. Made in America) Sheer size of the American market technological superiority skill level of American workers U.S. affluence American managers U.S. and the World Economy: early 1970s to early 1990s THESIS: U.S. displayed relatively poor performance primary indicators – – temporal comparisons: 50s and 60s vs. 70s and 80s cross-national comparisons: U.S. vs. other industrialized countries Temporal--real wage trends Growth in Median Family Income 3.00% 2.50% 2.00% 1.50% Annual grow th 1.00% 0.50% 0.00% 1947- 1967- 1973- 197967 73 79 89 Comparative--- Growth in real compensation Annual growth in per capita GNP, 1980-92 4.00% 3.50% 3.00% 2.50% 2.00% 1.50% United States Japan Germ any U.K. 1.00% Italy 0.50% France 0.00% Alternative Perspectives on relatively weak economic performance 1. A catch up and convergence phenomenon attributable to: – – – technological borrowing from the leader transfers of labor from agriculture to industry greater willingness of less well-off to work harder and divert resources from consumption to investment 2. evidence of relative economic failure and decline in economic competitiveness Example – John Agnew, 1987. The United States in the World Economy. Chapter 4. Level 1 Increased foreign investment by U.S. TNCs increased competition by foreignbased TNCs increased dependence on foreign sources of raw materials drain on U.S. economy of defense spending priorities of domestic Keynesian policy Level 2 Decline of U.S. relative labor productivity loss of technological leadership increased openness to foreign competition