* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Fear of floating wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Edmund Phelps wikipedia , lookup
Modern Monetary Theory wikipedia , lookup
Greg Mankiw wikipedia , lookup
Transformation in economics wikipedia , lookup
Money supply wikipedia , lookup
Interest rate wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Monetary policy wikipedia , lookup
Inflation targeting wikipedia , lookup
Full employment wikipedia , lookup
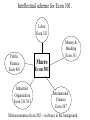
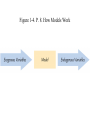
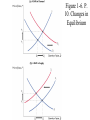
Chapter 1. Introduction Link to syllabus First Class Roll, Adds and Drops Exams, homework Macromodel Programs Link to Syllabus Link to mt’s webpage Goals of the course Major Themes Comments about textbook Econ 301 as center of the world Basic data Epilogue to Mankiw’s text. Goals of the course • Understand Macroeconomic phenomena – inflation, unemployment, exchange rates • Policy issues: Government spending and taxes, the deficit/debt. Social Security doesn’t get much play in this textbook. • Practice using models and graphs to study interactions of many variables • This course is a useful pre-req for grad school/MBA programs • Comments about textbook Major Themes • Classical Model – full employment • ‘Keynesian’ models – not necessarily full employment • Analyzed in terms of Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply. AD depends on IS-LM, which is a major building block. (also, IS*-LM*) • Aggregate Supply is not emphasized much. • Phillips curve is included, but not central • Short run/long run distinction. • Does more international than many other texts Intellectual scheme for Econ 301. Labor Econ 321 Public Finance Econ 481 Industrial Organization Econ 331/333 Macro Money & Banking Econ 311 Econ 301 International Finance Econ 347 Microeconomics-Econ 302—is always in the background Figure 1-1 p. 5. Real GDP per person in the US. Figure 1-2 p. 6. Inflation in the U.S. Figure 1-3 p. 7. Unemployment in U.S. Unemployment Rate, US Source: US Dept. of Labor http://data.bls.gov/timeseries/LNS14000000 Inflation in the U.S. Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics: http://data.bls.gov/pdq/SurveyOutputServlet?request_action=wh&graph_name=CU_cpibrief Epilogue to Mankiw text Four most important lessons of macroeconomics. 1. In the long run, a country’s capacity to produce goods and services determines the standard of living of its citizens. 2. In the short run, aggregate demand influences the amount of goods that a country produces 3. In the long run, the rate of money growth determines the rate of inflation, but does not affect the rate of unemployment 4. In the short run, policymakers who control monetary and fiscal policy face a tradeoff between inflation and unemployment The four most important unresolved questions in macro 1. How should policymakers try to raise the economy’s natural rate of output? 2. Should policymakers try to stabilize the economy? 3. How costly is inflation, and how costly is reducing inflation? 4. How big a problem is government debt? Note that the US currently suffers a recession, a large short term deficit, and the prospect of high long term debts. Figure 1-4. P. 8. How Models Work Figure 1-5. P. 9 Supply and Demand for Pizza Figure 1-6. P. 10. Changes in Equilibrium