* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download G - CURENT Education
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Electrical grid wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
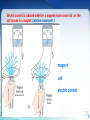
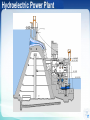
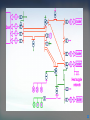
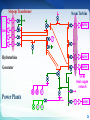
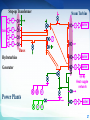
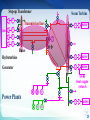
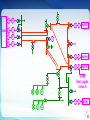
Introduction to Power System Dr. Jing Wang Head of Institute of Power Electronic and Electric Drive [email protected] I Where does electricity come from? II What is power system? I Where does electricity come from? III Do voltage and frequency matter? Michael Faraday 1791 -1867 3 magnet Coil electric current 4 Electric current is induced whether a magnet moves near coil or the coil moves in a magnet (relative movement ). magnet coil electric current 5 6 How can we keep the coil rotating like that? 7 Types of Power Plants Thermal Nuclear Conventional Sources Hydroelectric Wind Solar-PV Biomass Geothermal …… Non Conventional Sources Thermal Power Plant 9 9 Turbines 10 Steam turbine generator set Stator Rotor 11 12 12 Types of Power Plants Thermal Nuclear Hydroelectric Wind Solar-PV Biomass Geothermal …… Nuclear Power Plant 14 15 Types of Power Plants Thermal Nuclear Hydroelectric Wind Solar-PV Biomass Geothermal …… Hydroelectric Power Plant 17 Hydroturbine rotor Stator Rotor 18 Dams Itaipu Hoover 19 Online Materials 1. On electricity, power systems and smart grids Grid 101 - The Power Grid Explained:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5wF03-bqyJo Where energy comes from:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=__zB80Saglk Energy 101: Electricity Generation:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=20Vb6hlLQSg What Is the Smart Grid?:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JwRTpWZReJk 2. On Generators Nuclear Power: How Nuclear Power Plants Work :https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_UwexvaCMWA Thermal power plant:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rEJKiUYjW1E Hydro Power:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rnPEtwQtmGQ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tpigNNTQix8&list=PLACD8E92715335CB2&index=8 Pumped Storage hydropower plant:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Tt_NtTOJEE8 Wind Power: How Wind Turbines Generate Electricity:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mrnul6ixX90 Wind Turbines:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EYYHfMCw-FI&index=3&list=PLACD8E92715335CB2 Solar Power: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0elhIcPVtKE https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0elhIcPVtKE&list=PLACD8E92715335CB2&index=16 20 I Where does electricity come from? II What is power system? II What is power system? III Do voltage and frequency matter? 22 Steam Turbine G ~ G ~ boiler Hydroturbine G ~ boiler Generator G ~ boiler Dam G ~ G ~ || G ~ Heat supple network M ~ Power Plants G ~ M ~ boiler M ~ 23 Step-up Transformer Steam Turbine G ~ G ~ boiler Hydroturbine G ~ boiler Generator G ~ boiler Dam G ~ G ~ || G ~ Heat supple network M ~ Power Plants G ~ M ~ boiler M ~ 24 Transformers PURPOSE: to change the voltage • increase = “step-up” • decrease = “step-down” Why need to change Voltages? Often run hot, must be Why is that so? cooled, prone to explode. • oil inside • cooling fins and fans • blast walls 25 Electrical Substation 26 26 Step-up Transformer Steam Turbine G ~ G ~ boiler Hydroturbine G ~ boiler Generator G ~ boiler Dam G ~ G ~ || G ~ Buses Heat supple network M ~ Power Plants G ~ M ~ boiler M ~ 27 Buses uninsulated electrical conductors large cross-section = low resistance must be far from ground and other components to avoid arcing 28 Step-up Transformer G ~ Steam Turbine Transmission lines G ~ boiler Hydroturbine G ~ boiler Generator G ~ boiler Dam G ~ G ~ || G ~ Buses Heat supple network M ~ Power Plants G ~ M ~ boiler M ~ 29 30 31 32 33 Step-up Transformer G ~ Steam Turbine Transmission lines G ~ boiler Hydroturbine G ~ boiler Generator G ~ boiler Dam G ~ G ~ || G ~ Buses Step-down Transformer Distribution lines Heat supple network M ~ Power Plants G ~ M ~ boiler M ~ 34 Step-down transformer 35 35 To your house... 36 Step-up Transformer G ~ Steam Turbine Transmission lines G ~ boiler Hydroturbine G ~ boiler Generator G ~ boiler Dam G ~ G ~ || G ~ Buses Step-down Transformer Heat supple network M ~ Power Plants Consumers G ~ M ~ boiler M ~ 37 38 Electrical power system a network of electrical components used to generate generate, transmit, transmit distribute distribute and consume electric power 39 Electrical power system G ~ Dam G ~ G ~ G ~ boiler G ~ boiler G ~ boiler || G ~ Heat supple network M ~ G ~ M ~ boiler M ~ 40 Power Grid an interconnected network fortransmission transmitting and distributing distribution electricity from suppliers to consumers 41 Power Grid = Electrical power system – generators - consumers G ~ Dam G ~ G ~ G ~ boiler G ~ boiler G ~ boiler || G ~ Transmission System Distribution System Heat supple network M ~ G ~ M ~ boiler M ~ 42 G ~ Dam G ~ G ~ G ~ boiler G ~ boiler G ~ boiler || G ~ Heat supple network M ~ G ~ M ~ boiler M ~ 43 44 G ~ Dam 220kV G ~ G ~ G ~ boiler G ~ boiler G ~ boiler || G ~ 10.5kV 110kV 0.38kV Heat supple network 10kV M ~ 50Hz 60Hz G ~ M ~ boiler M ~ 45 I Where does electricity come from? II What is power system? III Do voltage and frequency matter? III Do voltage and frequency matter? Questions 1. What is the history of voltages and frequencies? 2. What are voltage levels? Why are they choosed as standards? 3. What kinds of frequencies are chosen as base frequency? Why is that so ? 4. Why are High Voltages Used to transmit power energy? Why is that so? 5. What conditions do we need to use AC or DC systems ? 47 48