* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Your Presentation (Name)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
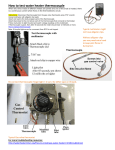
Temperature Sensors R•I•T Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTD) : consists of a small coil of platinum or nickel wire protected by a sheath of stainless steel. Its resistance increases with the temperature. The range of these transducers extends from 00 C to 6000 C (11120 F). R[T] = R[To] [ 1 + αo (T – To] Where T is temperature at which the resistance is desired To is the mid-point of valid temperature R[T] is the resistance at T predicted R[To] is the resistance at To from the table αo is the fractional change in temperature per unit of temperature at To Cont. The value α all metals will be on the order of 0.4% of the RTD resistance for every change of 10 C, in other words, the value is 0.004 / 0 C . RTD has drawbacks: Power dissipation factor Self heating effect Delay time constant non-lineariarity R•I•T Thermistors Thermistor is a semiconductor based transducers. It has very good sensitivity. It is 10%. It is good for small temperature variations. Drawbacks: Self heating effect Time constant Power Dissipation Time Delay R•I•T Thermocouple (TC) The thermocouple (TC) is a temperature sensor that produces a voltage directly as a function of temperature. The range is from -150 0 C to 2000 0 C Interpolation T(V) = T1 + [T2 - T1][V – V1]/[V - V1] R•I•T Cont. There are types E, J, K, C, R, S R and S are high temperature sensors used to measure temperature in the semiconductor furnace as the one in the Microelectronic Engineering clean room. R•I•T Thermocouple Comparison Data Type Elements mv/0 C Range0C Error(%FS) E Chromel/Constantan 0.044 0 to 800 0.5 J Iron/constantan 0.033 -250 to 700 0.75 K Chromel/Alumel 0.020 -250 to 1200 0.75 R & S Pt-Rh/Platinum 0.010 0 to 1400 0.25 T Copper/Constantan 0.040 -250 to 350 1.00 C Tungsten/rhenium 0.012 0 to 2000 0.5 R•I•T Appliction High output Reducing atm Oxidizing Corrosive Moist High temp. Displacement Sensors Potentiometric: Its resistance varies as its wiper position changes. Inexpensive Physical contact wears out after long hours of use, generating noise as a result. R•I•T Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT) LVDT is based on the electrical transformer The difference of output voltages of two secondary winding changes according to the position of the core. AC signal is used, typically 1000 Hz signal is used as the source signal. Phase sensitive detector can be used to convert AC to DC output. R•I•T Strain Gage Its resistance changes as the platinum wire changes its length and cross-sectional area. GF = (δR/R)/(δL/L) Where GF is gage factor δR/R is resistance ratio δL/L fractional change in length, which is called the strain. R•I•T