* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Aggregate Supply
Participatory economics wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Economic calculation problem wikipedia , lookup
Fei–Ranis model of economic growth wikipedia , lookup
Transformation in economics wikipedia , lookup
Long Depression wikipedia , lookup
2000s energy crisis wikipedia , lookup
2000s commodities boom wikipedia , lookup
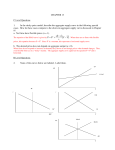
Aggregate Supply Chapter 11 — one week Definition AS is a schedule showing level of real domestic output available at each possible price level. Possible Shapes of Aggregate Short Run Supply Curve Horizontal SRAS Curve PL SRAS GDPr Horizontal Conditions: Substantial unemployment and excess capacity (unemployed resources) Economy is far below full employment Might be in a recession or depression Upwardsloping or Intermediate Range SRAS Curve PL SRAS GDPr Upsloping or Intermediate Range Conditions Closer to full-employment levels, which create upward pressure on prices Upward pressure on prices is caused by rising costs of doing business Vertical Range SRAS Curve PL SRAS GDPr Vertical Range SRAS Curve Conditions: Absolute capacity is assumed—the economy is unable to produce any more G & S for a long period of time Any attempt to increase output will bid up resource and product prices Putting it together SRAS PL C B A GDPr A = horizontal B = upsloping C = vertical Determinants of AS 1. Change in input prices: Availability of resources (4 factors) Prices of imported resources Market power of certain industries Determinants of AS cont. 2. Change in productivity can cause changes in per-unit production cost Productivity rises, unit production costs will • Shift to the right and lower prices Productivity falls, unit production cost will • Shift to the left and increase prices Determinates of AS cont. 3. Change in legal-institutional environment: Business taxes and or subsidies Cost of gov’t regulation Change in SRAS? or NC Determinate? 1. unions grow more aggressive; wage rates increase 2. labor productivity increases dramatically 3. OPEC successfully increases oil prices 4. computer technology brings new efficiency to industry 5. Gov’t spending increases 6. giant natural gas discovery decreases energy prices 7. low birth rate will decrease the labor force in the future. Change in SRAS? or NC 1. unions grow more aggressive; wage rates increase or shift to the left—change in input prices 2. labor productivity increases dramatically or shift to the right—change in productivity 3. OPEC successfully increases oil prices or shift to the left—change in input prices 4. computer technology brings new efficiency to industry or shift to the right—change in productivity 5. Gov’t spending increases NC—gov’t spending would shift the AD curve. 6. giant natural gas discovery decreases energy prices or shift to the right—change in input prices 7. low birth rate will decrease the labor force in the future. NC—will not affect aggregate supply for 16 years or more Homework Page 222 Numbers 1, 2, and 7 Long Run Aggregate Supply LRAS PL Output or GDPr Represents the Q of g & s a nation can produce over a sustained period of time using its productive resources efficiently LRAS is at full employment Developing more & better resources or improving tech. will shift the curve outward but it will still be vertical