* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Getting Started with Support
Standby power wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Electricity market wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Power supply wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
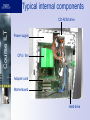
Course ILT Electricity and power systems Unit objectives Measure and describe the characteristics of electricity Identify static electricity and follow ESD safe practices when working with computers Describe the purpose and features of power supplies and install a new power supply into a PC Troubleshoot faulty power supplies Course ILT Topic A Topic A: Electricity and electronics Topic B: Static electricity Topic C: Power supplies Topic D: Power supply troubleshooting Course ILT Electricity characteristics Voltage Current Alternating or direct current Resistance and impedance Power and energy Course ILT Activity A-1 Examining the characteristics of electricity Course ILT Electrical safety Current can kill The 1–10–100 rule Calculating current V=i*r Resistance of the human body Course ILT Safety precautions Don’t touch exposed contacts Touch only insulated handles of tools Leave covers on equipment Work one-handed Don’t stick things into electrical sockets Remove jewelry, watches, etc. Keep hands clean and dry Don’t work in wet surroundings Course ILT Activity A-2 Considering electrical safety Course ILT Digital multimeter Course ILT Analog multimeter Course ILT Using a multimeter Measuring resistance Measuring voltage Measuring current Measuring continuity Course ILT Activity A-3 Measuring electrical values Course ILT Topic B Topic A: Electricity and electronics Topic B: Static electricity Topic C: Power supplies Topic D: Power supply troubleshooting Course ILT Static electricity Build up of charges Static dangers Discharge voltages – – – – 3,000+ volts to feel 8,000+ volts to see spark 35,000 volts on a dry day on carpet 1,000 volts can damage electronics Course ILT Prevent static build-up Don’t shuffle your feet Increase the humidity Keep yourself grounded Wear cotton, not synthetics Remove carpeting Use air ionization system Prevent static discharge Course ILT Equalize charge differences safely – Unplug the equipment – Touch its metal chassis or power supply Keep yourself and equipment connected – Wrist straps and anti-static mats – Static-safe bags Course ILT Static wrist strap Typical internal components Course ILT CD-ROM drive Power supply CPU / fan Adapter card Motherboard Hard drive Slide catches Course ILT Slide catch, move to open side of case Determining which side to open Course ILT Open this side to access components Ports and connectors attached to motherboard Removable front cover Course ILT Alignment holes Alignment posts Spring catches Course ILT Activity B-1 Opening the computer case while following proper ESD precautions Course ILT Topic C Topic A: Electricity and electronics Topic B: Static electricity Topic C: Power supplies Topic D: Power supply troubleshooting Course ILT A PC power supply Course ILT Voltage selection switch Course ILT Typical power requirements Motherboard 30 W Memory 10 W / 128 MB CPU 65 W or more Hard drive 5 – 15 W CD-ROM drive 10 – 20 W Floppy drive 5 – 10 W Adapter card 5 – 30 W Course ILT Standard outputs +3.3 V 14 A AGP video cards, motherboard -5 V 0.3 A ISA bus adapter cards +5 V 30 A Motherboard, CD/DVD drives, hard drives, PCI adapter cards, Pentium III and earlier processors +5 V 0.85 A “Soft power” switch -12 V 1A Older network adapters and serial ports +12 V 12 A CD/DVD drives, hard drives, Pentium 4 and Athlon processors, motherboard Course ILT Power_Good signal Signals CPU that power is stable and sufficient +5 V over specific wire Must arrive at correct time Peripheral power connector Course ILT “Molex” connector Floppy power connector Course ILT “Berg” connector SATA power connector Course ILT New, for Serial ATA drives Course ILT Wire colors Yellow = +12 V Red = +5 V Black = ground Course ILT Motherboard power connectors Course ILT Power supply form factors ATX/NLX 150 x 140 x 86 millimeters 486 and Pentium PCs First with softpower switch and 3.3V SFX 100 x 125 x 63.5 millimeters Pentium PCs No -5 V output for ISA cards WTX 150 x 230 x 86 (single fan) 224 x 230 x 86 (double fan) Pentium PCs No -5 V output for ISA cards Course ILT Activity C-1 Examining a power supply and connectors Course ILT Topic D Topic A: Electricity and electronics Topic B: Static electricity Topic C: Power supplies Topic D: Power supply troubleshooting Course ILT Troubleshooting symptoms Computer fails to boot when powered on, but boots after pressing Ctrl + Alt + Delete Computer intermittently stops working or reboots You don’t have sufficient power connectors to connect all the devices you want to install Computer fails to boot at all, with no lights or beeps; fans don’t start Computer fails to boot, but fans start Course ILT Activity D-1 Troubleshooting power supply problems Course ILT Unit summary Measured and described the characteristics of electricity Identified static electricity and followed ESD safe practices when working with computers Described the purpose and featurse of power supplies; and installed a new power supply into a PC Resolved faulty power supply problems