* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Population Dynamics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
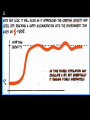
Populations Introduction to Population Dynamics I. Populations A. What is a population? A group of organisms of the same species that interbreed and live in the same place at the same time. 1. 2. II. Population Growth A. How are populations affected by resources available in the environment? 1. Resources determine how a given population will grow. B. 1. 2. 3. a. Populations grow when birth rate + immigration rate (# of organisms moving into a population) > death rate + emigration rate (# of organisms moving out of a population) III. Limiting Factors A. 1. Resources, nutrients (matter) and energy in short supply, limit how large a population can grow, therefore resources can be limiting factors. B. 1. Density-dependent limiting factors control population size when a population is large and crowded. a. examples: competition, predation, parasitism and crowding 2. Density-independent limiting factors control population size regardless of whether a population is large or small. a. examples: natural causes such as geothermal activity, extreme weather IV. Carrying Capacity & Population Growth A. Carrying Capacity- the number of individuals in a population that can be sustained indefinitely in a given ecosystem. -very difficult number to specify B. C. D. 1. 2. A. B. C.