* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology, Second Edition
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
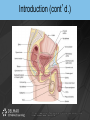
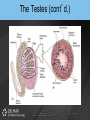
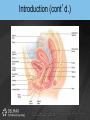
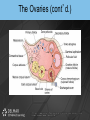
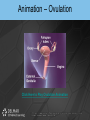
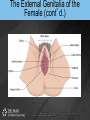
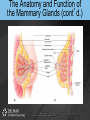
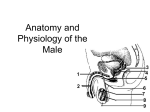
Chapter 19 THE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Introduction • Reproduction: process by which genetic material is passed from one generation to the next Introduction (cont’d.) • Meiosis produces sex cells – Sperm from male and egg from female join to form zygote – Zygote develops into embryo – Embryo develops into fetus THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Introduction • Testes: produce sperm and male sex hormones • Accessory glands: produce secretions • Accessory organs: scrotum • Penis: transporting and supporting structure Introduction (cont’d.) The Scrotum • • • • Outpouching of abdominal wall Supports the testes Divided internally by a septum Scrotal sac elevates and descends The Testes • Tunica albuginea: capsule covering with lobules • Convoluted seminiferous tubules – Spermatogenesis The Testes (cont’d.) • Spermatogenesis – Spermatogonia > primary spermatocytes > secondary spermatocytes > spermatids > spermatozoa • Sertoli cells: supply sperm cells with nutrients The Testes (cont’d.) • Interstitial cells of Leydig: produce testosterone The Testes (cont’d.) The Anatomy of the Spermatozoa • Three hundred million produced daily • Anatomy – Head: contains genetic material and acrosome • Acrosome has enzymes that aid sperm in penetrating covering of ovum – Middle piece: contains mitochondria – Tail: propels sperm The Anatomy of the Spermatozoa (cont’d.) • Anatomy of a sperm cell The Functions of Testosterone • Controls development, growth, and maintenance of male sex organs • Stimulates muscle buildup and bone development • Causes sperm maturation • Causes thyroid cartilage enlargement • Produces body hair patterns The Ducts of the System • Seminiferous tubules: transport sperm cells • Rete testis: network of ducts • Ductus epididymis: site of sperm cell maturation • Epididymis located on posterior border of testis The Ducts of the System (cont’d.) • Vas deferens: straightened portion of epididymis – Enclosed in spermatic duct • Ejaculatory duct: ejects spermatozoa into urethra The Ducts of the System (cont’d.) • Urethra: terminal duct – Prostatic urethra, cavernous urethra, urethral orifice The Accessory Glands • Seminal vesicles: produce viscous part of semen • Prostate gland: produces fluid part of semen • Bulbourethral glands: produce mucus Semen • • • • • • • Mixture of sperm cells and secretions Provides energy to the sperm via fructose Neutralizes acidity of vagina Acts as a transport medium Contains enzymes that activate sperm Average volume is 2.5 to 6 mL Seminalplasmin: destroys certain bacteria The Penis • Delivers spermatozoa to female reproductive tract • Glans penis: end of the shaft • Prepuce: loose skin covering glans penis – Circumcision: removal of prepuce The Penis (cont’d.) • Contains masses of spongy tissue with sinuses • Sinuses fill with blood resulting in erection – Compress veins so blood is retained – Help penis penetrate vagina • During ejaculation, sphincter at base of urinary bladder is closed THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Introduction • Primary sex organs – Ovaries • Accessory organs – Uterine tubes, uterus, vagina, external genitalia • Accessory glands: produce mucus Introduction (cont’d.) The Ovaries • Held in position by ligaments • Covered by germinal epithelium • Tunica albuginea: cortex contains ovarian follicles • Ovarian follicles: eggs in various developmental stages • Primary follicle: contains oocyte The Ovaries (cont’d.) The Ovaries (cont’d.) • Oogenesis – Begins in developing female fetus (700,000 produced) – Puberty: ovarian cycle begins • Primary oocyte: first meiotic division • Mature egg: second meiotic division The Uterine or Fallopian Tubes • Transport ova to the uterus • Infundibulum: funnel-shaped end with fimbriae • Cilia sweep an ovum into uterine tube • Egg moved by peristalsis toward uterus • Fertilization occurs in upper third of tube The Uterus • Site of menstruation, egg implantation and labor • Pear shaped • Uterine cavity: interior of the body • Cervical canal: interior of the cervix • Uterine wall: endometrium, myometrium, perimetrium The Menstrual Cycle • Menstrual phase – Endometrial lining shed along with blood and mucus – Ovarian follicles begin development • Preovulatory or proliferative phase – Secondary follicle matures into graafian follicle – Ovulation is rupturing of graafian follicle The Menstrual Cycle (cont’d.) • Postovulatory or secretory phase – Corpus luteum develops • Secretes estrogen and progesterone – If fertilization and implantation do not occur • Corpus luteum degenerates and new cycle starts – If fertilization and implantation occur • Corpus luteum maintained for four months Animation – Ovulation Click Here to Play Ovulation Animation The Functions of Estrogen • Development of female secondary sex characteristics – Breast development, pubic hair, fat deposits, widening of the pelvic bone • Enlargement of: – Uterine tubes, uterus, vagina, external genitalia The Vagina • • • • Passageway for menstrual flow Receptacle for the penis Lower portion of birth canal Fornix: surrounds vaginal attachment to cervix The External Genitalia of the Female • • • • • Vulva: external genitalia Labia: majora and minora Clitoris: erectile tissue Vestibule: vaginal and urethral orifices Glands: Skene’s and Bartholin’s The External Genitalia of the Female (cont’d.) THE PERINEUM The Perineum (cont’d.) • Diamond-shaped region at inferior end of trunk between buttocks and thighs • Divided into: – Anterior urogenital triangle containing external genitalia – Posterior anal triangle containing anus THE ANATOMY AND FUNCTION OF THE MAMMARY GLANDS The Anatomy and Function of the Mammary Glands (cont’d.) • • • • • Produce milk in females Contain 15 to 20 lobes with lobules Lobules contain milk-secreting cells Milk is conveyed through series of tubules Areola: circular pigmented area around nipple The Anatomy and Function of the Mammary Glands (cont’d.) PREGNANCY AND EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT Pregnancy and Embryonic Development (cont’d.) • Egg fertilization 12-24 hours after ovulation • Zygote: fertilized egg • Moves down uterine tube into uterus – Blastula • Zygote embeds in endometrium, placenta develops Pregnancy and Embryonic Development (cont’d.) • Primary germ layers – Ectoderm: skin and nervous system – Mesoderm: muscles and bones – Endoderm: linings of organs and glands • Amnion: fluid-filled sac – Attached to embryo by umbilical cord • Parturition: childbirth Summary • Discussed the organs of the male reproductive system • Discussed the role of testosterone • Described the process of spermatogenesis • Discussed the organs of the female reproductive system Summary (cont’d.) • Discussed the role of estrogen • Described the process of oogenesis • Described the phases of the menstrual cycle • Discussed pregnancy and embryonic development