* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DPCL Solid State Device Discrete Control Lecture
Fire-control system wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Light switch wikipedia , lookup
Resilient control systems wikipedia , lookup
Crossbar switch wikipedia , lookup
Control theory wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
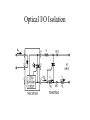
DPCL Solid State Device Discrete Control Lecture Discrete Input – Output, I/O All devices/control in this course have been “analog” measurements; level, flow, temperature etc. Discrete control implies two stable “states”, open-closed, on-off, etc. Inputs-Outputs Inputs are push buttons, various switches that sense physical conditions, such as pressure, level, temperature, proximity or limit etc. Outputs are used to control “on-off” devices such as solenoid valves, motors, relays, contactors etc. Terms used to represent discrete behaviour Binary 0 1 Voltage 0 to 1.5 V3.5 to 5 V(or opposite) Logic False True Switch OFF ON Level Low High Inputs – Switch Configurations SPST Single Pole Single Throw: SPDT Single Pole Double Throw: DPST Double Pole Single Throw: DPDT Double Pole Double Throw: Switches Process Switches are frequently used as safety interlocking devices. Interlock – shutdown system Pressure, level, temperature, flow vibration etc. The safe way to wire these devices is to assume that the normal process condition will result in a closed switch that is there will be current flow to the device during “normal” operation. This way wiring failures will “fail safe”, resulting in the alarmed or interlocked condition. Discrete I/O Interfacing The control equipment, either a programmable logic controller, PLC or a control system such as DeltaV Distributed Control System, DCS, requires its internal circuitry to be interfaced with these industrial electrical or electromechanical devices. 5V dc TTL (Transistor Transistor Logic) signals for this interface. Isolate computer wiring with “field” wiring, via optical or transformer coupling. Discrete I/O Interfacing The “field” or machine wiring may be either AC or DC powered. Examples of AC and DC interface Input Output Circuits shown in notes. Optical I/O Isolation LAB 4 ● ● For this lab, you will need to design, with DeltaV function blocks, a sequencing control function. Experiment 4