* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download light - GEOCITIES.ws
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Automotive lighting wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Street light wikipedia , lookup
Fluorescent lamp wikipedia , lookup
Safety lamp wikipedia , lookup
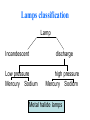
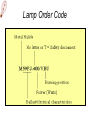
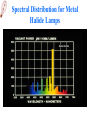
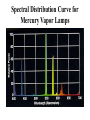
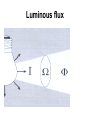
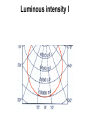
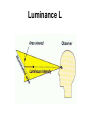
lamps Lamps classification Lamp Incandescent Low pressure Mercury Sodium discharge high pressure Mercury Sodium Metal halide lamps Incandescent lamps Lamp spectrum Strengths • • • • • • • • • • • • Low initial cost Excellent color rendition Instant starting Inexpensive dimming capability Small size, which allows it to be used in point fixtures, such as spot lamps Wide variety of shapes, sizes, colors and wattages are available Output unaffected by high or low ambient temperatures Simple to operate and install Requires no ballast High brightness light source Available in many colors Variety of filament design possibilities offer optical control, accurate distribution patterns and critical service operation Weaknesses • Relatively short useful life with poor overvoltage tolerance. At 10% over voltage, life is reduced about 75%! • Very inefficient source of light. On average, less than 10% of the wattage goes to produce light; the remainder becomes heat. • High heat component can create hidden energy costs due to increased cooling needs High Intensity Discharge • High Intensity Discharge or "HID" is the term commonly used to designate four distinct types of lamps that actually have very little in common. They are high pressure sodium, low pressure sodium, metal halide, and mercury vapor. Each requires a few minutes (one to seven) to come up to full output. Also, if power to the lamp is lost or turned off, the arc tube must cool to a given temperature before the arc can be re-struck and light produced. Up to seven minutes (for mercury vapor lamps) may be required. Metal Halide lamps Strengths • Designed for general lighting applications. • Relatively long lamp life. • Interchangeable with mercury lamps in many applications. • Concentrated source is easily controlled by special fixtures. • Good color rendering characteristic. • Light output is a bright crisp white light. • Twice as efficient as mercury lamps and 6 times as efficient as incandescent Weaknesses • • • • • • • Short life compared to other HID lamps (6,000 to 20,000 hours depending on size and manufacturer). Different lamps have to be used for base-up versus base down burning configurations. Horizontal operation may severely reduce lamp life. Require a ballast. Some lamp types require 2 to 5 minutes to warm-up before giving full light output and 10 minutes to cool-down. Others have instant restart capability. Color may vary from lamp to lamp (color shift) Many wattages require operation in enclosed fixtures due to the risk of lamp breakage upon failure. Lamp Order Code Burning Position Codes U – Universal H - Horizontal ONLY BU - Base Up BD - Base Down HBU - Horz to Base Up HBD - Horz to Base Down VBU - Vert to Base Up VBD - Vert to Base Down Spectral Distribution for Metal Halide Lamps Mercury Vapor lamps standard "white" mercury vapor lamps • Color Improved: very poor on reds, marginal color, not recommended. • Deluxe White, DX: increased red, good color, recommended. • Warm White Deluxe, WWX: excellent reds, excellent color, highly recommended, decreased lumens. Strengths • Three times as efficient as incandescent. • Available in a wide variety of ratings, colors, sizes and shapes. • Relatively low unit cost and a high average rated life (about 24,000 hours when operated on a 10 hour cycle). This is 24 times longer life than incandescent. Weaknesses • • • • • • • • • • Except for incandescents, they are the most inefficient source of light, with an efficacy in the 25 to 55 lumens per watt range. Mercury lamps may be greatly affected by lamp lumen depreciation and should be replaced after 24,000 hours. Poor lumen maintenance compared to other HID sources. Have a distinctive bluish cast light output. Require a maximum warm-up period of five to seven minutes before giving full light output, depending on lamp type, ballast and ambient temperature. They can be used only where this delay is acceptable. Four to five minute cooling and restart time. New outdoor installations are illegal under some state laws. Lamps are quite voltage sensitive. Unless special ballasts are used, care must be taken to keep the supply voltage within plus or minus 5% of the rated voltage. Mercury lamp ballasts are noisy. When this presents a problem, remote mounted ballasts may be an alternative. A special dimming ballast is required to dim mercury lamps Spectral Distribution Curve for Mercury Vapor Lamps Lamp Order Code (ANSI Code) Fluorescent lamps ballast starter Fluorescent lamps circuit Strengths • • • • • 4 to 5 times more efficient than incandescent, and an exceptionally long life (10 to 20 times greater than incandescent). Easy to maintain. Lamp life is greatly affected by the average number of hours the lamp is cycled on and off. The lamps are also low cost and available in a wide range of sizes and colors. Relatively low surface brightness and heat generation, and are relatively insensitive to small changes in building voltage. This can be very important where brownouts are common. Weaknesses • • • • • Most lamps are relatively large and require a relatively expensive fixture. The ballasts in fluorescent fixtures can have an objectionable hum (some louder than others). Ballasts are now given a noise rating. Quiet ballasts are recommended for office areas, louder and less expensive ballasts can be used in industrial facilities. Fluorescent lamps are temperature sensitive and may have difficulty starting at low temperatures. Also, lumen output drops at low and high temperatures. Special ballasts are available for low and high temperature applications. While dimming of fluorescents is possible, it requires special, relatively expensive ballasts. Spectral Distribution for the Standard Fluorescent Lamps Lamp Ordering Code High-press. sod. vap. lamps Strengths • • • • • • Most efficient member of the HID light family, 7 times as efficient as incandescent and over 2 times as efficient as mercury vapor. Warm-up period is 3-4 minutes, which is somewhat less than that of a mercury vapor or metal halide lamp. Long lamp life -- 24,000 hours. Excellent lumen maintenance. Wide range of lamp types with wattages ranging from 35 to 1000 watts. Most HPS lamps can operate in any position. Weaknesses • The light produced is a golden white color, which may not be appropriate for certain applications. • Requires a ballast. • Once started can take from five to ten minutes to reach full light output. They also require at least a one minute cool-down to re-strike. • End of life is characterized by on-off-on cycling, and continued operation can damage the lamp ballast if not replaced quickly. Lamp Order Code Spectral Distribution for High Pressure Sodium Lamp Low Pressure Sodium Strengths • Most energy efficient light source commercially available, with an efficacy of 100 to 185 lumens per watt. • Lamps have average life in the 14,000 to 18,000 hour range and have excellent lumen maintenance (very little reduction in lumen output over life of lamp). • Most lamps will restart immediately after interruption of power supply, but require some time to come up to full brightness. • Provides superior uniformity of light distribution over all HID lamps. Weaknesses • These lamps have the poorest color rendering characteristics. In fact, it is almost impossible to distinguish colors under an LPS lamp because light produced by this source is monochromatic (a single color). • Most expensive lamps to install. • Run time to full light output is the longest (7 to 15 minutes). • Wattage will increase over the life of the lamp to maintain lumen output. • Requires special disposal considerations. Spectral Distribution for a Low Pressure Sodium Lamp Lighting measurement units Radiation flux Luminous flux Luminous intensity I Illuminance E Luminance L Methods of lighting measurement Lighting measurement methods تعداد منابع روشنايي • تعداد رديف ها • نقاط اندازه گيري • •N •M P,Q,R,T سطح منظم با المپ منفرد P1+P2+P3+P4 4 =AI سطح منظم با يک رديف المپ بصورت پيوسته QN+P =AI N+1 سطح منظم با المپ های فضايي قرينه در دو يا چند رديف سطح منظم با المپ های فضايي قرينه دردو يا چند رديف )Q(N-1)+T(M-1)+P+R(N-1)(M-1 =AI NM سطح منظم با المپ های منفرد دريک رديف Q(N-1)+P =AI N سطح منظم با المپ هاي متصل و ممتد دردو يا چند رديف )QN+T(M-1)+P+RN(M-1 =AI )M(N-1 Measurement instruments • Hagner universal photometer • Hagner digital luxmeter Hagner universal photometer s1,2 Hagner universal photometer s1,2 Hagner universal photometer s1,2 Hagner universal photometer s1 Hagner universal photometer s1,2 Hagner universal photometer s3 Hagner universal photometer s3 Hagner universal photometer s3 View when looking into a Hagner photometer Hagner universal photometer s3 Hagner digital luxmeter