* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Freescale PowerPoint Template
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Solar car racing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-junction solar cell wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Shockley–Queisser limit wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
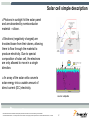
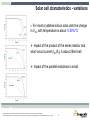
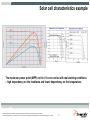
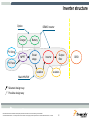
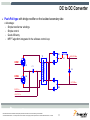
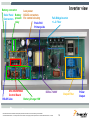
DC to AC Inverter for Solar Panel Stanislav Arendárik, (Aug 2010) TM Freescale Semiconductor Confidential and Proprietary Information. Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners. © Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2006. Main Topics Main topics: • • • • Solar panel description and characteristics Main parameters of the inverter Structure and block schematic of the inverter Blocks description Freescale Semiconductor Confidential and Proprietary Information. Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners. © Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2009. TM 1 Solar cell simple description Photons in sunlight hit the solar panel and are absorbed by semiconductor material – silicon. Electrons (negatively charged) are knocked loose from their atoms, allowing them to flow through the material to produce electricity. Due to special composition of solar cell, the electrons are only allowed to move in a single direction. An array of the solar cells converts solar energy into a usable amount of direct current (DC) electricity. source: wikipedia Freescale Semiconductor Confidential and Proprietary Information. Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners. © Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2009. TM 2 Solar cell characteristics A solar cell may be modeled by a current source in parallel with a diode, shunt and series resistances. IL represents the max current of the solar panel (short current) Diode forms the I-V characteristic Shunt resistor represents the leakage currents (very small) Series resistance represents the wiring losses Freescale Semiconductor Confidential and Proprietary Information. Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners. © Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2009. TM 3 Solar cell characteristics - variations For most crystalline silicon solar cells the change in VOC with temperature is about -0.50%/°C Impact of the product of the series resistor and short-circuit current (ISCRS) is about 25mV/cell. Impact of the parallel resistance is small. Freescale Semiconductor Confidential and Proprietary Information. Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners. © Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2009. TM 4 Solar cell characteristics example • The maximum power point (MPP) on the I-V curve varies with real working conditions – high dependency on the irradiance and lower dependency on the temperature. Freescale Semiconductor Confidential and Proprietary Information. Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners. © Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2009. TM 5 Maximum Power Point In the technical parameters of the solar cell panel are defined: • VMP – voltage at MPP • IMP – current at MPP The Inverter for the solar cell panel must achieve the operation on the MPP. This method is called as MPPT – maximum power point tracking. The presented inverter has implemented the P&O (perturb & observe) algorithm for MPPT. To get maximum power from a PV panel required operating at the optimum voltage. Freescale Semiconductor Confidential and Proprietary Information. Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners. © Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2009. TM 6 Selected range of the solar panels The amount of the solar cells is used to build one solar panel. Usually 72, 36, or other. For this design was selected panel with 72 cells, this implies MPP at 36V, which fairly corresponds to 3 x 12V lead acid batteries in series as the back-up for the power source for the inverter. This battery is used as the energy accumulator for the off-grid inverter usage. The characteristic of the selected solar panel: PMAX = 180W VSC = 44.4V VMP = 36V ISC = 5.25A IMP = 5A Freescale Semiconductor Confidential and Proprietary Information. Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners. © Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2009. TM 7 Inverter structure Option DEMO Inverter Charger Battery MPPT Boost stage PV String Output filter Inverter GRID PV Panel Isolation Isolation Main HW/SW Selected design way Possible design way Freescale Semiconductor Confidential and Proprietary Information. Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners. © Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2009. TM 8 Main Parameters of DC to AC Inverter Input voltage source Output voltage Lower than 3%; Fault Protection 400VA; Harmonic distortion of the output voltage This design aims 1-phase 230V 50Hz (115V 60Hz optional); Single design, just different power components; Tolerance +5% to -10%; Output power Voltage level from solar panel VMP = +36V Solar energy can be stored in Lead-Acid batteries Battery charger can be implemented (phase 2) Selected 3 pcs Lead-Acid batteries in series Output over-current, over-voltage, short-circuit; Input under-voltage; Signal output Serial link RS-485 to main system Freescale Semiconductor Confidential and Proprietary Information. Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners. © Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2009. TM 9 Block Diagram of DC to AC Inverter Block Diagram of Inverter The whole DC to AC inverter consists of main power parts: – – – – – MPP Tracking for solar panel output – software implemented DC low voltage to DC high voltage converter DC high voltage to AC sine output voltage inverter Output filter Isolated RS-485 line Associated control and fault detection circuits Both DC-DC converter and DC-AC inverter is controlled by one DSC MC56F8023. Freescale Semiconductor Confidential and Proprietary Information. Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners. © Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2009. TM 10 DC to DC Converter Push-Pull type with bridge rectifier on the isolated secondary side Advantage: • Simple transformer windings • Simple control • Good efficiency • MPPT algorithm integrated in the software control loop D1 +400V DCBus T1 L1 PWM1 Q1 C1 + C2 + PWM2 Q2 0V DCBus D2 0V DC In +36V DC In Freescale Semiconductor Confidential and Proprietary Information. Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners. © Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2009. TM 11 DC to DC Converter Push-Pull type control signals: Dmin Dmax U The duty-cycle for the PWM1 and PWM2 has the same value The PWM2 control signal is shifted of T/2 later against the PWM1 signal PWM 1 t U The actual duty-cycle value D depends on the actual power transferred through the transformer PWM 2 t PWM period T PWM Duty-cycle variation PWM 2 = PWM 1 + T/2 Dmax < 0.5 T Freescale Semiconductor Confidential and Proprietary Information. Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners. © Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2009. TM 12 DC to AC Inverter Full-bridge type inverter Advantages: • Simple +400V DCBus used to generate 230V AC • Simple PWM control • Simple reconstruction filter for AC line output • Can be controlled by half-bridge drivers or isolated gate transformers • Power MOSFETs or IGBTs can be used +400V DCBus AC Line_1 Q3 Q5 L2 C3 AC Line_2 PWM4 DRIVER Q4 Q6 PWM3 DRIVER 0V DCBus Freescale Semiconductor Confidential and Proprietary Information. Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners. © Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2009. TM 13 DC to AC Inverter +Umax Full-bridge type inverter control signals: -Umax U The PWM3 and PWM4 are complementary PWM 3 The duty-cycle varies ideal from zero to full period in sine amplitude and power line frequency t U Real duty-cycle varies from 5% to 95% of the period PWM 4 When the duty-cycle is <50%, the negative part of the output sine voltage is generated t PWM period T When the duty-cycle is >50%, the positive part of the output sine voltage is generated PWM Duty-cycle variation PWM 4 = PWM 3 D = (5% - 95%) T Freescale Semiconductor Confidential and Proprietary Information. Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners. © Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2009. TM 14 Output filter Integrated output EMI filter used Advantages: • Compact standard design • Good EMI properties • Sufficient load properties AC Line_1 Line L L3 C5 Line PE C4 C6 AC Line_2 Freescale Semiconductor Confidential and Proprietary Information. Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners. © Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2009. Line N TM 15 Auxiliary Power Supplies Auxiliary power supplies power the on-board circuitry The HW comparator enables the first DC/DC converter if the input voltage is > 18V DC from PV panel MOSFET MOSFETs DRIVERS TR PUSH-PULL +5VA-ISO DC/DC 0VA-ISO The main +12V DC power supply acts as the source for all other DC/DC converters +12V-ISO ISOL IGBT DC/DC +36V 0V-ISO DRIVERS FULLBRIDGE BAT Relay + +5VA-ISOA HW Comparator ISOL ANALOG DC/DC PV Two isolated power supplies provide the power for the isolated secondary side of the inverter PARTs 3 x 12V +12V ANALOG +5VA If the battery is connected, the inverter runs from battery and battery is charged by the solar panel +5VA 0V-ISOA PARTs +36V DC/DC +12V +5VA DC/DC +12V 0V +5VA 0V ANALOG 0VA PARTs +3.3V DC/DC The control DSC is placed on the primary low voltage side DSC +3.3V 0V Isolated circuitry Freescale Semiconductor Confidential and Proprietary Information. Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners. © Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2009. TM 16 Control circuits DSC MC56F8023 used Controls the DC/DC converter and DC/AC inverter MPPT software algorithm for the solar panel implemented Battery charger control – as option RS-485 line interface for supervisor’s line communication Output over-current, over-voltage, short-circuit and input under-voltage fuses implemented ON-GRID or OFF-GRID mode Freescale Semiconductor Confidential and Proprietary Information. Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners. © Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2009. TM 17 Battery connector Solar Panel Battery Connectors present relay Low power DC-DC converters For control circuitry Push-Pull Primary side DSC MC56F8023 Control Board RS-485 Line Battery Charger HW Inverter view Full-Bridge Inverter + L-C Filter DCBus +400V Freescale Semiconductor Confidential and Proprietary Information. Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners. © Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2009. Output Filter Power Output TM 18 Conclusion One standard DSC MC56F8023 used for whole inverter control Possibility of use as the ON-GRID or OFF-GRID connected inverter Possibility of use of wide range of the solar panels: One piece of the 36V type with the output power up to 450W Two pieces of the 18V types in series with the total output power up to 450W Inverters can be connected in parallel at the output to boost the output power in the OFF-GRID usage The inverter starts run when the sufficient amount of the power is available from the solar panel (if battery not connected) The 3 x 12V lead-acid batteries in series are used as the energy accumulator Freescale Semiconductor Confidential and Proprietary Information. Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners. © Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2009. TM 19 DEMO Connection DEMO Start-up sequence: Switch OFF both switches (down position) Connect load bulb (60W to 100W) at output Connect the solar panel Put The green LED shines, red LED not OFF-GRID switch “ON” (up position) Switch ON the main switch The “Fault” LED indicates the over-current – when shines, switch OFF the main switch, wait about 2030 sec and switch ON the main switch. Freescale Semiconductor Confidential and Proprietary Information. Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners. © Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2009. TM 20 Literature [1]: http://www.solarserver.com/knowledge/basic-knowledge/photovoltaics.html [2]: http://www.nikhef.nl/~h73/kn1c/praktikum/phywe/LEP/Experim/4_1_09.pdf [3]: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solar_cell [4]: http://www.freescale.com/webapp/sps/site/prod_summary.jsp?code=56F802X&tid=mDHp [5]: http://www.simosolar.com/uploadfile/learn/uploadfile/200904/20090417030623524.pdf Freescale Semiconductor Confidential and Proprietary Information. Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners. © Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2009. TM 21 TM