* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Handout #5 - Texas A&M University
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
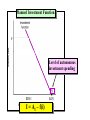
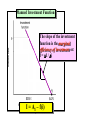
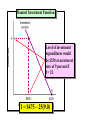
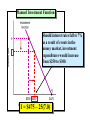
Slide Show #5 AGEC 430 Macroeconomics of Agriculture Spring 2010 Handout #5 GDP = C + I + G + X – M where: Investment expenditures represent 18-20% of GDP C = consumption expenditures I = investment expenditures G = government expenditures X = exports M = imports Annual level of gross private domestic investment. This is significant since it not only affects GDP but also indirectly affects the growth of the economy’s productive capacity and employment over the longer run. Annual percent change in gross private domestic investment. Note the decline is sharper than any recession dating back to the Great Depression. Let’s graph this function Planned Investment Function Level of autonomous investment spending I = AI – f(i) Planned Investment Function The slope of the investment function is the marginal efficiency of investment, or: f = I / i I = AI – f(i) Planned Investment Function Level of investment expenditures would be $250 at an interest rate of 9 percent if f = 25. I = $475 – 25(9.0) Planned Investment Function Should interest rates fall to 7% as a result of events in the money market, investment expenditures would increase from $250 to $300. I = $475 – 25(7.0) Effects of Profit Expectations An increase in profit expectations would cause businesses to expand their planned investment expenditures by $50 at the same interest rate I = $475 + $50 – 25(7.0) Average stock during year captured in the brackets… Handout #6 What is E(P) x E(Y)? What is E(P) x E(Y)? … Revenue Ratio of MVP to MIC. We know that profit maximizing firms will acquire inputs up to the point where MVP=MIC Expected output is given by the desired use of labor and capital. What is missing here? More on this shortly Can you give an example of a expenditure that represents: 1. A one-hoss shay 2. A geometric decay? Is there a pattern missing here? How do these capacity depreciation patterns compare to: 1. Tax depreciation? 2. Economic depreciation? Is there a subsidy from the IRS here? The market value of an asset declines the most percentage wise in the first year. This affects the current market value balance sheet. SL represents the straight line depreciation pattern. The DDB represents the more liberal double declining balance depreciation or MACRS pattern. This affects the book value balance sheet. Comparison of Depreciation Concepts Economic Depreciation Tax Depreciation Capacity Depreciation