* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Financial Operations - International Business (Our Global Economy).
Criticisms of socialism wikipedia , lookup
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Economic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Production for use wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Consumerism wikipedia , lookup
Protectionism wikipedia , lookup
Economic calculation problem wikipedia , lookup
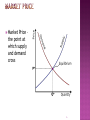
International Business: Our Global Economy 1 Scarcity – Refers to the limited resources available to satisfy the unlimited needs of people Economics – The study of how people choose to use limited resources to satisfy their unlimited needs and wants 2 6 Steps Define the problem Identify the alternatives Evaluate the alternatives Make a choice Take action on the choice Review the decision 3 Price is one of the most economic factors you encounter every day. The amount paid for goods and services results from economic decisions made by consumers, businesses, and governments. 4 Supply – the relationship between the amount of a good or service that businesses are willing and able to make available and the price. Demand – (the buyers side) the relationship between the amount of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase and the price. 5 Market Price – the point at which supply and demand cross 6 Inflation – an increase in the average prices of goods and services in a country To start a company that makes a product requires several elements. These elements are called factors of production 7 Natural Resources (Land) Human Resources (Labor) Capital Resources (Capital - $) 8 Command – government or central planning committee regulates amount, distribution, and price Market – individual companies and consumers make decisions about what, how and for whom items will be produced Mixed – where the economies are blended between government involvement in business and private ownership 9 Command Government regulates Government can even regulate what job you have Market Economy Companies and consumers make decisions Private Property, Profit Motive, Free Marketplace Mixed Economy Economy Some government involvement ex. France 10 Exists when a country can produce a good or service at a lower cost than another country 11 Exists when a country specializes in the production of a good or service at which it is relatively more efficient For example, if, using machinery, a worker in one country can produce both shoes and shirts at 6 per hour, and a worker in a country with less machinery can produce either 2 shoes or 4 shirts in an hour, each country can gain from trade because their internal trade-offs between shoes and shirts are different. The lessefficient country has a comparative advantage in shirts, so it finds it more efficient to produce shirts and trade them to the moreefficient country for shoes. 12 GDP Measures output of goods produces within it’s borders GNP (Gross Domestic Product) that a country (Gross National Product) Measures the total value of all goods and services produced by the resources of a country 13 Balance Difference between a country’s exports and imports Foreign of Trade Debt Amount a country owes to other countries Consumer Price Index (CPI) Federal Government report that shows price levels of products & services in different regions of a country 14 Literacy Level – countries with better education systems usually provide more goods and services that are of higher quality for their citizens Technology – automated production, distribution, and communication systems quickly allow companies to create and deliver goods, services, and ideas quickly Agricultural dependency – an economy that is involved in agriculture does not have manufacturing base for high quality products 15 Industrialized Country – strong business activity, technology and educated population Infrastructure – refers to nation’s transportation, communications, and utilities Less-Developed Country – little economic wealth and focus on agriculture and mining Developing Country – moving towards industrialization 16 Emerging Markets – Places where consumer incomes and buying power are increasing because of economic expansion 17 Gross Measures the output of goods that country produces within its borders Gross Domestic Product (GDP) National Product (GNP) Measures the total value of all goods and services produced by resources of a country *It’s like GDP except the goods could be made in other countries but using resources from your country 18 Balance of trade – difference between a country’s exports and imports Example – if a country imports more than it exports, it is an unfavorable balance of trade also known as a TRADE DEFICIT Foreign Exchange Rate – value of country’s money to another country Foreign Debt – amount a country owes to other countries CPI – Consumer Price Index is a federal govt. report published by Bureau of Labor 19