* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 幻灯片 1 - HUST
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
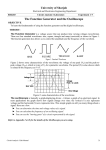
Department of Physics Ke sheng-zhi Contents 1. Objectives 2. Pre-lab Questions 3. Introduction & Apparatus 4. Procedure & Experiment 5. Problems 1. Objectives Learn how to handle the features of an oscilloscope Teach yourself the functions of a signal generator Measure the electric quantities of sine voltage signals Observe Lissajous figures (optional) 2. Pre-lab Questions What does a voltmeter do? What is a cathode ray? What will happen when an electron beam is moving in electric fields? Can you classify several typical waveforms? 2. Pre-lab Questions What does a voltmeter do? Analog voltmeters A digital voltmeter Voltmeters: measure the electrical potential difference between two points in an electric circuit. Do you know the other instruments which also can be used to determine the voltage ? 2. Pre-lab Questions What is a cathode ray? The deflections of the beam are visible if viewed closely with very low ambient light level. Cathode rays: streams of electrons observed in evacuated glass tubes that are equipped with a cathode (negative electrode) and an anode (positive electrode). Anode rays Anode Rays? Holes Cathode rays 2. Pre-lab Questions Electron beams moving in electric fields? y vy v y vz d vz Can you find out the vertical displacement y ? z 2. Pre-lab Questions Can you classify several typical waveforms? 3. Introduction & Apparatus OSCILLOSCOPE – The most commonly used instrument Cathode ray tube Vert. system Z-axis Y-axis Horiz. system X-axis 3. Introduction & Apparatus The Screen of the CRT Vy Signal VOLTS (Y-axis) Vertical axis Graticule Horizontal axis (X-axis) TIME t Cathode ray tube CRT – The heart of the oscilloscope Intensity grid Focusing Coil Electron beam Vy Cathode Electron gun Vert. plates Y-deflection Vx Horiz. plates X-deflection Zero signal Fluorescent screen The Time Base Generator and The Trigger Vy SLOPE+ TRIG. LEVEL Y-axis Periodic signal Vx X-axis Ramp signal t Tx Tx Oscilloscope Operating principle Oscilloscope Operating principle x y Vy Vx t x E x Vx t y E y Vy T Dx x V p D y y Oscilloscope Get acquainted with the CRT Screen Graticule Trace INTENSITY control Brightness FOCUS control Definition TRACE ROTATION control Slope POWER switch On/Off Oscilloscope Get acquainted with the Vertical system POSITION control Useless for X-Y POSITION control For CH2(Y) VERT MODE select switch VOLTS / DIV switches With calibrated steps AC-GND-DC Input coupling switches VARIABLE controls For continuous tuning CH2(Y) jack CH1(X) jack X-Axis input for X-Y Oscilloscope Get acquainted with the Horizontal system POSITION control Left or right SLOPE switch SEC / DIV switch With calibrated steps TRIG SOURCE switch Only use one CH LEVEL control Triggering point HORIZ MODE select switch AUTO always sweeping NORM stop triggering for zero signal X-Y mode operation CH1(X) → X-Axis signal VARIABLE control For continuous tuning Function Generator & Unknown Source Function Generator Unknown Source 4. Procedure & Experiment CAUTION HANDLE THE SCOPE WITH CARE. DO NOT CARRY IT AROUND. TURN THE KNOBS GENTLY. DO NOT LEAVE THE INTENSITY HIGHER THAN NECESSARY IN CASE OF DAMAGING THE SCREEN. Basic operations of the oscilloscope Peak-to-Peak Voltage Measurement Period Measurement Lissajous Figures (Optional) 4. Procedure & Experiment Basic operations of the oscilloscope Make sure the output of the YB1601 function generator is attached to the CH1(X) input of the YB43020B oscilloscope. 1. Turn on the POWER to the oscilloscope. 2. Set the FOCUS and INTENSITY control halfway. 3. Set the VERT. MODE setting to CH1(X). 4. Set HORIZ. trigger MODE to AUTO, the trigger LEVEL to the center of range, the TRIG. SOURCE to CH1(X) identical with the VET. MODE setting so that a stationary voltage curve can be easily displayed. 5. Set the SEC/DIV switch to 0.1 ms/DIV. 6. Set the VOLTS/DIV switch for CH1(X) to 0.5 V/DIV. 4. Procedure & Experiment 7. Se the VARIABLE controls rotated fully counterclockwise to the CAL positions, respectively. 8. Turn on the POWER to the function generator. 9. Select a sine waveform FUNCTION, set the frequency f = 1000 Hz. Adjust the AMPL control to zero. 9. Adjust the FOCUS and INTENSITY control to produce a not too bright but clear line. 10.Adjust the vertical POSITION control for CH1(X) of the oscilloscope until the trace is exactly on the center line of the vertical display. 11.Adjust the AMPL control of the signal generator, and watch. 4. Procedure & Experiment Peak-to-Peak Voltage Measurement Y Vertical scale V p p Dy Y Dy 1 V / DIV 1 V / cm Y 6.4 divisions 6.4 cm Snap to grid 4. Procedure & Experiment Period Measurement Snap to grid Horizontal scale X T Dx X Dx 0.2 ms / DIV 0.2 ms / cm X 4.4 divisions 4.4 cm 4. Procedure & Experiment Lissajous Figures (Optional) A Lissajous curve depicts the composition of simple harmonic motions in mutually perpendicular (X-Y) directions, produced by transverse electric forces exerting on an election moving along the Z-axis direction, which can be described by parametric equations: Vx Ax sin( 2 f x t ) Vy Ay sin( 2 f y t ) Vy CH2(Y) fx N y fy Nx CH1(X) Vx It can be done on an oscilloscope in X-Y mode. Whenever a stationary pattern is achieved, the frequency ratio fx / fy of the horizontal input to the vertical input is equal to the ratio Ny / Nx of the number of vertical to horizontal points of tangency to a rectangle that encloses the pattern, i.e., fx / fy is rational . 4. Procedure & Experiment Unknown frequency Measurement 1. Connect the unknown sine voltage source to the CH2(Y) input of the scope. 2. Turn on the POWER to the unknown source. 3. Set the horizontal sweep SEC/DIV switch at the position X-Y . 4. Use the COARSE and FINE control to adjust the frequency of the function generator patiently in order that the stationary patterns with ratio Ny / Nx = 1, 2, 2/3 are displayed on the screen, respectively. 5. Record the frequency reading fx from the function generator, draw the sketch map, and calculate the unknown frequency, respectively. 5. Problems Tilted & Blurred Traces Have a check 5. Problems Synchronous & Asynchronous Traces Have a check 5. Problems An interesting problem: The oscilloscope is in good condition, but no trace appears on the screen, why? (There are more than 2 answers !)


































![1. Higher Electricity Questions [pps 1MB]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000880994_1-e0ea32a764888f59c0d1abf8ef2ca31b-150x150.png)