* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download In groups of 3 - 4 discuss and answer the questions below
Survey
Document related concepts
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Production for use wikipedia , lookup
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Protectionism wikipedia , lookup
Post–World War II economic expansion wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
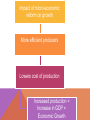
IN GROUPS OF 3 - 4 DISCUSS AND ANSWER THE QUESTIONS BELOW . WHAT IS AGGREGATE SUPPLY? WHAT DOES SUPPLY SIDE REFER TOO? WHAT WOULD SUPPLY SIDE POLICIES BE? HOW COULD THESE POLICIES INFLUENCE SUPPLY? SLO: Describe supply-side policies and apply then to economic models of growth SUPPLY SIDE MICRO-ECONOMIC POLICY Supply side= Policies that are directed at influencing supply in markets. Supply side policies will be focused on encouraging people to produce (supply) goods and services e.g. Lowering income tax Lowering capital gains tax rates, reducing regulation ( removing rules that restrict producers) According to supply-side economics, consumers will then benefit from a greater supply of goods and services at lower prices. NZ SUPPLY-SIDE POLICY HISTORY Tended to concentrate over the past 20years on state sector reform (Selling of government owned enterprises) and increasing deregulation of industry. Arguments for supply side policies The private sector producers can operate more efficiently than the state sector can. Private sector producers operate more efficiently with fewer rules and regulations State resources are more appropriately used to provide public and merit goods (health, education, roads, and welfare) than private goods (banking and communication) Impact of micro-economic reform on growth More efficient producers Lowers cost of production Increased production = Increase in GDP = Economic Growth EXAMPLE. PRIVATISATION OF TELEPHONE SERVICES Privatisation =Transferring ownership from the government to private firms. Market for Goods Price $ S S1 Se Privatisation often lead to reduced costs for producers S1 D Qe Q1 Quantity HOW DOES PRIVATISATION LEAD TO DECREASED COSTS FOR PRODUCERS? There is a difference in incentives between public and private sectors. A tax-funded government business has a monopoly (the only producer in the market) and thus has guaranteed revenues, regardless of performance. And its workers are protected both by unionization and by a civil service system which virtually guarantees continued employment and pay increases, regardless of performance. A private firm in a competitive market must win over its customers by offering them a superior combination of performance and price. If it fails to deliver adequately, its customers can go elsewhere. Private firms producing public services – even firms which competitively win exclusive contracts for a number of years – therefore operate far more efficiently than government monopolies. MICRO ECONOMIC REFORMS IN 1980S-1990S The Financial Sector Removed interest rate controls NZ dollar floated Government departments co-oporatised then privatised Post office split to – NZ Post, Post bank and telecom Railways were corporatised then sold Labour Market freed up Employment contracts act 1991 Trade protection policies removed Removal Tarriffs and Quotas Welfare benefits reduced Health Sector Reformed Try to make it operate more efficiently using business type model EXERCISE BOOKS PAGE 154-155 Read page 153-154