* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A fresh start for DECPG
Survey
Document related concepts
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Nouriel Roubini wikipedia , lookup
Post–World War II economic expansion wikipedia , lookup
Global financial system wikipedia , lookup
Great Recession in Russia wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and Its Discontents wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
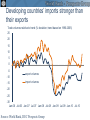
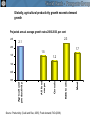
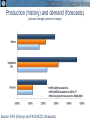
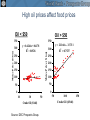
Transformational Changes in the Global Economy Trade, finance and commodities after the crisis Hans Timmer World Bank March 1, 2011 Trade, Finance, and Commodities • Trade dynamics illustrate that developing countries have become the drive of global growth Trade, Finance, and Commodities • Trade dynamics illustrate that developing countries have become the drive of global growth • Financial markets still show the reverberations of the financial crisis Trade, Finance, and Commodities • Trade dynamics illustrate that developing countries have become the drive of global growth • Financial markets still show the reverberations of the financial crisis • Food price increases reflect major changes in commodity markets Source: The World Bank Japan’s export growth was largely driven by Asian import demand during crisis Contribution to annualized q/q growth (%) Source: World Bank, DEC Prospects Group Developing countries’ imports stronger than their exports Trade volumes relative to trend (% deviation; trend based on 1990-2005) 25 20 15 10 5 0 -5 -10 -15 export volumes import volumes -20 -25 -30 Jan-06 Jul-06 Jan-07 Jul-07 Jan-08 Jul-08 Jan-09 Jul-09 Jan-10 Jul-10 Source: World Bank, DEC Prospects Group Share of developing countries in global trade more than doubled during last 20 years 0.45 0.40 South share of total world imports South import share from other South countries 0.35 0.30 0.25 0.20 0.15 0.10 0.05 0.00 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 Source: Comtrade data via WITS Source: The World Bank Source: The World Bank Source: The World Bank Developing countries have become driver of global trade • Sustained strong growth in developing countries is more crucial than rebalancing for global recovery • Developing countries should take the lead in trade negotiations Decline and recovery in capital flows was very concentrated percent of GDP 16 Short-term Debt 14 Bank 12 Bond 10 Portfolio Equity 8 FDI 6 4 2 0 -2 06-07 2008 2009 2010 06-07 2008 2009 2010 06-07 2008 2009 2010 06-07 2008 2009 2010 Top 9 Source: The World Bank Europe & Central Asia (excluding Turkey) Other Middle Low Income Bank NPLs remain elevated in Europe and Central Asia Median %-share of non-performing loans (NPLs) to total 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 2005 2006 2007 High Income with rising NPLs Developing Asia Other HICs 2008 2009 Europe and Central Asia Other Developing 2010 Capital flows put upward pressure on many currencies Real-effective exchange rate, January 2009=100 150 Brazil Russia India 140 Indonesia Thailand Malaysia Mexico South Africa Turkey 130 120 110 100 90 Jan-09 Apr-09 Jul-09 Oct-09 Source: International Monetary Fund Jan-10 Apr-10 Jul-10 Oct-10 Jan-11 Weak bank-lending implies private capital flows will not recover to pre-crisis levels for some time Net private capital flows to developing countries, $ billion in billions Source: The World Bank Percent of GDP From FDI inflow…… 7.0 Percent of GDP 6.0 5.0 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 0.0 1980 1983 1986 1989 1992 China 1995 1998 LMICs excl China 2001 2004 2007 …to FDI outflows 1.4 Percent of GDP 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 1980 1983 1986 1989 1992 China 1995 1998 LMICs excl China 2001 2004 2007 Developing countries’ role in financial markets will dramatically increase • Developing countries aim to become less dependent on dollar and US monetary policy. • Coming decade will show shift from ingoing FDI to outgoing FDI. • While high-income countries look for regulating financial markets, developing countries need to deepen markets, partly through liberalizing them. The recent boom was one of the largest, longest lasting and involved all commodities MUV-deflated US$ (2000=100) Agriculture Metals Oil Source: World Bank Source: The World Bank Technological progress increases the efficiency of resource use Commodity intensity of demand, index 1971 = 1 Source: World Bank. 367 1,000 Most major countries have passed the point where food demand grows much faster than population China Brazil Russia 18 45 135 India 0.4 1.1 2.9 8.1 GDP per capita (1,000 PPP $) Note : Curve fitted on a log scale. Source: World Bank Note: Curve fitted on a log scale 22.0 59.8 Globally, agricultural productivity growth exceeds demand growth Projected annual average growth rates 2000-2030, per cent 2.5 2.3 2.1 2.0 1.7 1.5 1.5 1.2 1.0 Source: Productivity (Coelli and Rao, 2005); Food demand, FAO (2006) Meat Edible oils Cereals Agricultural productivity 0.0 All food crops 0.5 Production (history) and demand (forecasts) (annual average percent change) Source: FAO (history) and FAO/OECD (forecasts) Causes of the boom • Sharp increase in Chinese demand for metals • Decades of weak prices, during which as much as ½ of global demand was being met from idle capacity • Impact of oil prices on agricultural prices • Adverse weather patterns • Larger role of financial market High oil prices affect food prices Oil < $50 Oil > $50 350 350 y = 0.4246x + 86.178 R2 = 0.0526 300 Maize Price ($/ton) Maize Price ($/ton) 300 250 200 150 100 250 200 150 100 50 50 0 0 10 30 Crude Oil ($/bbl) Source: DEC Prospects Group. y = 2.1166x - 3.3711 R2 = 0.7527 50 50 100 Crude Oil ($/bbl) 150 Improving our capacity to respond to commodity cycles Domestic policy agenda – Improve targeting of social welfare schemes – Invest in rural infrastructure and agricultural R&D – Be prepared to react rapidly because of long-term costs of even a relatively short bout of high food prices Global policy agenda – Proceed with trade liberalization, including improved disciplines governing export bans – Increase the financial independence of World Food Program – Improve information flows and coordination of food stocks Transformational Changes in the Global Economy Trade, finance and commodities after the crisis Hans Timmer World Bank March 1, 2011