* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
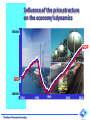
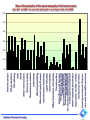
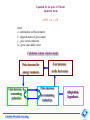
Influence of the price structure on the economy’s dynamics 5500000 GDP GDP 2000000 1980 ©Institute of Economic Forecasting 1990 1998 2010 2020 Influence of the different factors on economic dynamics of Russia IoEF RAS Illarionov A.N. 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 Total GDP growth 5,4 9 5 4 influence of external factors 0 9 7 9 influence of economic policy 5,4 0 -2 -5 Totаl GDP growth 5,4 9 5 4,3 5 influence of external factors 3,9 6 -3,7 0,6 1 influence of oil prices 3,2 4,9 -1,2 0,3 0,3 influence of the world economy 0,7 1,1 -2,5 0,3 0,3 1,5 3 8,7 3,7 4 influence of the tariffs 1,2 1,5 -4,7 influence of the state’s debt payments 2,1 -0,9 -2,1 -0,05 Influence of the internal factors ©Institute of Economic Forecasting -2,3 -0,3 -1,7 The faster relative growth of tariffs (prices) for the products of natural monopolies projected for the mid-term will inevitably result in 1) a sufficient redistribution of value added in favor of natural monopolies, and 2) an increase in the share of their costs of the total costs of the economy. Shares of natural monopolies and other branches in total value added 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% 2001 2002 Natural monopolies © Institute of Economic Forecasting 2003 2004 2005 Other branches 2006 ©Institute of Economic Forecasting Science and scientific services General government, finance Communal services Education, health, culture Other material production Agriculture and forestry Freight transport and communications for production purposes. Passenger transport and communications for non-production purposes. Trade and procurement Construction Other branches of industry Food industry Light industry Construction materials Wood and pulp & paper Machine-building Chemistry Non-ferrous metals Ferrous metals Other fuel sectors Coal Gas Oil refining Oil production Electric power Share of the production of the natural monopolies in the branches costs Years 2001 and 2006 г. (in case of the tariff growth in according to drafts of the MERT 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% Equation for the price I-O Model (in matrix form) p*A*X + va = p*X, where А - intermediate coefficient matrix; X - diagonal matrix of gross output; p - price vector (unknown), va - gross value added vector. Calculation scheme of prices model Price increase for Cost increase energy resources in the fuel sector Cost increase in consuming industries © Institute of Economic Forecasting Price increase in consuming industries Adaptation hypothesis Xij If X У А АХ АХр Xij va vap J Xj AX > X , then AXp AX > vap va gross output vector; final demand vector; intermediate coefficient matrix; intermediate consumption; intermediate consumption after price increase for the product of industry i; flows for industry I to industry J; value added; value added after price increase for the products of industry i AX+Y = X Industry i Xij Yi Xi AX Y X I quadrant of IOT III quadrant of IOT © Institute of Economic Forecasting va II quadrant of IOT Relative decrease in prices for products of natural monopolies in 1998 was an important factor of the industrial growth in 1999. Further decrease in these prices in 1999 sufficiently contributed to the positive economic dynamics in 2000. However, in 2000, average price growth in the natural monopolies started to exceed that in industry; as a result the relative gap in price levels shrunk, which correlated with a certain decline in production growth rates in industry in 2001-2002. Dynamics of the GDP and the integral index of relative prices in the natural monopolies sectors (one year lag) 1.200 1.100 1.000 0.900 0.800 0.700 0.600 1998 GDP index © Institute of Economic Forecasting 1999 2000 2001 2002 integral index of relative prices in the natural monopolies sectors (one year lag)