* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Impacts
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
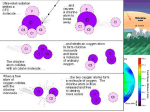
Human Impacts Ecology Unit Learning Goal 5 • http://www.cnn.com/video/#/video/world/20 10/10/05/vo.hungary.toxic.mud.spill.mtv?ir ef=allsearch Earth as an Island • All organisms that live on the Earth share a limited resource base and depend on it for their long-term survival. • • • • • • A resource for shelter and space A resource for food supply An energy source A source of recreation A major source of medicines Natural resource for industrial products. Resources • Renewable Resources that can regenerate or have a virtually unlimited supply. Nonrenewable Resources • Resources that cannot be replenished by natural processes. – Fossil Fuels • Coal • Oil • Natural Gas – Entire Ecosystems (sometimes) Natural Areas • Critical habitat for many plants and animals is disappearing. – If there is no place to find food and shelter organisms are forced to relocate or die. Categories of Biodiversity • Ecosystem Diversity The variety of habitats that exist on Earth. • Species Diversity The number of different species in the biosphere. • Genetic Diversity Different forms of genes present within a species. Ecosystem Services • • • • Solar Energy Oxygen Production Nutrient Recycling Purification of Air and Water • Pollination for food production • Soil fertility and erosion prevention • https://video.weber.k12.ut.us/vportal/Video Player.jsp?ccsid=9C18620AA93E4C409F 9DC4580642588A:1 Species at Risk • Factors leading to endangerment or extinction. – Habitat Destruction – Invasive Species – Overexploitation – Disease – Pollution • Eutrophication Occurs in aquatic environments when excessive nutrients are added resulting in a bloom of algae that robs the water of oxygen. Species at Risk • Extinct: A species that no longer exists. • Endangered: A species facing imminent extinction. • Threatened: a species likely to become endangered if limiting factors are not reversed. California Condor • As recently as the early 1800s, the California Condor occupied mountains along the Pacific coast from British Columbia to northern Baja California. By the mid-twentieth century, the population declined to a small population in south-central California. Through captive breeding, California Condors have been reintroduced to the coastal mountains of south-central California and the Grand Canyon area of northern Arizona. Condors prefer mountains, gorges, and hillsides, which create updrafts, thus providing favorable soaring conditions. Endangered Species Air quality • Air Quality is affected by pollutants that come from the combustion of fossil fuels. – Vehicles, homes, power plants, smelters, and other industries. • Smog can affect our health. Acid Rain • Acid rain is caused by the chemical conversion in the atmosphere of SO2 and NO2 into nitric acid and sulfuric acid. • Those are now monitored and controlled. Water Quality • Water is threatened by pollutants that enter the bodies of water. Biological Magnification • Concentration of a harmful substance increase in organisms at higher trophic levels in a food chain. • For example, if in one day a little fish eats 1,000 plankton and a whale eats 1,000 little fish, the whale is ingesting all the toxins that were in a million plankton! – (1,000 x 1,000 = 1,000,000) • Example – DDT and Bald Eagles Ozone Depletion • Ozone absorbs most of the UV radiation from the sun. – UV radiation may lead to many health concerns. • Depletion of the ozone has been linked to the uses of CFCs. • Today the use of most CFCs has been banned. • CFC molecules can stay in the atmosphere as long as a century. • We have yet to see the effect of the CFC ban. Climate Change • Average global temperatures at the Earth’s surface have increased 0.6 – 1.2oF since the late 1900’s. • Effect of Climate Change – Change in weather patterns. – Increase in severe weather. – Melting of the polar ice caps. – Change in habitat for organisms. – Change in entire ecosystems. Greenhouse Effect What Can People Do? • • • • • • • Use mass transit Use vehicles that get good gas mileage Use energy-efficient appliances. Recycle Conserve our resources. Clean up our messes. Preserve habitat • https://video.weber.k12.ut.us/vportal/Video Player.jsp?ccsid=8DA35001D77B22A067 95839265A1CA4B:1 We can do better!!! The End