* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Module 8 Inverters
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Electrical grid wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
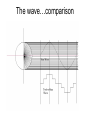
Fall 2009 Module 8 Inverters Inverters • Converts the DC power produced by the solar modules into AC power used on the utility grid History • Inverters have been the weaker link in PV systems • Early inverters were unreliable • Early inverters were inefficient which penalized an entire system Inverter Types • Square Wave • Modified square wave • Sine wave Square wave • Step-function or “square” alternating current output – Considerable harmonic distortion • For small resistive heating loads Modified Square Wave • Complex circuits used to switch DC into AC. • More appropriate for operating a wide variety of appliances • Still noise will be picked up by sensitive equipment Sine Wave • High quality wave form • Most common inverters today • Little harmonic distortion The wave…comparison Inverter manufacturers • • • • • • • SMA (Sunny Boy) Fronius Xantrex Outback PV Powered Kaco Enphase – Micro Inverters The Guts Some examples Enphase Micro-Inverter All Installed Installing SMA Optional Inverter Features • Remote control operation and datamonitoring • Load transfer switch-allows system to meet critical loads during power failure • Series and Parallel connectivity for multiple inverters • Individual module performance monitoring Ideal Inverter Features – now standard • • • • • • Maximum power point tracking (MPPT) Low harmonic distortion Near perfect Sine wave shape Ground Fault Protection AC/DC disconnects Weatherproof enclosure Specifying an inverter • Grid Tied:Watts Output AC-computed STC rated watts of PV panels • Stand-Alone: based on peak load • Input Voltage-usually between 75 and 480 VDC, called the window or range – Insure that the voltage will not drop or exceed this range because of climatic conditions or inverter will not function • Output Voltage:120, 240, 208, 480 • Frequency: U.S. is 60Hz Specifying an inverter • Grid Tied:Watts Output AC-computed STC rated watts of PV panels • Stand-Alone: based on peak load • Input Voltage-usually between 75 and 480 VDC, called the window or range – Insure that the voltage will not drop or exceed this range because of climatic conditions or inverter will not function • Output Voltage:120, 240, 208, 480 • Frequency: U.S. is 60Hz Grid Tied Inverter Sizing • Sized based on the amount of watts we pass through the system at any one time – Size of inverter is the labeled watts • an SMA 3000 is a 3000 watt inverter – The most power that will pass through this inverter is 3000 watts – If the output is 240 volts, the current will be 12.5 amps » 3000W ÷ 240v = 12.5 amps String Sizing Software And sized by… • PV system component package (grid tied) • The Grid Tied PV system will be based on other factors – Budget – Roof Size – Rebate/Tax incentives