* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Indonesia
Nouriel Roubini wikipedia , lookup
Balance of payments wikipedia , lookup
Global financial system wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Modern Monetary Theory wikipedia , lookup
Foreign-exchange reserves wikipedia , lookup
Fear of floating wikipedia , lookup
Pensions crisis wikipedia , lookup
Great Recession in Russia wikipedia , lookup
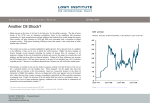
1997 Indonesia Financial Crisis Chris DeBose Edan Harris Agenda Part I Causes of the Crisis Part II During the Crisis Part III After the Crisis Causes of the Crisis Devaluation of the Indonesian rupiah Fundamental weakness in the economy Indonesian central bank continued the trade band policy and increased the currency band. Causes of the Crisis Devaluation of the Indonesian rupiah in relations to the dollar. 1997: Rp 2,600/USD 1 1998: Rp 11,000/USD 1 Highest - Lowest: Rp 15,000 – Rp 8,000 / USD 1 Causes of the Crisis Fundamental weakness in the economy Inadequate liquidity where banks and corporations had too little cash and current assets to pay of their current and maturing liabilities. Causes of the Crisis Fundamental weakness in the economy Excessive un-hedged and unsecured borrowing abroad by the private sector, specifically corporations and banks. Supported by inadequate supervisory institutions. Causes of the Crisis The cycle caused by lack of liquidity and over borrowing. Strong demand for dollars. Declining ability to repay loans Develop and increase financial issues Foreign investor with capital Foreign borrowing Unable to repay loans Causes of the Crisis Fundamental weakness in the economy Investment/Overinvestment of borrowed funds into speculative projects and export industries where growth was difficult to predict. Like luxury condos, steel, shipbuilding and others. Causes of the Crisis Increased the currency band. Indonesia responds by increase currency band on rupiah from 8% to 12% so the value of the currency had more room to fluctuate and to allow the currency to re-stabilize within the band. Manage floating exchange rate (SEEN AS STABLE) to a free floating exchange rate (SEEN AS UNSTABLE). Causes of the Crisis How does it all come together? As the strength of the of the Indonesian rupiah continually decreased. The over borrowing of foreign loans by the private sector (specifically private corporations) cause increased borrowing of the dollar. Corporations discarded rupiah (because of increase in debt under the rupiah), continuingly undermining the value of the rupiah. During the Crisis Effects on the Economy Massive Unemployment IMF Prescriptions After the Crisis Effects on the Economy The crisis is rooted in the private sector (particularly banking) Nearly all of the domestic businesses became insolvent Especially businesses in manufacturing and construction sector as well as in the urban services sector. Such as real estate and property sector, and the banking sector. During the Crisis Massive Unemployment It is estimated that nearly have of Indonesia’s citizens were pushed back below the poverty line as a result of the financial crisis. During the Crisis *Real GDP went down. During the Crisis *Number of Employed went down. During the Crisis *Employee Equivalent measures total hours work over average annual hours worked and it went down. During the Crisis * Average Hours Worked went up. During the Crisis *Average Income per Year went down. During the Crisis *Average Real Wage per Hours Worked went down. During the Crisis IMF Prescriptions Originally the IMF required that the government engage in strict austerity measures of fiscal and monetary policy. Draconian government cutbacks. i.e. food and energy subsidies and so forth. After it is was discovered that the original cause for the crisis was rooted in the private sector, IMF felt that is was necessary to implement measures to deal with the problems within it. Required reforms that would mimic American and European currency, banking and financial systems. Also they required the liquidation of half of the banks. (only 16 were liquidated) Additionally provided $40 billion worth in “rescue packages” for the banks. During the Crisis IMF Prescriptions This was especially true for the private banking sector, which the IMF sought to reform. Most importantly, the IMF requested that the Indonesian government “sell off ” or privatize government companies. It was believed that the Indonesian government was inefficient because of heavy government intervention in the public sector. Thus, the IMF believed that more liberalized government agencies would help them become more efficient, this would help eliminate the crisis. After the Crisis Stabilization of the currency. (Although it was enormously undervalued in comparison to pre-1997 levels). Massive student protest due the government cut backs of subsidies. This led to a drastic rise in food and energy prices. Increased inflation due to government cutting of subsides. Economic growth accelerated to 5.1 % in 2004, 5.6 in 2005 due to consumer consumption (3/4 of Indonesia GDP). Real per capita income reach 1996/1997 levels. Unemployment rate was 9.75% in 2007. After the Crisis Here is a video illustrating the aftermath of the IMF policies that were implemented. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_VjMyvPJ3hE&feature= player_detailpage