* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5 Electricity Show
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
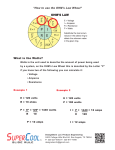
Electricity Complete the following notes. Review of Energy & Power • Energy is ability to do work • Work is a mass moving a distance with an applied force • Power is the amount of work done in a given amount of time. • Power is or is not energy? • What are the six forms of energy? • What are the two types of energy? • What are the three sources of energy? Electricity • Current is the flow of electrons • Voltage is the force of electricity • Conductors provides an easy path for electricity to flow • Load is the part of the circuit that changes the energy movement into some useful form of energy Electricity • Amperes (amps) is how the flow of electrons are measured • Direct Current (DC) is one direction of flowing electrons • Alternating Current (AC) is two way street of flowing electrons Electricity • Resistance is an opposing force between hot and negative • Ohm is the measure of the resistance • Insulator is a material that does not easily conduct an electric current Electricity • How to figure out what the amps are: • How to figure out how much kilowatts used: • I = P/E • kWh = P x h 1000 • kWh-kilowatt per hour • P-Watts • h-hours • I-Amps • P-Watts • E-Volts Electricity • Lets figure amps • 60 Watt Bulb, on 120 Volts of energy, what is the amps? • Lets figure amps • 34 Watts (3 bulbs), on 120 Volts of energy, what is the amps? • I = 60 / 120 • I = 0.5 A (amps) • I = (34 x 3) / 120 • I = 0.85 A Electricity • Kilowatt-hours • TV, 250 Watts, running for 1.5 hours, what is the kWh? • Kilowatt-hours • Heater, 4500 Watts, running for 1 hour, what is the kWh? • kWh= 250 x 1.5 1000 • kWh= 0.375 • kWh = 4500 x 1 1000 • kWh = 4.5 Electricity • So we know how to find our Kilowatt-hour figures now. Lets look at how much money it would cost to run an item. Using the heater at 4.5 kWh, it costs per hour ___? • Cost = kWh x $0.13 • C = 4.5 x 0.13 • C = $0.56 per hour Electricity • Assignment: • Take what information you have got on electric items from your house and figure out how many amps your house needs. • Then figure out how many kilowatt-hours you demand plus how much it costs to run these items per hour. • On Monday, March 5, we will discuss this plus you will have a test over these notes.