* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download projectilessatellites and gravity
Analytical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Brownian motion wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Length contraction wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
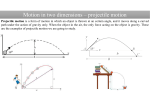
PROJECTILES Projectile Motion-Inertia and Falling Objects http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=F92FQdnLlSc Flaming piano tossed by trebuchet Projectile Defined Any object that moves through air or space under the influence of gravity. Horizontal Motion Associated with a Projectile Object is launched horizontally Object continues in horizontal direction a constant speed due to its inertia. No increase or decrease in speed Vertical Motion Associated with a Projectile Object’s motion is changed due to the force of gravity. Object increases or decreases in speed Projectile Path Principles The greater the object’s horizontal motion (or speed), the wider the arc of its curved path. If thrown from the same height, both projectiles will land at the same time even if their horizontal speeds are different. See Figures 14.1 and 14.3 on page 263. Constructing the path of a projectile: use centimeters as scale 1 m = 1 cm Horizontal Velocity = --- m/s Calculate distance fallen using d = 1/2gt2 , use rounded g = 10 m/s2 1s 2s 3s 4s The Motion of a Curved Projectile The motion of a curved projectile consists of two components. --Horizontal Motion --Vertical Motion This curve is called a parabola. Horizontal Motion Associated with a Projectile Horizontal motion is initiated by an unbalanced force Object continues in horizontal direction a constant speed due to its inertia. No increase or decrease in speed Vertical Motion Associated with a Projectile Object’s motion is changed due to the force of gravity. Object increases or decreases in speed Freefall Equations for Calculating the Path of Projectile Horizontal Motion – For horizontal motion, assume a constant speed (equal distance over equal time) Vertical Motion – Use freefall equations • • • • v = gt (how fast object falls) d = ½gt2 (how far object falls) t= square root of 2d/g (how long it takes for an object to fall) remember, g = 9.8 m/s2 Mapping the Path of a Projectile Step One: Determine the horizontal velocity and how far the object travels each second. Step Two: Calculate how far the projectile falls for each second that passes. Neglect air resistance. Step Three: Assume 1 m = 1 cm and use this scale for measuring string lengths and horizontal distances Step four: Tape the strings on the meter stick at the appropriate horizontal distances per second. Applications http://www.physicsclassroom.com/Class/vectors/ U3L2a.html