* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Microphone Types and Designs .
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Sound level meter wikipedia , lookup
Sound recording and reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Sound reinforcement system wikipedia , lookup
Transmission line loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
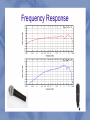
Microphone Types and Designs John Lewis Kilgore 9/19/2012 PHY3091 Introduction A microphone is a type of transducer. Early microphones were invented for communication purposes. Later modifications were made to design as the microphone was used more in entertainment industry. Introduction Different situations call for the need of different microphone designs as well different pickup patterns. Need to consider factors such as the source, the location of the source and the environment of the source. Overview of a Microphone Diaphragm—part of microphone which receives the vibration from sound waves. Thickness and material of diaphragm are changed depending on the sound waves you wish to pick up. How it works? Electrical circuit is used to change these detected vibrations into an electrical signal that “images” the sound with an output voltage or current. Different Types of Microphones Microphone types we will discuss today: Carbon Button Ribbon Dynamic Condenser Carbon Button Microphone— Historical Design Thomas Alva Edison and Sir Emile Berliner filled patents for Carbon Button Microphone in 1877. Edison's design became the accepted design and patent. This is a popular microphone for telephones as well as early radio and speeches. Carbon Button Microphone Diaphragm: Thin Metal Plate The diaphragm is connected to a button full of carbon power. A voltage is applied across the button. Sound pressure changes the resistance through the button by compressing/decompressing the carbon by pushing the plate. Carbon Button—Design Diagram Ribbon Microphone Diaphragm: Thin piece of metal foil suspended in a magnetic field. Vibrations in ribbon produce a small voltage which is then stepped up by a transformer. Diaphragm is very easily damaged by wind or loud incoming sounds. Ribbon Microphone— Design Diagram Dynamic Microphone Diaphragm: Plastic Diaphragm pushes a coil of wire suspended in a magnetic field. Durable design and versatile use. A reverse of a loudspeaker. Dynamic Microphone— Design Diagram Condenser Microphone Diaphragm: Thin metal strip suspended next to a charged electric plate. This creates a capacitor. Diaphragm moves in and out and changes electrical capacitance. Requires a power source for the charged plate. Distorts easily and has a flat frequency response. Condenser Microphone-Design Diagram Frequency Response Microphone Pickup Patterns Pickup patterns help to reduce unwanted signal from getting pickups Popular patterns: Monodirectional, Bidirectional, Cardioid, and Omnidirectional Sources http://www.mediacollege.com/audio/microphones/dynamic.htm lhttp://www.cybergeo.com/music/microphones/ http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/audio/mic.html http://lloydmicrophoneclassics.com/mic_history.html http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microphone http://ffden-2.phys.uaf.edu/212_fall2003.web.dir/David_BonifaceJones/Page2.htm