* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AtmStructure
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
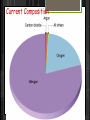
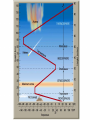
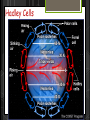
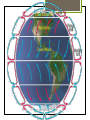
Structure of the Earth’s Atmosphere * Chemical Composition * Vertical Layers * Coriolis Force * Hadley Cells Current Composition Atmospheric Composition today Troposphere Surface layer - 30,000 ft Heated from below General T structure dec. w/height Convection - weather, clouds form from rising air which cools by pressure drop, and clouds dissipate as air falls and heats. Stratosphere Heated by ozone absorbing UV light UV breaks apart ozone into O2 + atomic oxygen - get energy release and heating. higher altitudes efficiently absorbs UV at 200 and 350 nm. lower altitudes less efficiently absorbs UV at 44 and 80 nm Temperature 7 – 30 miles inversion - no convection, no weather. Mesosphere Mass of atmosphere 0.1% Density is too low for ozone chemistry to heat get normal trend we saw in troposphere– lower T with inc. altitude. 30-50 miles Ionosphere (= Thermosphere) Density so low Space Shuttle orbits here, with little drag T can be very high; 4,000F. But no significant heat because density low. Heated by ionization by UV from the sun, and the solar wind. Hadley Cells Hadley, Ferrel, Polar Cells Earth’s atmosphere divides into 3 cells. Coriolis deflection sets the major constraint on how many cells the atmosphere of a planet divides into. stronger for more rapid rotation. size of the planet and speed of rotation which determines number of cells Hadley Cell Solar heating at equator is strongest - causing rising convective air which is pushed north and south at the tropopause At ~30deg latitude deflected enough by Coriolis force to be moving almost due east. Meets air moving down from the north (Ferrel Cell air) and both descend, warming and drying Trade Winds - return of surface wind to equator Coriolis Effect 6 min YouTube (start 1min in for merry-go-round demo)