* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download lec12-elec
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
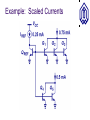
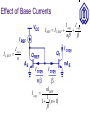
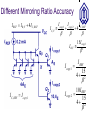
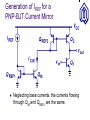
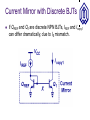
Current Mirrors OUTLINE Cascode Stage (cont’d) supplementary remarks Current Mirrors Reading: Chapter 9.2 Review: Cascode Stage Rout The impedance seen looking into the collector can be boosted significantly by using a BJT for emitter degeneration, with a relatively small reduction in headroom. Rout [1 g m (rO 2 || r 1 )]rO1 rO 2 || r 1 Rout g m1rO1 rO 2 || r 1 Temperature and Supply-Voltage Dependence of Bias Current Circuits should be designed to operate properly over a range of supply voltages and temperatures. For the biasing scheme shown below, I1 depends on the temperature as well as the supply voltage, since VT and IS depend on temperature. I1 I S e VBE / VT VBE R2 VCC R1 R2 Concept of a Current Mirror Circuit designs to provide a supply- and temperature-independent current exist, but require many transistors to implement. “golden current source” A current mirror is used to replicate the current from a “golden current source” to other locations. Current Mirror Circuitry Diode-connected QREF produces an output voltage VX that forces Icopy1 to be equal to IREF, if Q1 is identical to QREF. Current mirror concept Generation of required VBE I copy1 I S ,1 I S , REF Current Mirror Circuitry I copy1 I REF VT ln VX VT ln I I S , 1 S , REF I REF Bad Current Mirror Example 1 If the collector and base of QREF are not shorted together, there will not be a path for the base currents to flow, so that Icopy is zero. Bad Current Mirror Example 2 Although it provides a path for base currents to flow, this biasing approach is no better than a resistive voltage divider. Multiple Copies of IREF Multiple copies of IREF can be generated at different locations by applying the current mirror concept to multiple transistors. I copy , j IS, j I S , REF I REF Current Scaling By scaling the emitter area of Qj by a factor of n with respect to the emitter area of QREF, Icopy,j is scaled by a factor of n with respect to IREF. This is equivalent to placing n unit-sized transistors in parallel. I copy , j nI REF Example: Scaled Currents Fractional Scaling I REF A fraction of IREF can be created in Q1 by scaling up the emitter area of QREF. VX 3I S exp VT I copy I copy 1 I REF 3 VX I S exp VT Example: Different Mirroring Ratios Using the concept of current scaling and fractional scaling, Icopy1 = 0.05mA and Icopy2 = 0.5mA, derived from a single 0.2mA reference current source (IREF). Effect of Base Currents I REF I C , REF I C , REF I copy n I copy nI REF 1 1 n 1 I copy n I copy Improved Mirroring Accuracy Use QF (rather than IREF) to supply the base currents of QREF and Q1, reduce the mirroring error by a factor of . I REF I B , F I C , REF I copy I copy IC ,F I E ,F n I C , REF I copy n I B,F I copy 1 2 1 n I copy nI REF 1 1 2 n 1 Different Mirroring Ratio Accuracy I REF I B , F 4 I C , REF IC ,F I copy1 I copy2 4 I B,F I copy1 I C , REF 15I copy1 2 I REF 15 4 2 I C , REF I copy1 I copy 2 10I REF 15 4 2 PNP Current Mirror A PNP BJT current mirror can be used as a currentsource load for an NPN BJT amplifier stage. Generation of IREF for a PNP-BJT Current Mirror Neglecting base currents, the currents flowing through QM and QREF2 are the same. Current Mirror with Discrete BJTs If QREF and Q1 are discrete NPN BJTs, IREF and Icopy1 can differ dramatically, due to IS mismatch.