* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Railway Foundation - Sheffield Hallam University
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Railway Foundation
Electronic, Electrical and
Processor Engineering
Microprocessor Systems
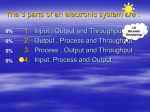
• Four main components
– Microprocessor
– Memory
– Inputs
– Outputs
• Memory
– ROM types – program and fixed data
– RAM (Read & Write) – Data variables
1
Microprocessor
• Circuit is driven by a clock signal
• The microprocessor has internal registers.
• The action performed is determined by a
set of binary instructions stored in ROM
• A reset starts the microprocessor at a
predetermined point in the program
(usually location 0)
2
Inputs & Outputs
• Normally Digital I/O ( two levels ‘0’ & ‘1’)
• Normally parallel i.e grouped – 8bit Ports
What about analogue signals?
– Analogue to Digital Converter (ADC)
– Digital to Analogue Converter (DAC)
• Other devices include hardware timers
and counters
• Digital data can also be in a serial format
(e.g. RS232, RS 485 are serial standards)
3
Microcontrollers
• Integration of all required components
onto one chip.
• Many manufacturers – Microchip,
Freescale, Intel, Infineon, Philips, ARM
etc. producing different microprocessors
• Many microcontrollers with same
microprocessor but differ in other
components.
• Used in embedded products.
4
Examples
Rail - Points Heating Control
Systems
5
Programming
• Can be done at different levels
– Object (machine) binary code
– Assembly language
– High level language ( e.g. ‘C’ language)
– Graphical (e.g. LabVIEW)
• Internal architecture
• Memory Map
• Programmers Model – different for
programming at different levels
6
An example machine instruction
EXAMPLES
Machine code –
0110111100001000
means move the value
from W reg. to file
register 00001000 i.e 8
Assembly –
Count
EQU
8
MOVWF Count
A program called an
assembler converts it to
the binary object code.
7
An Assembler program
Program
Line
Numbers
000000
000000
000000
000002
000004
000004
000006
000008
9693
9681
8681
9681
D7FD
00050
00051
00053
00054
00055
00056
00057
00058
00059
00060
00061
00062
00063
00064
00065
;Constants
LED
equ 3
;LED bit 3 on PORTB
;Reset vector
; This code will start executing when a reset occurs.
ORG
0x0000
;Start of main program
Start:
bcf TRISB,LED
bcf PORTB,LED
Loop:
bsf PORTB,LED
bcf PORTB,LED
bra Loop
ROM
location
Object
code in
HEX
format
Labels
Assembly
instructions
;Set PortB bit 3 as an o/p
;set LED off
;while(1)
; turn led on
; turn led off
;endwhile
Comments
Begin with ;
8
C Programming
• Portable
• High level – Abstract
• Standard constructs
– Variables – various data types
– Selection ( if statements)
– Loops (while, for, do)
– Standard operations (+-*/)
– Logical and bit-wise operations (AND OR
XOR etc.)
9
Simple ‘C’ outline
Selection - two types
if (comparison is true )
{
Do this once;
}
Loops
while (comparison is true )
{
KEEP Doing this;
}
if (comparison is true)
{
do this;
}
else
{
do that;
}
Comparisons:== is equal to
!= is not equal to
> is greater than
< is less than
>= is greater or equal to
<= is less than or equal to
Misc.
Defining variables
// starts a comment
unsigned char i; //8 bit value
i++;
int x;
// 16 bit signed
unsigned int y;
// 16 bit value
// increment by one
i--;
// decrement by one
&&
// logical AND
||
// logical OR
10
Graphical Programming
• LabVIEW is a graphical programming language that
uses icons instead of lines of text to create applications.
• In contrast to text-based programming languages,
where instructions determine program execution,
LabVIEW uses dataflow programming, where data
determine execution.
11
Practical approach
• Treat as a programmable digital device
• Choose device based on number and
types of input and outputs
• Write program:– Define inputs and outputs
– Read input data, process data and generate
outputs
• Requires knowledge of a programming
language and microcontroller specific
features.
12
Analogue to Digital Converter
• n bits – determines the resolution
• Reference voltage sets the input range
• often have an analogue multiplexer to
allow several input channels to use a
single ADC
n bits
ADC
Analogue input voltage
Reference voltages (one is
usually analogue ground)
13
Example 8 bit ADC
•
•
•
•
•
Reference voltage of 0v and +5v
input voltage range = 5v - 0v = 5V
Number of digital values (steps) = 2n=28=256
Note! values range from 0 to 255
Resolution = Reference voltage range = 5
Number of digital values
256
=0.01953125 = 19.53125mV
• This is the smallest change in voltage that can be
detected
14
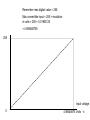
Remember max digital value = 255.
Max convertible input = 255 × resolution
in volts = 255 × 0.01953125
= 4.980468755
255
Input voltage
0
4.98046875 Volts
15
Digital Conversion
Digital value
3
0.05859375
2
0.0390625
1
0.01953125
Analogue input voltage
0
16