* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circular Flow fin - Business-TES
Survey
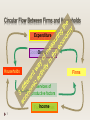
Document related concepts
Transcript
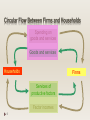
To define the terms in the Circular flow of income Explain the inter-relationship between expenditure, income and production To explain why injections = leakages. There are ‘measuring national income’ notes to go along with this powerpoint. 1 Households FIRMS Government 2 Goods and services Households Firms FOP Input: Household includes workers, managers, entrepreneurs etc. i.e. people 3 Spending on goods and services Households Firms FOP incomes 4 Spending on goods and services Goods and services Households Firms Services of productive factors Factor incomes 5 Expenditure Income 6 the sum of incomes all factor incomes Output the sum of expenditures in the economy the sum of output (value added) produced in the economy All three approaches are should give you the same final figure for national output Spending on Expenditure goods and services GoodsOutput and services Households Firms Services of productive factors Income Factor incomes 7 Total value added Gross domestic product (GDP) 8 is the economy’s net output after deducting goods used during production to avoid double counting E.g. egg, milk, flour used for making muffins. MUFFINS. Final Good. measures the output produced by factors of production located in the domestic economy over a period of time, usually a year. Leakages (in terms of flow of payment) 9 money paid to the households but not returned to firm Or flow of payments that started from firms but did not return back to firms e.g. household savings, net taxes and imports Spending on goods and services Leakages Households Firms Factor incomes 10 Injections (in terms of flow of payment) are revenue for firms not from sales to household e.g. investment by firms, government purchases and exports 11 Spending on goods and services Injections Households Firms Factor incomes 12 Government spends money on goods & services (G) finances welfare payments, i.e. transfer payments (B) this spending is financed by taxes (T) Foreign Sector: Export (X) made at local economy but sold abroad Import (M) 13 made abroad and bought at local economy. Domestic Output (GDP) is either Factor Incomes are spent on 14 Consumed (C) Invested (I) (INCREASE IN STOCK OF CAPITAL) Bought by the Government (G) Bought by the foreigners, net exports (X-M) Consumption (C) Saving (S) Paying taxes net of benefits (T-B) GDP = C + I + G + (X – M) Factor Income = C + S + (T – B) Since everything produced in the economy generates equivalent factor income Domestic Output (GDP) = Factor Incomes 15 Domestic Output Factor Incomes C + I + G + (X – M) = C + S + (T – B) C: Consumption I: Investment G: Government Expenditure X-M: Net exports 16 C: Consumed S: Savings T-B: Taxes Net of Benefits Domestic Output Factor Incomes C + I + G + (X – M) = C + S + (T – B) rearrange I+G+X = Total Injections 17 S + (T – B) + M Total Leakages 18 Y= National Income C = Consumption I = Investment G = Government Expenditure (X-M) =Net Exports GDP = C + I + G + (X – M) 19 Gross domestic product (GDP) measures the output produced by factors of production located in the domestic economy over a period of time, usually a year. 20 Gross National Product (GNP) total income of citizens wherever it is earned = GDP + Net Property Income (NPI) IF GDP < NPI the citizens of the local economy are producing less than the citizens from abroad. It means that citizens from abroad in the local economy plus locals make the local economy GDP smaller than its Citizens abroad and in the local economy together GNP. 21 Depreciation: Gross: DOES NOT TAKE IN ACCOUNT DEPRECIATION (wear and tear of capital stock). Only the increase in stock. Net National Product = GNP – Depreciation 22 Nominal GDP / GNP Measures national output at current prices = value of all goods at current prices Real GDP / GNP 23 Measures output at base year prices e.g. value of today's national output at 1995 prices Allows us eliminate the effect of price changes and see how real output evolves over time 24 25 26 Who’s the richest? 27 28 Does NOT take in account other variables like: 29 Does not separate K or C goods. Underground economy is not taken in account Externalities are not taken in account. Self consumption activities or household activities are not taken in account. Other issues which reflect standard of living. Education, Health, environment, security, freedom, discrimination, etc… Income distribution (inequality) 30