* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download L 4 pigments - WHSPhotosynthesis
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
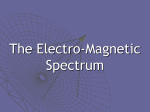
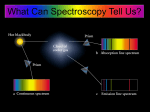
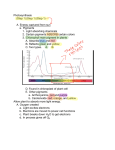
The Light-Dependent Reactions The LIGHT-DEPENDENT REACTIONS take place within the thylakoid membranes of the grana thylakoid membranes of granum The light dependent reactions begin when the energy in sunlight is captured by the light absorbing pigments located within the grana The Light-Dependent Reactions LIGHT AND PIGMENTS Light energy travels in packets called photons The energy content of a photon depends upon the wavelength of the light The shorter the wavelength, the higher the photon energy The energy associated with a photon of light is called a quantum of energy Blue light has a relatively short wavelength whilst red light has a relatively long wavelength Plants are able to absorb a wide range of wavelengths because they contain a variety of pigments with different structures and absorption properties THE ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM Visible light represents only a small fraction of the full spectrum of electromagnetic radiation produced by the sun Plant pigments absorb light energy with wavelengths that fall within this visible spectrum Visible light Gamma rays 400 X- Rays UV Infrared 500 600 Wavelength (nm) Radar Short wave 700 Radio waves 750 Photosynthetic Pigments of the Green Plant Pigments can be extracted from finely chopped leaves by grinding the tissues in acetone When the pigment extract is subjected to ascending paper chromatography, the pigments can be analysed and identified solvent front carotene phaeophytin xanthophyll chlorophyll a The principal plant pigments found in green plants are the chlorophylls (a and b) and the carotenoids (carotene and xanthophyll) chlorophyll b origin The role of these pigments is to capture light energy and each of the pigments absorb various wavelengths to different extents ABSORPTION SPECTRA When a beam of light is passed through a glass prism, the visible spectrum of white light is obtained When a beam of light is first passed through a solution of leaf extract, then an absorption spectrum is obtained Black bands appear in the spectrum where particular wavelengths of light have been absorbed Predominantly, wavelengths at the blue and red ends of the spectrum have been absorbed ABSORPTION SPECTRA The spectrum obtained by passing white light through a leaf pigment extract shows us the wavelengths that the pigments absorbed More detailed information about the absorption process can be obtained using a spectrometer The degree of absorption at each wavelength can be measured for both the total plant extract and the individual pigments This information can be used to generate an ABSORPTION SPECTRUM GRAPH In a similar way, the effectiveness of different wavelengths of light in bringing about photosynthesis can also be determined The rate of photosynthesis at different wavelengths can be experimentally measured This information can be used to generate an ACTION SPECTRUM GRAPH ABSORPTION AND ACTION SPECTRA GRAPHS 100 80 60 60 40 40 absorption spectrum 20 0 400 500 600 700 w a v e l e n g t h / n m of 80 photosynthesis action spectrum 20 rate % absorption 100 0 Although all wavelengths between 400 and 700 nm are absorbed by the plant extract, maximum absorption occurs in the violet/blue and red regions of the spectrum There is a close correlation between the action spectrum and the absorption spectrum The rate of photosynthesis is largely determined by the amount of light of different wavelengths being absorbed