* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rethinking the use of Concept maps
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
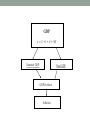
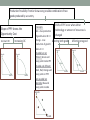
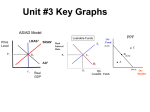
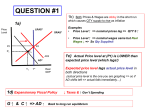
RETHINKING THE USE OF CONCEPT MAPS Mariya Burdina University of Central Oklahoma How can I get to the library? What’s the difference between income and price elasticity? Temporal contiguity principle Students learn better when corresponding words and “pictures” are presented simultaneously rather than successively • Mayer, 2004 Traditional concept maps • A concept map is a diagram showing the relationships among concepts • Satisfies temporal contiguity principle GDP map (Nora Buchman, Scribd) GDP 𝛾 = 𝐶 + 𝐼 + 𝐺 + 𝑁𝑋 Nominal GDP Real GDP GDP Deflator Inflation Spatial principle • Students learn better when corresponding words and pictures are presented near rather than far from each other • Mayer, 2004 Conceptual chapter map • A graphical tool for organizing concepts • Shows links among concepts • Provides brief explanation of the concepts • Satisfies temporal contiguity principle • Satisfies spatial principle Use • Review tool for a topic or a chapter • Drawn on the board by instructor • Completed with the help of students • Distributed to students • Used during in-class assignments/quizzes • Option for “revising” a chapter map Production Possibility Frontier • Slope • Constant • Increasing • Points: • inside • outside • on PPF • Corners • Shifts in PPF • Affecting one good • Affecting both goods Production Possibility Frontier show every possible combination of two goods produced by a country Shifts of PPF occur when either Slope of PPF shows the Opportunity Cost Constant OC Good A Increasing OC Good A Good B Good B Intercepts: technology or amount of resources is Red – max production changed of good A when B = 0 Orange - max Affecting one good Affecting both goods production of good B when A = 0 Good A Good A Possible but not efficient: Green and every point inside PPF Possible and efficient: Black, Red, Orange and Good B Good B every point on PPF Not possible but desirable: Blue and every point outside PPF A Good Good B Demand, Supply, Market Equilibrium • Law of demand • Shifts of demand curve • Law of supply • Shifts of supply curve • Market equilibrium • Surplus • Shortage • Changes in market equilibrium Market Demand Changing price: Increasing price decreases Qd Decreasing price increases Qd Supply Changing Demand: Changing Supply: Number of consumers Popularity Future prices Change in income: - Normal goods - Inferior goods Number of Sellers Better technology Future prices Input prices Prices/popularity of similar goods Changes in Equilibrium Algorithm: 1) Draw the D and S curves and show the equilibrium 2) Decide whether event shifts S curve or D curve or both 3) Decide in which direction curve(s) shifts. 4) Illustrate the shifts using the graph 5) Use supply-demand diagram to identify new equilibrium P and Q. Changing price: Increasing price increases Qs Decreasing price decreases Qs “Evidence” • Students use concept maps in class • A-ha moments • Reduced load of questions during the in-class assignment “Evidence” • Business statistics • Normal vs. Standard Normal vs. Uniform • Hypothesis testing • Intermediate Microeconomics • Max utility vs. Min cost • EV vs. CV Practical strategies • Introduce maps as a review before in class assignment • Assign “revise” the map instead of the “create” the map • Keep it simple (Coherence Principle) • Students learn better when extraneous material is excluded rather than included • Think what’s important and what is not. Only the most important things should be included in the map Practical strategies • Keep it colorful to emphasize important points • Make sure that assignment can be answered with concept map • Provide links and definitions; allow space for student to fill in with examples “Evidence” • Principles of Micro • PPF • Opportunity Cost and Trade • Demand, Supply and Equilibrium • Elasticity • Surplus • Public goods • Cost • Market comparison • Each type of market • Principles of Macro • GDP • Inflation • Productivity and growth • Savings and Investment • Unemployment • Open market economy Next step: Class Experiment • Conceptual chapter map in Principles of Macroeconomics • 2 classes of students: • Chapter map for in-class assignment for Class 1 • Notes for in-class assignment for Class 2 • No notes for the test • Chapter map for quiz for Class 1 • Notes for quiz for Class 2 • No notes for the test