* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Saving and Investment in China
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
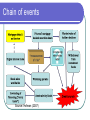
Subprime problems and global financial sector turmoil—the impact on China’s economy, financial system, and implications for policy CBRC Banking Forum September 21, 2007 Louis Kuijs, World Bank Beijing Outline What happened in the US and global financial markets? What may be the impact on the global economy and financial system? Possible impact on China Via direct exposure of China’s financial institutions Via financial market channels Economic impact Simulation results What about decoupling? Policy considerations Macro policy Structural policies in the financial sector The scale of things The US Subprime Mortgage Perspective (US$ Trillion). Total US Mortgage market o/w sub-prime o/Adjustable Rate Mortgage o/w securitized Market in 10 1.5 0.75 0.15 Memorandum Items World Debt Securities 39.0 o/w Domestic Debt Securities 20.5 o/w International Debt Securities 18.4 US Collateralized Debt Obligations 0.9-1.2 Global Collateralized Debt Obligations 1.5-2.0 Credit Default Swaps (Notional Amount) 28.8 o/w Gross Market Value 0.5 World Stock market Capitalization 50.1 World GDP 45.1 Source: BIS, Chicago Federal Reserve bank, IMF, Financial Times, Credit Lyonnais. Relaxation of credit standards Underwriting Standards in Subprime Home-Purchase Loans ARM Share 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 Interest-Only Low- No- Debt Payments-to-Average Loan-toARM Share Doc Share Income Ratio Value Ratio 73.8% 80.0% 80.1% 89.4% 93.3% 91.3% Source: Freddie Mac. 0.0% 2.3% 8.6% 27.2% 37.8% 22.8% 28.5% 38.6% 42.8% 45.2% 50.7% 50.8% 39.7 40.1 40.5 41.2 41.8 42.4 84.04 84.42 86.09 84.86 83.24 83.35 Credit worsening in the US sub prime mortgage market Subprime 60 Day Delinquencies by Mortgage Vintage Year (adjustable rate mortgages, in percent of payments due) 12% 2006 10% 2005 8% 6% 2004 4% 2003 2% 0% 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 Months after Origination Source: JPMorgan Chase & Co. 55 60 65 70 75 80 Chain of events Source: Hofman (2007) Risk is being reassessed Source: JP Morgan Chase and Co However, so far, spill-over to emerging markets remains low 2,000.0 Emerging Market Bond Index Spreads 12/31/1993 - 8/10/2007 JPMPTOT(BSPRD) U$ 1,800.0 JPMPASI(BSPRD) U$ 1,600.0 JPMPBRA(BSPRD) U$ JPMPRUS(BSPRD) U$ 1,400.0 JPMGCHN(BSPRD) U$ 1,200.0 1,000.0 800.0 600.0 400.0 200.0 0.0 12/31/93 12/31/94 12/31/95 12/31/96 12/31/97 12/31/98 12/31/99 12/31/00 12/31/01 12/31/02 12/31/03 12/31/04 12/31/05 12/31/06 Source: Bloomberg Possible impact on China Via direct exposure of China’s financial institutions Via financial market channels Economic impact Simulation results What about decoupling? Effect on China’s financial markets is so far limited China Capital account relatively closed Large current account surplus puts upward pressure on the exchange rate and feeds liquidity Strong growth and confidence Insurance (reserves) limited effect on domestic financial markets Impact via economic linkages Economic impact in US (and other countries) Wealth effects Repricing of risk Housing market The economic impact would affect China’s economy Table. Impact of a consumption slowdown in the US (Impact on GDP in first year, in percent) Normal monetary policy No/no effective monetary response in the US policy response in the US US Brazil China India Indonesia Russia South Africa Turkey -0.9 -0.1 -0.2 -0.1 0.0 0.0 0.1 -0.1 -1.0 -0.3 -0.5 -0.2 -0.3 -0.2 -0.2 -0.2 Source: World Bank staff estimates, using the OEF model. However, China is well-placed to absorb the economic impact Global slowdown Lower overall growth Lower exports and trade surplus Lower commodity prices and inflation More drastic slowdown China has room policy easing is possible, if necessary Financial sector policy implications Monitoring and reviewing Structural policies in the financial sector To watch Developments in international capital market (link up with BIS, IMF, WB) Unusual sales patterns in capital market (CSRC) Interbank market liquidity and rates (PBC) Unusual balance of payments movements (SAFE) Exposure of financial institutions to international risk (CBRC, CSRC) Exposure of large SOEs to international risk To review Contingency plans to counter possible financial problems (liquidity provision, financial institution failure) Exchange of information (regular meetings among relevant authoritiesMOF, PBC, SAFE, CBRC, CSRC) What are implications for financial sector policies? Implications for financial regulation and risk management in US and other countries Implications for China